
Sabon Gari
Encyclopedia
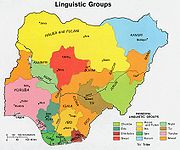
Northern Nigeria
Northern Nigeria is a geographical region of Nigeria. It is more arid and less densely populated than the south. The people are largely Muslim, and many are Hausa...
and south central Niger
Niger
Niger , officially named the Republic of Niger, is a landlocked country in Western Africa, named after the Niger River. It borders Nigeria and Benin to the south, Burkina Faso and Mali to the west, Algeria and Libya to the north and Chad to the east...
whose residents are not indigenous to Hausa lands.
History
Permanent communities of strangers segregated from the indigenous population had existed in Northern Nigeria and other parts of West Africa long before the arrival of the British at around 1900. Although living segregated from the Hausa population, residents of these communities were ultimately subject to the authority of the local emirEmir
Emir , meaning "commander", "general", or "prince"; also transliterated as Amir, Aamir or Ameer) is a title of high office, used throughout the Muslim world...
.
The establishment of British colonial rule under Frederick Lugard
Frederick Lugard
Frederick John Dealtry Lugard, 1st Baron Lugard GCMG, CB, DSO, PC , known as Sir Frederick Lugard between 1901 and 1928, was a British soldier, mercenary, explorer of Africa and colonial administrator, who was Governor of Hong Kong and Governor-General of Nigeria .-Early life and education:Lugard...
and the construction of new railway lines led to a large influx of laboreres and traders from Southern Nigeria. The immigrants, which were mostly Igbo
Igbo people
Igbo people, also referred to as the Ibo, Ebo, Eboans or Heebo are an ethnic group living chiefly in southeastern Nigeria. They speak Igbo, which includes various Igboid languages and dialects; today, a majority of them speak English alongside Igbo as a result of British colonialism...
and Yoruba people
Yoruba people
The Yoruba people are one of the largest ethnic groups in West Africa. The majority of the Yoruba speak the Yoruba language...
, settled in new towns or Sabon Garuruwa, as these new towns were called by the local Hausa people. The Cantonments Proclamation of 1914 institutionalized this system of residential segregation. The Sabon Garuruwa became Native Reservations, officially reserved for employees of the government and commercial firms, and in practice inhabited by residents not indigenous to Northern Nigeria.
British colonial rule in Northern Nigeria was indirect, leaving the emirs in power, albeit as part of the colonial administration. In the beginning the Sabon Garuruwa were administrated by the emirs. This changed with the Township Ordinance of 1917, which placed the Sabon Garuruwa and their residents under direct British rule. Sabon Gari residents were granted more rights than those under the administration of the local emir. For example, residents of a Sabon Gari could send representatives to the advisory board responsible for a township, or could choose between courts administering Muslim law or British law.
Sabon Garuruwa were established in all major cities of Northern Nigeria, most notably in Kano
Kano
Kano is a city in Nigeria and the capital of Kano State in Northern Nigeria. Its metropolitan population is the second largest in Nigeria after Lagos. The Kano Urban area covers 137 sq.km and comprises six Local Government Area - Kano Municipal, Fagge, Dala, Gwale, Tarauni and Nassarawa - with a...
, Kaduna
Kaduna
Kaduna is the state capital of Kaduna State in north-central Nigeria. The city, located on the Kaduna River, is a trade center and a major transportation hub for the surrounding agricultural areas with its rail and road junction. The population of Kaduna is at 760,084 as of the 2006 Nigerian census...
and Zaria
Zaria
Zaria may refer to:*Zaria, a city in Kaduna State, Nigeria*Zaria , or Zoria, the Slavic goddess of beauty*Countess Zaria of Orange-Nassau, Jonkvrouwe van Amsberg, a member of the Dutch royal family...
. One exception was Maiduguri
Maiduguri
Maiduguri, also fondly called Yerwa by its locals, is the capital and the largest city of Borno State in north-eastern Nigeria. The city sits along the seasonal Ngadda River which disappears into the Firki swamps in the areas around Lake Chad...
, which never had a Sabon Gari. A typical city or town in Northern Nigeria would consist of the old city within fortified walls and inhabited by indigenous Hausa or Fulani people. The Sabon Gari would house immigrants mostly from Southern Nigeria. The Tudun Wada would house people from Northern Nigeria that were not indigenous to the local area. Europeans would live in the European Reservation Areas.
Over time the initially strict residential segregation would partially break down. Eventually a typical Sabon Gari would house a diversity of people from all parts of Nigeria and to a lesser extent from other parts of West Africa. For example, in 1939 various ethnic groups were represented in the Sabon Gari of Kaduna as follows: 27% were Hausa
Hausa people
The Hausa are one of the largest ethnic groups in West Africa. They are a Sahelian people chiefly located in northern Nigeria and southeastern Niger, but having significant numbers living in regions of Cameroon, Ghana, Cote d'Ivoire, Chad and Sudan...
, 11% were Igbo
Igbo people
Igbo people, also referred to as the Ibo, Ebo, Eboans or Heebo are an ethnic group living chiefly in southeastern Nigeria. They speak Igbo, which includes various Igboid languages and dialects; today, a majority of them speak English alongside Igbo as a result of British colonialism...
, 19% were Yoruba
Yoruba people
The Yoruba people are one of the largest ethnic groups in West Africa. The majority of the Yoruba speak the Yoruba language...
, 15% were Nupe people
Nupe
The Nupe, traditionally called the Tapa by the neighbouring Yoruba, are an ethnic group located primarily in the Middle Belt and northern Nigeria, and are the dominant group in Niger and an important minority in Kwara State.-History:...
and 28% were other ethnicities.
Sabon Garuruwa today
Even today Sabon Garuruwa are predominantly inhabited by people from Southern Nigeria. Ethnic tensions between groups from southern and northern Nigeria lead to frequent riots in the Sabon Garuruwa of northern cities. With the introduction of ShariaSharia
Sharia law, is the moral code and religious law of Islam. Sharia is derived from two primary sources of Islamic law: the precepts set forth in the Quran, and the example set by the Islamic prophet Muhammad in the Sunnah. Fiqh jurisprudence interprets and extends the application of sharia to...
law in the northern states of Nigeria some Sabon Garuruwa with its predominantly Christian population have become the place of officially forbidden activities like alcohol consumption, gambling and prostitution.
Zinder
Zinder
Zinder is the second largest city in Niger, with a population of 170,574 by 2005 was estimated to be over 200,000...
and Maradi, the two largest Hausa cities in Niger
Niger
Niger , officially named the Republic of Niger, is a landlocked country in Western Africa, named after the Niger River. It borders Nigeria and Benin to the south, Burkina Faso and Mali to the west, Algeria and Libya to the north and Chad to the east...
's Hausa speaking southeast retain Sabon Gari districts.

