
Scale-Free Ideal Gas
Encyclopedia
The scale-free ideal gas (SFIG) is a physical model assuming a collection of non-interacting elements with an stochastic
proportional growth. It is the scale-invariant
version of an ideal gas
. Some cases of city-population, electoral results and cites to scientific journals can be approximately considered scale-free ideal gases.
If k is the size of the elements, being k1 and kM the minimum and maximum allowing sizes respectively, and v = dk/dt is the growth, the bulk probability density function
F(k, v) of a scale-free ideal gas follows
Stochastic
Stochastic refers to systems whose behaviour is intrinsically non-deterministic. A stochastic process is one whose behavior is non-deterministic, in that a system's subsequent state is determined both by the process's predictable actions and by a random element. However, according to M. Kac and E...
proportional growth. It is the scale-invariant
Scale invariance
In physics and mathematics, scale invariance is a feature of objects or laws that do not change if scales of length, energy, or other variables, are multiplied by a common factor...
version of an ideal gas
Ideal gas
An ideal gas is a theoretical gas composed of a set of randomly-moving, non-interacting point particles. The ideal gas concept is useful because it obeys the ideal gas law, a simplified equation of state, and is amenable to analysis under statistical mechanics.At normal conditions such as...
. Some cases of city-population, electoral results and cites to scientific journals can be approximately considered scale-free ideal gases.
If k is the size of the elements, being k1 and kM the minimum and maximum allowing sizes respectively, and v = dk/dt is the growth, the bulk probability density function
Probability density function
In probability theory, a probability density function , or density of a continuous random variable is a function that describes the relative likelihood for this random variable to occur at a given point. The probability for the random variable to fall within a particular region is given by the...
F(k, v) of a scale-free ideal gas follows
-

where N is the total number of elements, Ω = ln k1/kM is the logaritmic "volume" of the system,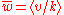 is the mean relative growth and
is the mean relative growth and 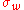 is the standard deviation of the relative growth. The entropyEntropyEntropy is a thermodynamic property that can be used to determine the energy available for useful work in a thermodynamic process, such as in energy conversion devices, engines, or machines. Such devices can only be driven by convertible energy, and have a theoretical maximum efficiency when...
is the standard deviation of the relative growth. The entropyEntropyEntropy is a thermodynamic property that can be used to determine the energy available for useful work in a thermodynamic process, such as in energy conversion devices, engines, or machines. Such devices can only be driven by convertible energy, and have a theoretical maximum efficiency when...
equation of state is
-
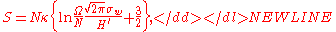
where is a constant that accounts for dimensionality and
is a constant that accounts for dimensionality and 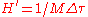 is the elementary volume in phase space, with
is the elementary volume in phase space, with  the elementary time and M the total number of allowed discrete sizes. This expression has the same form as the one-dimensional ideal gas, changing the thermodynamical variables (N, V, T) by (N, Ω,σw).
the elementary time and M the total number of allowed discrete sizes. This expression has the same form as the one-dimensional ideal gas, changing the thermodynamical variables (N, V, T) by (N, Ω,σw).
Zipf's law may emerge in the external limits of the density since it is a special regime of scale-free ideal gases.
-

