.gif)
Robots (computer game)
Encyclopedia
Robots is a computer game originally developed for the Berkeley Software Distribution
—a derivative of Unix
—by Ken Arnold
. In the turn-based game, players are tasked with escaping robots programmed to kill them. Since then it has been reproduced as clone games for various platforms.
s, which have been programmed with only a single objective: to kill the player.
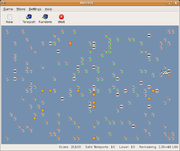
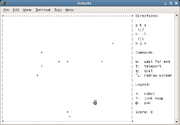 The game is turn-based. In the original game the player character starts at a randomly selected location. In some derivative versions, such as the GNOME
The game is turn-based. In the original game the player character starts at a randomly selected location. In some derivative versions, such as the GNOME
version, the player starts at the centre of the grid. The robots start at randomly selected locations on the grid. Every time the player character moves a square in any direction (horizontally, vertically, or diagonally), each robot moves one square closer to him, in whichever direction is the shortest way.
If the player character collides with a robot, he dies and the game ends. However, the robots are also fatal to each other - when two robots collide, they both die, leaving behind a scrap heap. These scrap heaps are also fatal to robots.
The player can also teleport
into a randomly selected location in cases where escape is otherwise impossible. A teleportation counts as a move. However, because the location is randomly selected, it is possible that the player teleports right into the path of a robot. In some versions of the game, there is a "safe teleport" feature which the player may use a limited number of times (for instance once per level) and there may also be a close-range weapon which kills all robots within the immediate vicinity, the use of which would be limited in a similar way.
When all robots on a level are dead, the player moves onto another level, with more robots. Traditionally, the number of robots increases by ten each level.
s in the British Doctor Who
TV show. Tim Hartnell
also wrote a BASIC
version called Robot Minefield which involved fleeing from four robots on a small field of landmines
. The game was more difficult than Robots since the player lacked the ability to teleport. Moreover, robots could merge into each other without being destroyed. In addition, the player could only move in four directions (North, South, East, West) while the robots had the ability to move diagonally. The game was played in real time; as the player pondered his move, the robots would continue converging toward him. This version was published in the 1983 Giant Book of Computer Games.
Berkeley Software Distribution
Berkeley Software Distribution is a Unix operating system derivative developed and distributed by the Computer Systems Research Group of the University of California, Berkeley, from 1977 to 1995...
—a derivative of Unix
Unix
Unix is a multitasking, multi-user computer operating system originally developed in 1969 by a group of AT&T employees at Bell Labs, including Ken Thompson, Dennis Ritchie, Brian Kernighan, Douglas McIlroy, and Joe Ossanna...
—by Ken Arnold
Ken Arnold
Kenneth Cutts Richard Cabot Arnold is an American computer programmer well known as one of the developers of the 1980s dungeon-crawling computer game Rogue, for his contributions to the original Berkeley distribution of Unix, for his books and articles about C and C++ Kenneth Cutts Richard Cabot ...
. In the turn-based game, players are tasked with escaping robots programmed to kill them. Since then it has been reproduced as clone games for various platforms.
Gameplay
Robots is played on a two-dimensional rectangular grid. The objective of the game is to escape from a number of robotRobot
A robot is a mechanical or virtual intelligent agent that can perform tasks automatically or with guidance, typically by remote control. In practice a robot is usually an electro-mechanical machine that is guided by computer and electronic programming. Robots can be autonomous, semi-autonomous or...
s, which have been programmed with only a single objective: to kill the player.

GNOME
GNOME is a desktop environment and graphical user interface that runs on top of a computer operating system. It is composed entirely of free and open source software...
version, the player starts at the centre of the grid. The robots start at randomly selected locations on the grid. Every time the player character moves a square in any direction (horizontally, vertically, or diagonally), each robot moves one square closer to him, in whichever direction is the shortest way.
If the player character collides with a robot, he dies and the game ends. However, the robots are also fatal to each other - when two robots collide, they both die, leaving behind a scrap heap. These scrap heaps are also fatal to robots.
The player can also teleport
Teleportation
Teleportation is the fictional or imagined process by which matter is instantaneously transferred from one place to another.Teleportation may also refer to:*Quantum teleportation, a method of transmitting quantum data...
into a randomly selected location in cases where escape is otherwise impossible. A teleportation counts as a move. However, because the location is randomly selected, it is possible that the player teleports right into the path of a robot. In some versions of the game, there is a "safe teleport" feature which the player may use a limited number of times (for instance once per level) and there may also be a close-range weapon which kills all robots within the immediate vicinity, the use of which would be limited in a similar way.
When all robots on a level are dead, the player moves onto another level, with more robots. Traditionally, the number of robots increases by ten each level.

Other versions
Some versions of Robots are called Zombies. Others are called Daleks, after the DalekDalek
The Daleks are a fictional extraterrestrial race of mutants from the British science fiction television series Doctor Who. Within the series, Daleks are cyborgs from the planet Skaro, created by the scientist Davros during the final years of a thousand-year war against the Thals...
s in the British Doctor Who
Doctor Who
Doctor Who is a British science fiction television programme produced by the BBC. The programme depicts the adventures of a time-travelling humanoid alien known as the Doctor who explores the universe in a sentient time machine called the TARDIS that flies through time and space, whose exterior...
TV show. Tim Hartnell
Tim Hartnell
Tim Hartnell was an Australian journalist, self-taught programmer and extremely prolific, bestselling author of books and magazines on computer games. His company, Interface Publications , produced titles for all of the machines in the home computer market, including Sinclair machines...
also wrote a BASIC
BASIC
BASIC is a family of general-purpose, high-level programming languages whose design philosophy emphasizes ease of use - the name is an acronym from Beginner's All-purpose Symbolic Instruction Code....
version called Robot Minefield which involved fleeing from four robots on a small field of landmines
Land mine
A land mine is usually a weight-triggered explosive device which is intended to damage a target—either human or inanimate—by means of a blast and/or fragment impact....
. The game was more difficult than Robots since the player lacked the ability to teleport. Moreover, robots could merge into each other without being destroyed. In addition, the player could only move in four directions (North, South, East, West) while the robots had the ability to move diagonally. The game was played in real time; as the player pondered his move, the robots would continue converging toward him. This version was published in the 1983 Giant Book of Computer Games.
External links
- Manual for the OpenBSD version
- GNOME Robots is an open source Robots game for the GNOME desktop.
- Cross-platform version in Tcl/Tk
- http://ctho.ath.cx/games/robots/Cross-platform version in JavaScriptJavaScriptJavaScript is a prototype-based scripting language that is dynamic, weakly typed and has first-class functions. It is a multi-paradigm language, supporting object-oriented, imperative, and functional programming styles....
] - Cross-platform version in Java (software platform)
- http://sourceforge.net/projects/robotsgame/Windows version in C++C++C++ is a statically typed, free-form, multi-paradigm, compiled, general-purpose programming language. It is regarded as an intermediate-level language, as it comprises a combination of both high-level and low-level language features. It was developed by Bjarne Stroustrup starting in 1979 at Bell...
]

