
Sales process
Encyclopedia
A sales process, also known as a sales tunnel or a sales funnel, is a systematic approach to selling a product or service. A growing body of published literature approaches the sales process from the point of view of an engineering
discipline (see sales process engineering
).
Reasons for having a well thought-out sales process include seller and buyer risk management, standardized customer interaction in sales, and scalable revenue generation. A major advantage of approaching the subject of sales from a "process point of view" is that it offers a host of well-tested design and improvement tools from other successful disciplines and process-oriented industries. In turn, this offers potential for quicker progress. Quality expert Joseph Juran observed, "There should be no reason our familiar principles of quality and process engineering would not work in the sales process". A sales team's fundamental job is to move a greater number of larger deals through the sales process in less time.
Specific steps or stages in a sales process vary from company to company but generally include the following elements:
An alternate but similar series of steps is as follows:
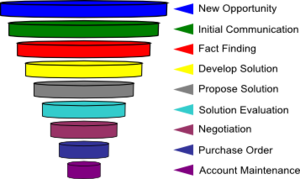
These eight steps of the sales process is more current/accurate compared to traditional sales. These are the typical steps taken, which are usually obtained in the same order, however can vary depending on the current situation. These steps of the sales process are given (pg. 66) and explained in one of the most influential sales textbooks written by Gregory A. Rich, Rosann L. Spiro, and William J Stanton, entitled "Management of a Sales Force" Twelfth Edition.
Mapping a process provides a starting point for further careful analysis and continuous improvement. Diagramming a process flow is considered to be one of the seven basic quality improvement tools. Elements in the list above (among many others) have been described and/or flow-charted in the published literature. Some examples have primarily focused on functions performed by a sales "department". At least one cross-functional approach depicts and integrates a variety of interdependent areas, such as sales, marketing
, customer service
, and information systems
.
From a seller's point of view, a sales process mitigates risk by stage-gating deals based on collection of information or execution of procedures that gate movement to the next step - Of the large number of initially interested persons on the narrow end of orders only a fraction of the initially interested people remain and actually place an order.. This controls seller resource expenditure on non-performing deals. Ideally this also prevents buyers from purchasing products they don't need though such a benefit requires ethical intentions by the seller. Because of the uncertainty of this assurance, buyers often have a buying or purchasing process. The interface between the selling and buying process has also been diagrammed.
A formalized sales process is generally more common for companies that either have complex sales cycles, large revenue risks that require systematic assurance of revenue generation, and/or those that choose to use a more consultative sales approach (e.g. Saturn, IBM, Hewlett-Packard).
An effective sales process can be described through steps that walk a salesperson from meeting the prospect all the way through closing the sale. Often a bad sales experience can be analyzed and shown to have skipped key steps. This is where a good sales process mitigates risk for both buyer and seller. A solid sales process also has the dramatic impact of forecasting accuracy and predictability in revenue results.
Many companies develop their own sales process; however, off the shelf versions are available from a number of companies in the sales performance improvement industry. A large number of these methods have been described by their promoters in books available to the public, primarily addressing tactics employed by an individual sales representative. These provide a customizable process and a set of electronic tools that can be freestanding or can be integrated if required with the company's SFA, CRM
, or other opportunity management system.
Engineering
Engineering is the discipline, art, skill and profession of acquiring and applying scientific, mathematical, economic, social, and practical knowledge, in order to design and build structures, machines, devices, systems, materials and processes that safely realize improvements to the lives of...
discipline (see sales process engineering
Sales process engineering
Sales process engineering has been described as “the systematic application of scientific and mathematical principles to achieve the practical goals of a particular sales process". Selden pointed out that in this context, sales referred to the output of a process involving a variety of functions...
).
Reasons for having a well thought-out sales process include seller and buyer risk management, standardized customer interaction in sales, and scalable revenue generation. A major advantage of approaching the subject of sales from a "process point of view" is that it offers a host of well-tested design and improvement tools from other successful disciplines and process-oriented industries. In turn, this offers potential for quicker progress. Quality expert Joseph Juran observed, "There should be no reason our familiar principles of quality and process engineering would not work in the sales process". A sales team's fundamental job is to move a greater number of larger deals through the sales process in less time.
Specific steps or stages in a sales process vary from company to company but generally include the following elements:
- Initial contact
- Application of Initial Fit Criteria
- Sales leadSales leadA sales lead, or Sales Lead, is the identification of a person or entity that has the interest and authority to purchase a product or service. This step represents the first stage of a sales process. The lead may have a corporation or business associated with the person. Sales leads are generic...
