
Royal Saltworks at Arc-et-Senans
Encyclopedia
The Saline Royale is a historical building at Arc-et-Senans
in the department of Doubs
, eastern France
. It is next to the Forest of Chaux
and about 35 kilometers from Besançon
. The architect was Claude-Nicolas Ledoux (1736–1806), a prominent Parisian architect of the time. The work is an important example of an early Enlightenment
project in which the architect based his design on a philosophy that favored arranging buildings according to a rational geometry and a hierarchical relation between the parts of the project.
The Institut Claude-Nicolas Ledoux has taken on the task of conservator and is managing the site as a monument. UNESCO
added the "Salines Royales" to its List of World Heritage Sites in 1982.
Today, the site is mostly open to the public. It includes, in the building the coopers used, displays by the Ledoux Museum of other futuristic projects that were never built. Also, the salt production buildings house temporary exhibitions.
The train line from Besançon
to Bourg-en-Bresse
passes just next to the salt works. The station for Arc-et-Senans is only a few dozen meters from the site.
was an essential and valuable commodity. At the time, salt was widely used for the preservation of foods such as meat or fish. The ubiquity of salt use caused the French government to impose a tax its consumption, the gabelle
. This was a mandatory requirement that all people over the age of 8 years buy an amount of salt per year at a price that the government had set. Collection of the gabelle was the responsibility of the Ferme Générale
.
As a region, Franche-Comté
was relatively well-endowed with salt springs due to subterranean seams of halite
. Consequently, there were a number of small salt works, such as those at Salins-les-Bains
and Montmorot
, that extracted salt by boiling water over wood fires. The salt works were constructed close to the springs and drew on wood brought from nearby forests. After many years of exploitation, the forests were becoming more and more rapidly denuded, with the result that wood had to be brought from farther and farther away, at greater and greater cost. Furthermore, over time the salt content of the brine was dropping. This led the experts of the Ferme Générale to consider exploiting even small springs, an initiative that the King's council stopped in April 1773. Part of the problem was that it was impossible to build evaporation buildings because Salins-les-Bains sat in a small valley.
The Fermiers Généraux decided to explore a more mechanised and efficient method of extraction. The concept was to construct a purpose-built factory near the forest of Chaux in the Val d'Amour, i.e., with the brine was to be brought to the factory by a newly constructed canal.
appointed Ledoux Commissioner of the Salt Works of Lorraine
and Franché-Comté. As Commissioner, Ledoux was responsible for inspecting the different saltworks in eastern France. This gave him an opportunity to see many different saltworks, including those at Salins-les-Bains and Lons-le-Saunier, and to learn from them what one might want if designing a factory from scratch.
Two years later, Madame du Barry
supported Ledoux's nomination to membership in the Royal Academie of Architecture. This permitted him to style himself as Royal Architect. (He was already the architect for the Ferme générale
, the private customs and excise operation that collected many taxes on behalf of the king, under 6-year contracts.) It was on the basis of his positions as Inspector of the Saltworks and as Royal Architect that he received the commission to design the Royal Saltworks at Arc-et-Senans.
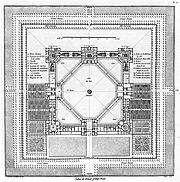
Unconstrained by any practical considerations, the project was ambitious, innovative, and a break with traditional approaches. What Ledoux did was to impose a rigid geometry on the overall design. The buildings were placed around the edges of an immense square, and linked to each other by porticoes; no building stood in isolation. To speed connections between buildings, Ledoux introduced covered arcades that linked the midpoints of adjacent sides, forming a square within the square. Columns abounded. The buildings themselves were replete with them, and 144 Doric
columns supported the covered arcades.
Ledoux's plan envisaged that the central square courtyard would be where the factory would keep its firewood. At each corner of the square, and at the mid-points of each side stood two-story, square buildings that would house the various parts of the operation. In front were the quarters for the guards, a chapel, and a bakery. On the sides were workshops for the coopers and other workmen. At the base was the factory itself. Gardens were to surround the site to provide the workers with a supplement to their income. Lastly, a wall would surround the entire complex to protect it from theft.
