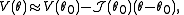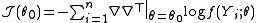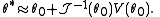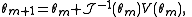Scoring algorithm
Encyclopedia
In statistics
, Fisher's
scoring algorithm is a form of Newton's method
used to solve maximum likelihood
equations numerically
.
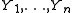 be random variable
be random variable
s, independent and identically distributed with twice differentiable p.d.f.
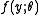 , and we wish to calculate the maximum likelihood estimator (M.L.E.)
, and we wish to calculate the maximum likelihood estimator (M.L.E.)  of
of 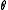 . First, suppose we have a starting point for our algorithm
. First, suppose we have a starting point for our algorithm 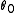 , and consider a Taylor expansion
, and consider a Taylor expansion
of the score function
,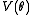 , about
, about 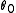 :
:
where
is the observed information matrix
at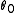 . Now, setting
. Now, setting 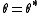 , using that
, using that 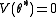 and rearranging gives us:
and rearranging gives us:
We therefore use the algorithm
and under certain regularity conditions, it can be shown that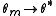 .
.
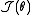 is usually replaced by
is usually replaced by 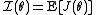 , the Fisher information
, the Fisher information
, thus giving us the Fisher Scoring Algorithm:
Statistics
Statistics is the study of the collection, organization, analysis, and interpretation of data. It deals with all aspects of this, including the planning of data collection in terms of the design of surveys and experiments....
, Fisher's
Ronald Fisher
Sir Ronald Aylmer Fisher FRS was an English statistician, evolutionary biologist, eugenicist and geneticist. Among other things, Fisher is well known for his contributions to statistics by creating Fisher's exact test and Fisher's equation...
scoring algorithm is a form of Newton's method
Newton's method
In numerical analysis, Newton's method , named after Isaac Newton and Joseph Raphson, is a method for finding successively better approximations to the roots of a real-valued function. The algorithm is first in the class of Householder's methods, succeeded by Halley's method...
used to solve maximum likelihood
Maximum likelihood
In statistics, maximum-likelihood estimation is a method of estimating the parameters of a statistical model. When applied to a data set and given a statistical model, maximum-likelihood estimation provides estimates for the model's parameters....
equations numerically
Numerical analysis
Numerical analysis is the study of algorithms that use numerical approximation for the problems of mathematical analysis ....
.
Sketch of Derivation
Let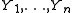 be random variable
be random variableRandom variable
In probability and statistics, a random variable or stochastic variable is, roughly speaking, a variable whose value results from a measurement on some type of random process. Formally, it is a function from a probability space, typically to the real numbers, which is measurable functionmeasurable...
s, independent and identically distributed with twice differentiable p.d.f.
Probability density function
In probability theory, a probability density function , or density of a continuous random variable is a function that describes the relative likelihood for this random variable to occur at a given point. The probability for the random variable to fall within a particular region is given by the...
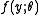 , and we wish to calculate the maximum likelihood estimator (M.L.E.)
, and we wish to calculate the maximum likelihood estimator (M.L.E.)  of
of 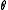 . First, suppose we have a starting point for our algorithm
. First, suppose we have a starting point for our algorithm 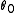 , and consider a Taylor expansion
, and consider a Taylor expansionTaylor series
In mathematics, a Taylor series is a representation of a function as an infinite sum of terms that are calculated from the values of the function's derivatives at a single point....
of the score function
Score (statistics)
In statistics, the score, score function, efficient score or informant plays an important role in several aspects of inference...
,
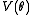 , about
, about 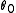 :
:where
is the observed information matrix
Observed information
In statistics, the observed information, or observed Fisher information, is the negative of the second derivative of the "log-likelihood"...
at
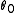 . Now, setting
. Now, setting 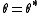 , using that
, using that 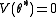 and rearranging gives us:
and rearranging gives us:We therefore use the algorithm
and under certain regularity conditions, it can be shown that
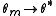 .
.Fisher scoring
In practice,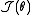 is usually replaced by
is usually replaced by 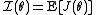 , the Fisher information
, the Fisher informationFisher information
In mathematical statistics and information theory, the Fisher information is the variance of the score. In Bayesian statistics, the asymptotic distribution of the posterior mode depends on the Fisher information and not on the prior...
, thus giving us the Fisher Scoring Algorithm:
-
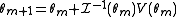 .
.