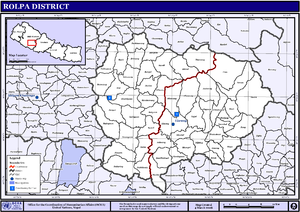
Rolpa District
Encyclopedia
Rolpa
Rolpa' onMouseout='HidePop("50675")' href="/topics/Rapti_Zone">Rapti
Zone
of Nepal
's Mid-Western
Region
. Rolpa covers an area of 1,879 km² with population (2001) of 210,004. Livang
is the district's administrative center.
 By Nepalese standards, Rolpa is an underdeveloped area plagued by low life expectancy (52 years) and poverty (averaging below $100 per capita). It was a major flashpoint in the 1996-2006 Civil War
By Nepalese standards, Rolpa is an underdeveloped area plagued by low life expectancy (52 years) and poverty (averaging below $100 per capita). It was a major flashpoint in the 1996-2006 Civil War
.
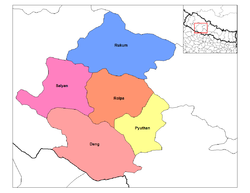
Adjoining districts are Dang to the south, Pyuthan
to the east, Salyan
to the west and Rukum
to the north. Before the unification of Nepal by Prithvi Narayan Shah
in 1769 Rolpa was a buffer between the Chaubisi
confederation of small kingdoms to the east and the Baise confederation to the west.
 Most of Rolpa is rugged highlands populated by the indigenous Kham Magar
Most of Rolpa is rugged highlands populated by the indigenous Kham Magar
nationality. The highlands are drained southward by the Mardi Khola (stream) from a complex of 3,000 to 4,000 meter ridges about 50 kilometers south of the Dhaulagiri
Himalaya. This mountainous barrier historically isolated Rolpa by encouraging travelers between India and Tibet to detour to follow easier routes to the east or west, while east-west travelers found easier routes to the north or south. Irrigated ricefields
along the Mardi Khola are of limited extent because it has a narrow inner gorge. Those that exist are monopolized by Pahari
Hindus and Newars, leaving the indigenous Kham with upland fields unsuited to rice cultivation. Upland harvests of maize
, millet
and barley
are invariably insufficient and so Rolpa has chronic food deficits.
Food deficits have driven upland Kham into growing market crops better suited to the terrain than grain, although marketing fruit and vegetables beyond adjacent districts was hampered by lack of roads. As long as marijuana
and charas
(hashish
) were legal in Nepal they were grown and processed in Rolpa and sent to Kathmandu to be sold in government monopoly stores. However the government gave in to international pressure and stopped buying these products in 1976, causing the district to lose an important source of cash income. Kham also make ends meet by selling their labor. They work as agricultural laborers in other districts, as porters, as soldiers
and as general laborers, but their input is devalued by Rolpa's underdeveloped education infrastructure. There is no post-secondary education in the district, and students who speak more Khamkura
than Nepali
are disadvantaged in primary and secondary education because Nepali is the medium of instruction and the national examination system selects against students who are not proficient in it. Without educational credentials Kham lack access to the more desirable jobs.
The various grievances of Rolpa's population made the district ripe for revolt. It became a "Maoist Stronghold" of the Communist Party of Nepal
. In May 2002 a major battle between Maoist guerillas and the army was fought at Lisne Lekh near the Rolpa-Pyuthan border.
Rolpa' onMouseout='HidePop("50675")' href="/topics/Rapti_Zone">Rapti
Rapti Zone
Rapti Anchal in the Mid-Western Development Region of Nepal. It is named after the West Rapti River which drains Rolpa, Pyuthan and part of Dang district. The remainder of Dang and part of Salyan are drained by the Babai. The remainder of Salyan and all of Rukum are drained by the Bheri.The...
Zone
Zones of Nepal
Nepal is divided into 14 administrative zones , and 75 districts . The 14 administrative zones are grouped into five development regions...
of Nepal
Nepal
Nepal , officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal, is a landlocked sovereign state located in South Asia. It is located in the Himalayas and bordered to the north by the People's Republic of China, and to the south, east, and west by the Republic of India...
's Mid-Western
Mid-Western Region, Nepal
Mid-Western Region is one of Nepal's five development regions. Westward from the Central region surrounding Kathmandu are the Western, Mid-Western and finally Far-Western regions. Counter-intuitively, Mid-Western lies west of Western....
Region
Regions of Nepal
Nepal is divided into 14 administrative zones , which are divided into 75 districts . The 14 administrative zones are grouped into five development regions...