It was the project's grandiose vision that blocked its realization. No industrial building of the period was equally imposing. The king rejected the project. He particularly objected to the extensive use of columns, features that he felt were more appropriate for churches and palaces. He also objected to the chapel being relegated to a corner.
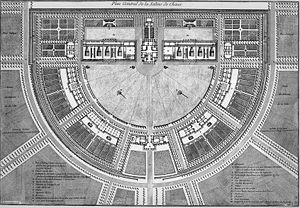 In his own critical review of the project, Ledoux stated that he had put too much weight on the conventions of a factory to the neglect of symbolic aspects. The result was a flat, uniform design based on bi-lateral symmetry, rather than one that would have a marked center of gravity. The design also recalled the traditional communal buildings of the time such as convents, monasteries, hospitals, large farms, and the like. Furthermore, since ancient times, architects had recognized that plans such as Ledoux's were vulnerable to the spread of fire and not very hygienic, with throughout the day some part of the site being in the shade. Lastly, critics pointed out that the project did not take into account the geographic or geological constraints.
In his own critical review of the project, Ledoux stated that he had put too much weight on the conventions of a factory to the neglect of symbolic aspects. The result was a flat, uniform design based on bi-lateral symmetry, rather than one that would have a marked center of gravity. The design also recalled the traditional communal buildings of the time such as convents, monasteries, hospitals, large farms, and the like. Furthermore, since ancient times, architects had recognized that plans such as Ledoux's were vulnerable to the spread of fire and not very hygienic, with throughout the day some part of the site being in the shade. Lastly, critics pointed out that the project did not take into account the geographic or geological constraints.
had signed the edict authorizing the construction of the saltworks on 29 April 1773, and after approval of Ledoux' second design, construction began in 1775. The city was never started, however. All that was completed was the diameter and a semicircle of buildings of the saltworks.
 In the second design, the entrance building sits at the mid-point of the semicircle and contains on one side guardrooms and on the other a prison and a forge. Other buildings on the semicircle include on the left, as one faces the entrance, quarters for carpenters and laborers, and on the right, marshals and coopers. At the center of the circle is the house of the Director, which has a belvedere on top. A monumental staircase led to a chapel that was destroyed by fire in 1918, following a lightning strike. On either side of the Director's house are the saltworks themselves. These two buildings are 80 meters long, 28 meters wide, and 20 meters high. They contain the drying ovens, the heating pots, the "Sales des Bosses", and the salt stores. At each intersection of the diameter and the semicircle sit buildings that housed the works' clerks. Behind the Director's house there is an elegant, small stables for the Director's horses.
In the second design, the entrance building sits at the mid-point of the semicircle and contains on one side guardrooms and on the other a prison and a forge. Other buildings on the semicircle include on the left, as one faces the entrance, quarters for carpenters and laborers, and on the right, marshals and coopers. At the center of the circle is the house of the Director, which has a belvedere on top. A monumental staircase led to a chapel that was destroyed by fire in 1918, following a lightning strike. On either side of the Director's house are the saltworks themselves. These two buildings are 80 meters long, 28 meters wide, and 20 meters high. They contain the drying ovens, the heating pots, the "Sales des Bosses", and the salt stores. At each intersection of the diameter and the semicircle sit buildings that housed the works' clerks. Behind the Director's house there is an elegant, small stables for the Director's horses.
The support of salt works by a state monopoly probably explains why this building is so grand. The gabelle was very unpopular and was one of the complaints that led to the French Revolution
. The Revolution itself probably curtailed the building of the ideal city.
s of salt per year at its peak, all of which was exported to Switzerland. All production ceased in 1895 following a lawsuit that the inhabitants of Arc-and-Senans initiated, protesting the pollution of nearby wells. At the same time, the salt works was having difficulty in the face of competition from sea salt
brought by rail.
