
Scalar boson
Encyclopedia
Explanation
The name "scalar boson" arises from quantum field theoryQuantum field theory
Quantum field theory provides a theoretical framework for constructing quantum mechanical models of systems classically parametrized by an infinite number of dynamical degrees of freedom, that is, fields and many-body systems. It is the natural and quantitative language of particle physics and...
. It refers to the particular transformation properties under Lorentz transformation
Lorentz transformation
In physics, the Lorentz transformation or Lorentz-Fitzgerald transformation describes how, according to the theory of special relativity, two observers' varying measurements of space and time can be converted into each other's frames of reference. It is named after the Dutch physicist Hendrik...
. Boson means that it has an integer-valued spin
Spin (physics)
In quantum mechanics and particle physics, spin is a fundamental characteristic property of elementary particles, composite particles , and atomic nuclei.It is worth noting that the intrinsic property of subatomic particles called spin and discussed in this article, is related in some small ways,...
, the scalar fixes this value to 0.
Examples
- Various known composite particles are scalar bosons, e.g., the alpha particle and the pi meson. Among the scalar mesons, one distinguishes between the scalarScalar mesonIn high energy physics, a scalar meson is a meson with total spin 0 and even parity . Compare to pseudoscalar meson....
and pseudoscalarPseudoscalar mesonIn high energy physics, a pseudoscalar meson is a meson with total spin 0 and odd parity . Compare to scalar meson.Pseudoscalar mesons are commonly seen in proton-proton scattering and proton-antiproton annihilation...
mesons, which refers to their transformation property under parityParity (physics)In physics, a parity transformation is the flip in the sign of one spatial coordinate. In three dimensions, it is also commonly described by the simultaneous flip in the sign of all three spatial coordinates:...
.
- The only fundamental scalar boson in the standard modelStandard ModelThe Standard Model of particle physics is a theory concerning the electromagnetic, weak, and strong nuclear interactions, which mediate the dynamics of the known subatomic particles. Developed throughout the mid to late 20th century, the current formulation was finalized in the mid 1970s upon...
of elementary particle physics is the Higgs bosonHiggs bosonThe Higgs boson is a hypothetical massive elementary particle that is predicted to exist by the Standard Model of particle physics. Its existence is postulated as a means of resolving inconsistencies in the Standard Model...
. It is the only elementary particleElementary particleIn particle physics, an elementary particle or fundamental particle is a particle not known to have substructure; that is, it is not known to be made up of smaller particles. If an elementary particle truly has no substructure, then it is one of the basic building blocks of the universe from which...
in the Standard Model that has not yet been experimentally measured (November 2011). There are various other hypothetical fundamental scalar bosons, including the inflatonInflatonThe inflaton is the generic name of the hypothetical and hitherto unidentified scalar field that may be responsible for the hypothetical inflation in the very early universe...
.
- One very popular quantum field theory, which uses scalar bosonic fields and is introduced in many introductory books to quantum field theories for pedagogical reasons, is the so called
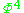 -theory. It usually serves as toy model to introduce into the basic concepts of the field.
-theory. It usually serves as toy model to introduce into the basic concepts of the field.
See also
- Scalar mesonScalar mesonIn high energy physics, a scalar meson is a meson with total spin 0 and even parity . Compare to pseudoscalar meson....
- Pseudoscalar mesonPseudoscalar mesonIn high energy physics, a pseudoscalar meson is a meson with total spin 0 and odd parity . Compare to scalar meson.Pseudoscalar mesons are commonly seen in proton-proton scattering and proton-antiproton annihilation...
- Quantum field theoryQuantum field theoryQuantum field theory provides a theoretical framework for constructing quantum mechanical models of systems classically parametrized by an infinite number of dynamical degrees of freedom, that is, fields and many-body systems. It is the natural and quantitative language of particle physics and...
- Scalar field theoryScalar field theoryIn theoretical physics, scalar field theory can refer to a classical or quantum theory of scalar fields. A field which is invariant under any Lorentz transformation is called a "scalar", in contrast to a vector or tensor field...
- Vector bosonVector bosonIn particle physics, a vector boson is a boson with the spin quantum number equal to 1.The vector bosons considered to be elementary particles in the Standard Model are the gauge bosons or, the force carriers of fundamental interactions: the photon of electromagnetism, the W and Z bosons of the...