. Rolpa covers an area of 1,879 km² with population (2001) of 210,004. Livang
Livang
Liwang is a district headquarter and village development committee of Rolpa District in the Rapti Zone of south-western Nepal. At the time of the 1991 Nepal census it had a population of 1381....
is the district's administrative center.

Nepal Civil War
The Nepali Civil War was a conflict between government forces and Maoist rebels in Nepal which lasted from 1996 until 2006...
.
Adjoining districts are Dang to the south, Pyuthan
Pyuthan District
Pyuthan District of 212,484. Pyuthan Khalanga is the district's administrative center.-Geography:Pyuthan borders Dang Deukhuri District to the southwest along the crest of the Mahabharat Range and extends about 50 km northeast through the Middle Hills to a 3,000+ meter ridge that is both...
to the east, Salyan
Salyan District
Salyan District of 213,500. The district's administrative center is named Salyan or Salyan Khalanga.The district is known for its Hindu temples including Shiva temples in Chhayachhetra and Laxmipur, and the Devi temple at Khairabang in Hiwalcha VDC, one of nine in Nepal...
to the west and Rukum
Rukum District
Rukum District of 188,438. Musikot is the district's administrative center.Rukum district has many potential tourist attractions that remain unexplored. There is 5,849 meter Mt. Sisne , also called virgin mountain. Nobody claims to have conquered this mountain yet. Rukum is also called "the...
to the north. Before the unification of Nepal by Prithvi Narayan Shah
Prithvi Narayan Shah
Prithvi Narayan Shah, King of Nepal was the first king of the House of Shahs to rule Nepal. He is credited for starting the campaign for a unified Nepal, which had been divided and weakened under Malla confederacy. He was the ninth generation descendant of Dravya Shah , the founder of the ruling...
in 1769 Rolpa was a buffer between the Chaubisi
Chaubisi rajya
Chaubisi rajya -- literally "24 principalities" -- were sovereign and intermittently allied petty kingdoms in the Gandaki River Basin, a major Himalayan tributary of the Ganges....
confederation of small kingdoms to the east and the Baise confederation to the west.

Kham Magar
Kham Magar and Northern Magar are descriptive terms invented by academic linguists and anthropologists for a nationality in the Middle Hills of mid-western Nepal inhabiting highlands extending through eastern Rukum and northern Salyan, Rolpa and Pyuthan Districts in Rapti Zone as well as adjacent...
nationality. The highlands are drained southward by the Mardi Khola (stream) from a complex of 3,000 to 4,000 meter ridges about 50 kilometers south of the Dhaulagiri
Dhaulagiri
Dhaulagiri is Earth's seventh highest mountain at ; one of fourteen over eight thousand metres. Dhaulagiri was first climbed May 13, 1960 by a Swiss/Austrian expedition....
Himalaya. This mountainous barrier historically isolated Rolpa by encouraging travelers between India and Tibet to detour to follow easier routes to the east or west, while east-west travelers found easier routes to the north or south. Irrigated ricefields
Paddy field
A paddy field is a flooded parcel of arable land used for growing rice and other semiaquatic crops. Paddy fields are a typical feature of rice farming in east, south and southeast Asia. Paddies can be built into steep hillsides as terraces and adjacent to depressed or steeply sloped features such...
along the Mardi Khola are of limited extent because it has a narrow inner gorge. Those that exist are monopolized by Pahari
Pahari people
The Pahari people, ; also called Pahadi, Parbati, Khāsā, or Chhetri, are an Indo-Aryan ethnic group of the Himalaya living in Nepal, India, and Pakistan. In Nepal, the Pahari constituted the single largest ethnic group at about 20,000,000, or three-fifths of the Nepalese population through the 1990s...
Hindus and Newars, leaving the indigenous Kham with upland fields unsuited to rice cultivation. Upland harvests of maize
Maize
Maize known in many English-speaking countries as corn or mielie/mealie, is a grain domesticated by indigenous peoples in Mesoamerica in prehistoric times. The leafy stalk produces ears which contain seeds called kernels. Though technically a grain, maize kernels are used in cooking as a vegetable...
, millet
Millet
The millets are a group of small-seeded species of cereal crops or grains, widely grown around the world for food and fodder. They do not form a taxonomic group, but rather a functional or agronomic one. Their essential similarities are that they are small-seeded grasses grown in difficult...
and barley
Barley
Barley is a major cereal grain, a member of the grass family. It serves as a major animal fodder, as a base malt for beer and certain distilled beverages, and as a component of various health foods...
are invariably insufficient and so Rolpa has chronic food deficits.