As mentioned above, a lightning bolt in 1918 destroyed the chapel. In April 1926, some of the buildings were dynamite
d, and many of the trees on the site were cut down. Still, on November 30, 1926, after a review that began in 1923, the Commission for Monuments declared the central pavilion and the entryway historical monuments. The Society for the Eastern Saltworks, still the owner of the Arc-et-Senans site, was not pleased with the decision. On 10 June 1927 the department of Doubs
acquired the salt works and commenced restoration work in 1930.
During 1938, the site housed a camp for Spanish Republican
refugees. Then, during October 1939, at the outbreak of World War II
, the French military installed an anti-aircraft battery
in the courtyard area. Also, a unit of engineers occupied some of the buildings. Still, February 20, 1940, saw the publication of the official announcement of the classification of the salt works and its surrounding wall as historical monuments.
In June 1940, German troops took up residence. From May 1941 to September 1943, the French authorities established an internment camp to hold the area's gypsies and others with no fixed address (Centre de Rassemblement des tziganes et nomades).
After the war, there was an extensive public campaign by artists, journalists and writers from the region to encourage the authorities to protect the site.
In 1965, Marcel Bluwal
used the director's house for the tomb of the Commander in his television adaptation of Molière
's Dom Juan
.
Since 1973, the royal salt works and the Institut Claude-Nicolas Ledoux have been members of the European network of cultural sites. Then in 1982, UNESCO listed the salt works as a World Heritage Site.
has been added to the listing for Arc-et-Senans in the World Heritage list. It has been the venue for several cultural events and exhibitions in recent years.
Arc-et-Senans
Arc-et-Senans is a commune in the Doubs department in the Franche-Comté region in eastern France.The Royal Saltworks, a UNESCO World Heritage Site since 1982, are located here.-Population:-References:*...
in the department of Doubs
Doubs
Doubs is a department the Franche-Comté region of eastern France named after the Doubs River.-History:As early as the 13th century, inhabitants of the northern two-thirds of Doubs spoke the Franc-Comtois language, a dialect of Langue d'Oïl. Residents of the southern third of Doubs spoke a dialect...
, eastern France
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
. It is next to the Forest of Chaux
Forest of Chaux
The Forest of Chaux is the second largest forest in France. Its 20,493 hectares are located in the region of Franche-Comté on the plains east of the Jura mountains....
and about 35 kilometers from Besançon
Besançon
Besançon , is the capital and principal city of the Franche-Comté region in eastern France. It had a population of about 237,000 inhabitants in the metropolitan area in 2008...
. The architect was Claude-Nicolas Ledoux (1736–1806), a prominent Parisian architect of the time. The work is an important example of an early Enlightenment
Age of Enlightenment
The Age of Enlightenment was an elite cultural movement of intellectuals in 18th century Europe that sought to mobilize the power of reason in order to reform society and advance knowledge. It promoted intellectual interchange and opposed intolerance and abuses in church and state...
project in which the architect based his design on a philosophy that favored arranging buildings according to a rational geometry and a hierarchical relation between the parts of the project.
The Institut Claude-Nicolas Ledoux has taken on the task of conservator and is managing the site as a monument. UNESCO
UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations...
added the "Salines Royales" to its List of World Heritage Sites in 1982.
Today, the site is mostly open to the public. It includes, in the building the coopers used, displays by the Ledoux Museum of other futuristic projects that were never built. Also, the salt production buildings house temporary exhibitions.
The train line from Besançon
Besançon
Besançon , is the capital and principal city of the Franche-Comté region in eastern France. It had a population of about 237,000 inhabitants in the metropolitan area in 2008...
to Bourg-en-Bresse
Bourg-en-Bresse
Bourg-en-Bresse is a commune in eastern France, capital of the Ain department, and was capital of the former province of Bresse . It is located north-northeast of Lyon.The inhabitants of Bourg-en-Bresse are known as Burgiens.-Geography:...
passes just next to the salt works. The station for Arc-et-Senans is only a few dozen meters from the site.
