Round function
Encyclopedia
In topology
and in calculus
, a round function is a scalar function ,
,
over a manifold
 , whose critical point
, whose critical point
s form one or several connected component
s, each homeomorphic to the circle
 , also called critical loops. They are special cases of Morse-Bott functions.
, also called critical loops. They are special cases of Morse-Bott functions.
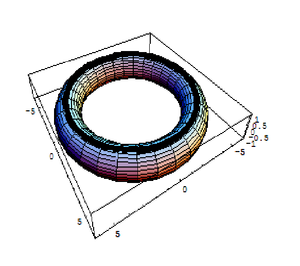
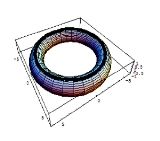
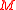 be the torus. Let
be the torus. Let
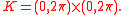
Then we know that a map
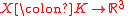
given by
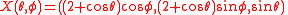
is a parametrization for almost all of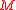 . Now, via the projection
. Now, via the projection 
we get the restriction
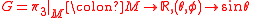
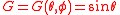 is a function whose critical sets are determined by
is a function whose critical sets are determined by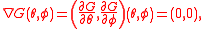
this is if and only if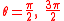 .
.
These two values for give the critical sets
give the critical sets
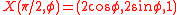
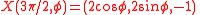
which represent two extremal circles over the torus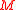 .
.
Observe that the Hessian
for this function is
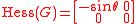
which clearly it reveals itself as of
at the tagged circles, making the critical point degenerate, that is, showing that the critical points are not isolated.
Topology
Topology is a major area of mathematics concerned with properties that are preserved under continuous deformations of objects, such as deformations that involve stretching, but no tearing or gluing...
and in calculus
Calculus
Calculus is a branch of mathematics focused on limits, functions, derivatives, integrals, and infinite series. This subject constitutes a major part of modern mathematics education. It has two major branches, differential calculus and integral calculus, which are related by the fundamental theorem...
, a round function is a scalar function
 ,
,over a manifold
Manifold
In mathematics , a manifold is a topological space that on a small enough scale resembles the Euclidean space of a specific dimension, called the dimension of the manifold....
 , whose critical point
, whose critical pointCritical point (mathematics)
In calculus, a critical point of a function of a real variable is any value in the domain where either the function is not differentiable or its derivative is 0. The value of the function at a critical point is a critical value of the function...
s form one or several connected component
Connected space
In topology and related branches of mathematics, a connected space is a topological space that cannot be represented as the union of two or more disjoint nonempty open subsets. Connectedness is one of the principal topological properties that is used to distinguish topological spaces...
s, each homeomorphic to the circle
Circle
A circle is a simple shape of Euclidean geometry consisting of those points in a plane that are a given distance from a given point, the centre. The distance between any of the points and the centre is called the radius....
 , also called critical loops. They are special cases of Morse-Bott functions.
, also called critical loops. They are special cases of Morse-Bott functions.
For instance
For example, let be the torus. Let
be the torus. Let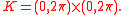
Then we know that a map
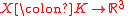
given by
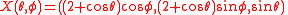
is a parametrization for almost all of
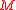 . Now, via the projection
. Now, via the projection 
we get the restriction
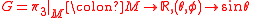
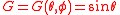 is a function whose critical sets are determined by
is a function whose critical sets are determined by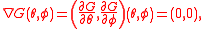
this is if and only if
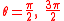 .
.These two values for
 give the critical sets
give the critical sets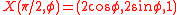
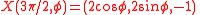
which represent two extremal circles over the torus
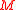 .
.Observe that the Hessian
Hessian matrix
In mathematics, the Hessian matrix is the square matrix of second-order partial derivatives of a function; that is, it describes the local curvature of a function of many variables. The Hessian matrix was developed in the 19th century by the German mathematician Ludwig Otto Hesse and later named...
for this function is
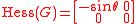
which clearly it reveals itself as of

at the tagged circles, making the critical point degenerate, that is, showing that the critical points are not isolated.