Food deficits have driven upland Kham into growing market crops better suited to the terrain than grain, although marketing fruit and vegetables beyond adjacent districts was hampered by lack of roads. As long as marijuana
Cannabis (drug)
Cannabis, also known as marijuana among many other names, refers to any number of preparations of the Cannabis plant intended for use as a psychoactive drug or for medicinal purposes. The English term marijuana comes from the Mexican Spanish word marihuana...
and charas
Charas
Charas is the name given to a hashish form of cannabis which is hand-made in Afghanistan, Pakistan, Nepal and India. It is made from the resin of the cannabis plant...
(hashish
Hashish
Hashish is a cannabis preparation composed of compressed stalked resin glands, called trichomes, collected from the unfertilized buds of the cannabis plant. It contains the same active ingredients but in higher concentrations than unsifted buds or leaves...
) were legal in Nepal they were grown and processed in Rolpa and sent to Kathmandu to be sold in government monopoly stores. However the government gave in to international pressure and stopped buying these products in 1976, causing the district to lose an important source of cash income. Kham also make ends meet by selling their labor. They work as agricultural laborers in other districts, as porters, as soldiers
Gurkha
Gurkha are people from Nepal who take their name from the Gorkha District. Gurkhas are best known for their history in the Indian Army's Gorkha regiments, the British Army's Brigade of Gurkhas and the Nepalese Army. Gurkha units are closely associated with the kukri, a forward-curving Nepalese knife...
and as general laborers, but their input is devalued by Rolpa's underdeveloped education infrastructure. There is no post-secondary education in the district, and students who speak more Khamkura
Kham language
Kham -- narrowly defined -- is a complex of Tibeto-Burman Magaric languages spoken natively in isolated highlands of Rolpa and Rukum districts of Rapti and the westernmost part of Baglung district in Dhaulagiri Zone by western clans of the Magar tribe, called collectively Kham Magar or Northern...
than Nepali
Nepali language
Nepali or Nepalese is a language in the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European language family.It is the official language and de facto lingua franca of Nepal and is also spoken in Bhutan, parts of India and parts of Myanmar...
are disadvantaged in primary and secondary education because Nepali is the medium of instruction and the national examination system selects against students who are not proficient in it. Without educational credentials Kham lack access to the more desirable jobs.
The various grievances of Rolpa's population made the district ripe for revolt. It became a "Maoist Stronghold" of the Communist Party of Nepal
Communist Party of Nepal
The Communist Party of Nepal was founded in Calcutta, India, on April 29, 1949. CPN was formed to struggle against the autocratic Rana regime, feudalism and imperialism. The founding general secretary was Pushpa Lal Shrestha....
. In May 2002 a major battle between Maoist guerillas and the army was fought at Lisne Lekh near the Rolpa-Pyuthan border.
Historic/Cultural/Archeological Sites
- Bhama Odar
- Chaturbhuj Panchayan
- Devi and Khadga Temple, Durga Bhawani, Durga Temple
- Gajulkot
- Jaljala, Jankot Jhankristhan
- Kalika Devi, Khungrikot, Kot Maula
- Pateswari Temple
- Shivalaya mandir
Village Development Committees (VDCs)
- AreshAreshAresh is a village development committee in Rolpa District in the Rapti Zone of north-eastern Nepal. At the time of the 1991 Nepal census it had a population of 2801 people living in 497 individual households....
- BhawangBhawangBhawang is a village development committee in Rolpa District in the Rapti Zone of north-eastern Nepal. At the time of the 1991 Nepal census it had a population of 3730 people living in 678 individual households....
, Mirul, Budhagaun - DhawangDhawangDhawang is a village development committee in Rolpa District in the Rapti Zone of north-eastern Nepal. At the time of the 1991 Nepal census it had a population of 3855 people living in 683 individual households....
, DubidandaDubidandaDubidanda is a village development committee in Rolpa District in the Rapti Zone of north-eastern Nepal. At the time of the 1991 Nepal census it had a population of 3870 people living in 661 individual households....
, DubringDubringDubring is a village development committee in Rolpa District in the Rapti Zone of north-eastern Nepal. At the time of the 1991 Nepal census it had a population of 4005 people living in 736 individual households.... - Iriwang
- FagamFagamFagam or Gwaram is a town in Jigawa State, Nigeria.-Geography:Fagam is located at and has a population of 16,329. It is 55 km southwest of Azare and 15 km southwest of Foggo along the Jama'are River, also known as the Bunga River....