Background
In the 18th century saltEdible salt
Salt, also known as table salt, or rock salt, is a mineral that is composed primarily of sodium chloride , a chemical compound belonging to the larger class of ionic salts. It is essential for animal life in small quantities, but is harmful to animals and plants in excess...
was an essential and valuable commodity. At the time, salt was widely used for the preservation of foods such as meat or fish. The ubiquity of salt use caused the French government to impose a tax its consumption, the gabelle
Gabelle
The gabelle was a very unpopular tax on salt in France before 1790. The term gabelle derives from the Italian gabella , itself from the Arabic qabala....
. This was a mandatory requirement that all people over the age of 8 years buy an amount of salt per year at a price that the government had set. Collection of the gabelle was the responsibility of the Ferme Générale
Ferme générale
The Ferme générale was, in ancien régime France, essentially an outsourced customs and excise operation which collected duties on behalf of the king, under six-year contracts...
.
As a region, Franche-Comté
Franche-Comté
Franche-Comté the former "Free County" of Burgundy, as distinct from the neighbouring Duchy, is an administrative region and a traditional province of eastern France...
was relatively well-endowed with salt springs due to subterranean seams of halite
Halite
Halite , commonly known as rock salt, is the mineral form of sodium chloride . Halite forms isometric crystals. The mineral is typically colorless or white, but may also be light blue, dark blue, purple, pink, red, orange, yellow or gray depending on the amount and type of impurities...
. Consequently, there were a number of small salt works, such as those at Salins-les-Bains
Salins-les-Bains
Salins-les-Bains is a commune in the Jura department in Franche-Comté in eastern France.Salins owes its name to its saline waters, used for bathing and drinking. There are also salt works and gypsum deposits. In 2009 the historic saltworks were added to the list of UNESCO World Heritage sites...
and Montmorot
Montmorot
Montmorot is a commune in the Jura department in Franche-Comté in eastern France in the western suburb of Lons-le-Saunier.- Geography :The Vallière flows westward through the southern part of the commune and crosses the village.- References :*...
, that extracted salt by boiling water over wood fires. The salt works were constructed close to the springs and drew on wood brought from nearby forests. After many years of exploitation, the forests were becoming more and more rapidly denuded, with the result that wood had to be brought from farther and farther away, at greater and greater cost. Furthermore, over time the salt content of the brine was dropping. This led the experts of the Ferme Générale to consider exploiting even small springs, an initiative that the King's council stopped in April 1773. Part of the problem was that it was impossible to build evaporation buildings because Salins-les-Bains sat in a small valley.
The Fermiers Généraux decided to explore a more mechanised and efficient method of extraction. The concept was to construct a purpose-built factory near the forest of Chaux in the Val d'Amour, i.e., with the brine was to be brought to the factory by a newly constructed canal.
Claude Nicolas Ledoux
On September 20, 1771, Louis XVLouis XV of France
Louis XV was a Bourbon monarch who ruled as King of France and of Navarre from 1 September 1715 until his death. He succeeded his great-grandfather at the age of five, his first cousin Philippe II, Duke of Orléans, served as Regent of the kingdom until Louis's majority in 1723...
appointed Ledoux Commissioner of the Salt Works of Lorraine
Lorraine (province)
The Duchy of Upper Lorraine was an historical duchy roughly corresponding with the present-day northeastern Lorraine region of France, including parts of modern Luxembourg and Germany. The main cities were Metz, Verdun, and the historic capital Nancy....
and Franché-Comté. As Commissioner, Ledoux was responsible for inspecting the different saltworks in eastern France. This gave him an opportunity to see many different saltworks, including those at Salins-les-Bains and Lons-le-Saunier, and to learn from them what one might want if designing a factory from scratch.
