
Risk reversal
Encyclopedia
Risk Reversal investment strategy
A risk-reversal consists of being long (buying) an out of the money call and being short (i.e. selling) an out of the money put, both with the same maturity.A risk reversal is a position in which you simulate the behavior of a long, therefore it is sometimes called a synthetic long. This is an investment strategy that amounts to both buying and selling out-of-money options simultaneously. In this strategy, the investor will first make a market hunch, if that hunch is bullish he will want to go long. However, instead of going long on the stock, he will buy an out of the money call option, and simultaneously sell an out of the money put option. Presumably he will use the money from the sale of the put option to purchase the call option. Then as the stock goes up in price, the call option will be worth more, and the put option will be worth less.
If an investor holds the underlying (stock or FX) and sells a risk reversal, then he has a collar
Collar (finance)
In finance, a collar is an option strategy that limits the range of possible positive or negative returns on an underlying to a specific range.-Structure:A collar is created by an investor being:* Long the underlying...
position. i.e.
- Underlying - Risk_Reversal = collarCollar (finance)In finance, a collar is an option strategy that limits the range of possible positive or negative returns on an underlying to a specific range.-Structure:A collar is created by an investor being:* Long the underlying...
Risk reversal (measure of vol-skew)
Risk Reversal can refer to the manner in which similar out-of-the-money call and put optionsOption (finance)
In finance, an option is a derivative financial instrument that specifies a contract between two parties for a future transaction on an asset at a reference price. The buyer of the option gains the right, but not the obligation, to engage in that transaction, while the seller incurs the...
, usually foreign exchange option
Foreign exchange option
In finance, a foreign-exchange option is a derivative financial instrument that gives the owner the right but not the obligation to exchange money denominated in one currency into another currency at a pre-agreed exchange rate on a specified date.The FX options market is the deepest, largest and...
s, are quoted by Finance
Finance
"Finance" is often defined simply as the management of money or “funds” management Modern finance, however, is a family of business activity that includes the origination, marketing, and management of cash and money surrogates through a variety of capital accounts, instruments, and markets created...
dealers. Instead of quoting these options' prices, dealers quote their volatility
Volatility (finance)
In finance, volatility is a measure for variation of price of a financial instrument over time. Historic volatility is derived from time series of past market prices...
.
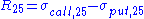
In other words, for a given maturity, the 25 risk reversal is the vol of the 25 delta call less the vol of the 25 delta put. The 25 delta put is the put whose strike has been chosen such that the delta is -25%.
The greater the demand for an options contract, the greater its volatility and its price. A positive risk reversal means the volatility of calls is greater than the volatility of similar puts, which implies a skewed distribution of expected spot returns composed of a relatively large number of small down moves and a relatively small number of large upmoves.
Other external links
- Reuters description: http://glossary.reuters.com/index.php?title=Risk_Reversal
- Investopedia description: http://www.investopedia.com/terms/r/riskreversal.asp
- Quant Principle: Risk Reversal Case Study