- GaamGaamGaam is a village development committee in Rolpa District in the Rapti Zone of north-eastern Nepal. At the time of the 1991 Nepal census it had a population of 4349 people living in 880 individual households....
, GajulGajulGajul is a village development committee in Rolpa District in the Rapti Zone of north-eastern Nepal. At the time of the 1991 Nepal census it had a population of 4263 people living in 778 individual households....
, Gairigaun, Ghartigaun, GhodagaunGhodagaunGhodagaun is a village development committee in Rolpa District in the Rapti Zone of north-eastern Nepal. At the time of the 1991 Nepal census it had a population of 2417 people living in 476 individual households....
, GumchalGumchalGumchal is a village development committee in Rolpa District in the Rapti Zone of north-eastern Nepal. At the time of the 1991 Nepal census it had a population of 2893 people living in 539 individual households.... - HarjangHarjangHarjang is a village development committee in Rolpa District in the Rapti Zone of north-eastern Nepal. At the time of the 1991 Nepal census it had a population of 2011 people living in 360 individual households....
- Jelwang, JaimakasalaJaimakasalaJaimakasala is a village development committee in Rolpa District in the Rapti Zone of north-eastern Nepal. At the time of the 1991 Nepal census it had a population of 2626 people living in 491 individual households....
, JankotJankotJankot is a village development committee in Rolpa District in the Rapti Zone of north-eastern Nepal. At the time of the 1991 Nepal census it had a population of 2553 people living in 500 individual households....
, JauliPokhari, JedwangJedwangJedwang is a village development committee in Rolpa District in the Rapti Zone of north-eastern Nepal. At the time of the 1991 Nepal census it had a population of 3168 people living in 591 individual households....
, JhenamJhenamJhenam is a village development committee in Rolpa District in the Rapti Zone of north-eastern Nepal. At the time of the 1991 Nepal census it had a population of 5307....
, JinawangJinawangJinawang is a village development committee in Rolpa District in the Rapti Zone of north-eastern Nepal. At the time of the 1991 Nepal census it had a population of 3822 people living in 615 individual households....
, ungar,] - Korchawang, KaretiKaretiKareti is a village development committee in Rolpa District in the Rapti Zone of north-eastern Nepal. At the time of the 1991 Nepal census it had a population of 1808 people living in 380 individual households....
, KhumelKhumelKhumel is a village development committee in Rolpa District in the Rapti Zone of north-eastern Nepal. At the time of the 1991 Nepal census it had a population of 2439 people living in 449 individual households....
, KhungriKhungriKhungri is a village development committee in Rolpa District in the Rapti Zone of north-eastern Nepal. At the time of the 1991 Nepal census it had a population of 3564 people living in 695 individual households....
, KotgaunKotgaunKotgaun is a village development committee in Rolpa District in the Rapti Zone of north-eastern Nepal. At the time of the 1991 Nepal census it had a population of 3335 people living in 307 individual households....
, KureliKureliKureli is a village development committee in Rolpa District in the Rapti Zone of north-eastern Nepal. At the time of the 1991 Nepal census it had a population of 3024.... - Liwang
- Masina,[Mijhing
- NuwagaunNuwagaunNuwagaun is a village development committee in Rolpa District in the Rapti Zone of north-eastern Nepal. At the time of the 1991 Nepal census it had a population of 3725 people living in 689 individual households....
- PachhawangPachhawangPachhawang is a village development committee in Rolpa District in the Rapti Zone of north-eastern Nepal. At the time of the 1991 Nepal census it had a population of 4581 people living in 695 individual households....
, Pakhapani, ang] - RangkotRangkotRangkot is a village development committee in Rolpa District in the Rapti Zone of north-eastern Nepal. At the time of the 1991 Nepal census it had a population of 3180 people living in 565 individual households....
, angsi, [Rank] - akhi,Seram, Sirpa,Siuri,]
- TalawangTalawangTalawang is a village development committee in Rolpa District in the Rapti Zone of north-eastern Nepal. At the time of the 1991 Nepal census it had a population of 4686 people living in 846 individual households....
, TewangTewangTewang is a village development committee in Rolpa District in the Rapti Zone of north-eastern Nepal. At the time of the 1991 Nepal census it had a population of 2127 people living in 370 individual households....
, ThawangThawangThawang is a village development committee in Rolpa District in the Rapti Zone of north-eastern Nepal. At the time of the 1991 Nepal census it had a population of 3867 people living in 785 individual households.... - wa,]
- Badachaur, wama], [Wot,]