Two years later, Madame du Barry
Madame du Barry
Jeanne Bécu, comtesse du Barry was the last Maîtresse-en-titre of Louis XV of France and one of the victims of the Reign of Terror during the French Revolution.-Early life:...
supported Ledoux's nomination to membership in the Royal Academie of Architecture. This permitted him to style himself as Royal Architect. (He was already the architect for the Ferme générale
Ferme générale
The Ferme générale was, in ancien régime France, essentially an outsourced customs and excise operation which collected duties on behalf of the king, under six-year contracts...
, the private customs and excise operation that collected many taxes on behalf of the king, under 6-year contracts.) It was on the basis of his positions as Inspector of the Saltworks and as Royal Architect that he received the commission to design the Royal Saltworks at Arc-et-Senans.

The first plan
Without even having received any request from the king, Ledoux decided to design a saltworks. The project was something of an abstraction as he had no site in mind. This also freed him give free rein to his imagination. He presented the resulting project in April 1774 to Louis XV.Unconstrained by any practical considerations, the project was ambitious, innovative, and a break with traditional approaches. What Ledoux did was to impose a rigid geometry on the overall design. The buildings were placed around the edges of an immense square, and linked to each other by porticoes; no building stood in isolation. To speed connections between buildings, Ledoux introduced covered arcades that linked the midpoints of adjacent sides, forming a square within the square. Columns abounded. The buildings themselves were replete with them, and 144 Doric
Doric order
The Doric order was one of the three orders or organizational systems of ancient Greek or classical architecture; the other two canonical orders were the Ionic and the Corinthian.-History:...
columns supported the covered arcades.
Ledoux's plan envisaged that the central square courtyard would be where the factory would keep its firewood. At each corner of the square, and at the mid-points of each side stood two-story, square buildings that would house the various parts of the operation. In front were the quarters for the guards, a chapel, and a bakery. On the sides were workshops for the coopers and other workmen. At the base was the factory itself. Gardens were to surround the site to provide the workers with a supplement to their income. Lastly, a wall would surround the entire complex to protect it from theft.
It was the project's grandiose vision that blocked its realization. No industrial building of the period was equally imposing. The king rejected the project. He particularly objected to the extensive use of columns, features that he felt were more appropriate for churches and palaces. He also objected to the chapel being relegated to a corner.

The second plan
Ledoux designed the semicircular complex to reflect a hierarchical organization of work. The complete plan included the building of an ideal city forming a perfect circle, like that of the sun. Louis XVLouis XV of France
Louis XV was a Bourbon monarch who ruled as King of France and of Navarre from 1 September 1715 until his death. He succeeded his great-grandfather at the age of five, his first cousin Philippe II, Duke of Orléans, served as Regent of the kingdom until Louis's majority in 1723...
had signed the edict authorizing the construction of the saltworks on 29 April 1773, and after approval of Ledoux' second design, construction began in 1775. The city was never started, however. All that was completed was the diameter and a semicircle of buildings of the saltworks.

The support of salt works by a state monopoly probably explains why this building is so grand. The gabelle was very unpopular and was one of the complaints that led to the French Revolution
French Revolution
The French Revolution , sometimes distinguished as the 'Great French Revolution' , was a period of radical social and political upheaval in France and Europe. The absolute monarchy that had ruled France for centuries collapsed in three years...
. The Revolution itself probably curtailed the building of the ideal city.
Since the end of salt production
The salt works produced 40,000 quintalQuintal
Quintal may refer to:* Quintal , a unit of mass* Quartal and quintal harmony in music* Quintal, Haute-Savoie, a commune of the Haute-Savoie département in France* Stéphane Quintal, NHL ice hockey player...
s of salt per year at its peak, all of which was exported to Switzerland. All production ceased in 1895 following a lawsuit that the inhabitants of Arc-and-Senans initiated, protesting the pollution of nearby wells. At the same time, the salt works was having difficulty in the face of competition from sea salt
Sea salt
Sea salt, salt obtained by the evaporation of seawater, is used in cooking and cosmetics. It is historically called bay salt or solar salt...
brought by rail.