- Need identificationNeed identification-Seven Stages:The full Selling Process consists of:# preapproach# approach# need identification# presentation# handling objections# closing the sale# post-sale follow-up....
- Qualified prospectQualified prospectAn qualified prospect is an organization which has expressed the need for the products or services of the seller.There is much debate in the sales profession as to what constitutes an actual "qualified" prospect...
- ProposalProposal (business)A business proposal is a written offer from a seller to a prospective buyer.Business proposals are often a key step in the complex sales process—i.e., whenever a buyer considers more than price in a purchase.-Overview:...
- NegotiationNegotiationNegotiation is a dialogue between two or more people or parties, intended to reach an understanding, resolve point of difference, or gain advantage in outcome of dialogue, to produce an agreement upon courses of action, to bargain for individual or collective advantage, to craft outcomes to satisfy...
- ClosingClosing (sales)Closing is a sales term which refers to the process of making a sale. The sales sense springs from real estate, where closing is the final step of a transaction. In sales, it is used more generally to mean achievement of the desired outcome, which may be an exchange of money or acquiring a...
- Deal TransactionDeal TransactionThe deal transaction is the hub of global commerce. A deal transaction is a unique event where money exchanges hands in return for a product or service. The “transaction experience” is the buying, selling, and marketing cycle defined as the pre- and post-effects of that unique sale.The...
An alternate but similar series of steps is as follows:

- Prospecting/Initial contact
- Preapproach- planning the sale
- Approach
- Need assessment
- Presentation
- Meeting objections
- Gaining commitment
- Follow-up
These eight steps of the sales process is more current/accurate compared to traditional sales. These are the typical steps taken, which are usually obtained in the same order, however can vary depending on the current situation. These steps of the sales process are given (pg. 66) and explained in one of the most influential sales textbooks written by Gregory A. Rich, Rosann L. Spiro, and William J Stanton, entitled "Management of a Sales Force" Twelfth Edition.
Mapping a process provides a starting point for further careful analysis and continuous improvement. Diagramming a process flow is considered to be one of the seven basic quality improvement tools. Elements in the list above (among many others) have been described and/or flow-charted in the published literature. Some examples have primarily focused on functions performed by a sales "department". At least one cross-functional approach depicts and integrates a variety of interdependent areas, such as sales, marketing
Marketing
Marketing is the process used to determine what products or services may be of interest to customers, and the strategy to use in sales, communications and business development. It generates the strategy that underlies sales techniques, business communication, and business developments...
, customer service
Customer service
Customer service is the provision of service to customers before, during and after a purchase.According to Turban et al. , “Customer service is a series of activities designed to enhance the level of customer satisfaction – that is, the feeling that a product or service has met the customer...
, and information systems
Information systems
Information Systems is an academic/professional discipline bridging the business field and the well-defined computer science field that is evolving toward a new scientific area of study...
.
From a seller's point of view, a sales process mitigates risk by stage-gating deals based on collection of information or execution of procedures that gate movement to the next step - Of the large number of initially interested persons on the narrow end of orders only a fraction of the initially interested people remain and actually place an order.. This controls seller resource expenditure on non-performing deals. Ideally this also prevents buyers from purchasing products they don't need though such a benefit requires ethical intentions by the seller. Because of the uncertainty of this assurance, buyers often have a buying or purchasing process. The interface between the selling and buying process has also been diagrammed.
A formalized sales process is generally more common for companies that either have complex sales cycles, large revenue risks that require systematic assurance of revenue generation, and/or those that choose to use a more consultative sales approach (e.g. Saturn, IBM, Hewlett-Packard).
An effective sales process can be described through steps that walk a salesperson from meeting the prospect all the way through closing the sale. Often a bad sales experience can be analyzed and shown to have skipped key steps. This is where a good sales process mitigates risk for both buyer and seller. A solid sales process also has the dramatic impact of forecasting accuracy and predictability in revenue results.
Many companies develop their own sales process; however, off the shelf versions are available from a number of companies in the sales performance improvement industry. A large number of these methods have been described by their promoters in books available to the public, primarily addressing tactics employed by an individual sales representative. These provide a customizable process and a set of electronic tools that can be freestanding or can be integrated if required with the company's SFA, CRM
Customer relationship management
Customer relationship management is a widely implemented strategy for managing a company’s interactions with customers, clients and sales prospects. It involves using technology to organize, automate, and synchronize business processes—principally sales activities, but also those for marketing,...
, or other opportunity management system.

