
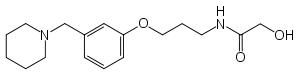
Roxatidine
Encyclopedia
Roxatidine acetate is a specific and competitive H2 receptor antagonist. The antisecretory effect of roxatidine acetate is mediated by its main metabolite, roxatidine.
Pharmacodynamic
studies revealed that 150 mg of roxatidine acetate were optimal in suppressing gastric acid
secretion, and that a single bedtime dose of 150 mg was more effective than a dose of 75 mg twice daily in terms of inhibiting nocturnal acid secretion.
Roxatidine acetate has no antiandrogen
ic effects and does not influence drug-metabolizing
enzyme
s in the liver.
It is currently sold in South Africa
under the tradename Roxit.
Pharmacodynamic
Pharmacodynamics
Pharmacodynamics is the study of the biochemical and physiological effects of drugs on the body or on microorganisms or parasites within or on the body and the mechanisms of drug action and the relationship between drug concentration and effect...
studies revealed that 150 mg of roxatidine acetate were optimal in suppressing gastric acid
Gastric acid
Gastric acid is a digestive fluid, formed in the stomach. It has a pH of 1 to 2 and is composed of hydrochloric acid , and large quantities of potassium chloride and sodium chloride...
secretion, and that a single bedtime dose of 150 mg was more effective than a dose of 75 mg twice daily in terms of inhibiting nocturnal acid secretion.
Roxatidine acetate has no antiandrogen
Antiandrogen
Antiandrogens, or androgen antagonists, first discovered in the 1960s, prevent androgens from expressing their biological effects on responsive tissues. Antiandrogens alter the androgen pathway by blocking the appropriate receptors, competing for binding sites on the cell's surface, or affecting...
ic effects and does not influence drug-metabolizing
Drug metabolism
Drug metabolism is the biochemical modification of pharmaceutical substances by living organisms, usually through specialized enzymatic systems. This is a form of xenobiotic metabolism. Drug metabolism often converts lipophilic chemical compounds into more readily excreted polar products...
enzyme
Enzyme
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions. In enzymatic reactions, the molecules at the beginning of the process, called substrates, are converted into different molecules, called products. Almost all chemical reactions in a biological cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates...
s in the liver.
It is currently sold in South Africa
South Africa
The Republic of South Africa is a country in southern Africa. Located at the southern tip of Africa, it is divided into nine provinces, with of coastline on the Atlantic and Indian oceans...
under the tradename Roxit.