As mentioned above, a lightning bolt in 1918 destroyed the chapel. In April 1926, some of the buildings were dynamite
Dynamite
Dynamite is an explosive material based on nitroglycerin, initially using diatomaceous earth , or another absorbent substance such as powdered shells, clay, sawdust, or wood pulp. Dynamites using organic materials such as sawdust are less stable and such use has been generally discontinued...
d, and many of the trees on the site were cut down. Still, on November 30, 1926, after a review that began in 1923, the Commission for Monuments declared the central pavilion and the entryway historical monuments. The Society for the Eastern Saltworks, still the owner of the Arc-et-Senans site, was not pleased with the decision. On 10 June 1927 the department of Doubs
Doubs
Doubs is a department the Franche-Comté region of eastern France named after the Doubs River.-History:As early as the 13th century, inhabitants of the northern two-thirds of Doubs spoke the Franc-Comtois language, a dialect of Langue d'Oïl. Residents of the southern third of Doubs spoke a dialect...
acquired the salt works and commenced restoration work in 1930.
During 1938, the site housed a camp for Spanish Republican
Second Spanish Republic
The Second Spanish Republic was the government of Spain between April 14 1931, and its destruction by a military rebellion, led by General Francisco Franco....
refugees. Then, during October 1939, at the outbreak of World War II
World War II
World War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis...
, the French military installed an anti-aircraft battery
Anti-aircraft warfare
NATO defines air defence as "all measures designed to nullify or reduce the effectiveness of hostile air action." They include ground and air based weapon systems, associated sensor systems, command and control arrangements and passive measures. It may be to protect naval, ground and air forces...
in the courtyard area. Also, a unit of engineers occupied some of the buildings. Still, February 20, 1940, saw the publication of the official announcement of the classification of the salt works and its surrounding wall as historical monuments.
In June 1940, German troops took up residence. From May 1941 to September 1943, the French authorities established an internment camp to hold the area's gypsies and others with no fixed address (Centre de Rassemblement des tziganes et nomades).
After the war, there was an extensive public campaign by artists, journalists and writers from the region to encourage the authorities to protect the site.
In 1965, Marcel Bluwal
Marcel Bluwal
Marcel Bluwal is a French film director and screenwriter. He has directed 40 films since 1955.-External links:...
used the director's house for the tomb of the Commander in his television adaptation of Molière
Molière
Jean-Baptiste Poquelin, known by his stage name Molière, was a French playwright and actor who is considered to be one of the greatest masters of comedy in Western literature...
's Dom Juan
Dom Juan
Dom Juan or The Feast with the Statue is a French play by Molière, based on the legend of Don Juan. Molière's characters Dom Juan and Sganarelle are the French counterparts to the Spanish Don Juan and Catalinón, characters who would later become familiar to opera goers as Don Giovanni and Leporello...
.
Since 1973, the royal salt works and the Institut Claude-Nicolas Ledoux have been members of the European network of cultural sites. Then in 1982, UNESCO listed the salt works as a World Heritage Site.
In the new millenium
Since June 29, 2009, the salt works at Salins-les-BainsSalins-les-Bains
Salins-les-Bains is a commune in the Jura department in Franche-Comté in eastern France.Salins owes its name to its saline waters, used for bathing and drinking. There are also salt works and gypsum deposits. In 2009 the historic saltworks were added to the list of UNESCO World Heritage sites...
has been added to the listing for Arc-et-Senans in the World Heritage list. It has been the venue for several cultural events and exhibitions in recent years.
External links
- Lien vers les Salines de Salins-les-Bains
- Saline Royale. Official site from Institut Claude-Nicolas Ledoux
- Royal Saltworks of Arc-et-Senans at UNESCO.org

