
Risk-loving
Encyclopedia
In economics
and finance
, a risk lover is a person who has a preference for risk
. While most investors
are considered risk averse, one could view casino goers as risk loving. If offered either €50 or a 50% chance of each of €100 and nothing, a risk seeking person would prefer the gamble even though the gamble and the sure thing both have the same expected value
; in fact, the risk lover would be indifferent to accepting a less than 50% chance of €100 versus the sure €50 (how much less would depend on how risk loving the person is). The risk lover would also be indifferent to a 50% chance of each of €X and nothing versus the sure €50, where €X is some amount less than €100 (again, how much less would depend on how risk loving the person is).
The risk-loving behavior can be observed in the negative domain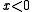 for Prospect theory
for Prospect theory
value functions, where the functions are convex for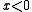 ; while the functions are concave for
; while the functions are concave for  .
.
. The utility function whose expected value is maximized is convex
for a risk lover, concave
for a risk averse agent, and linear for a risk neutral
agent. Its convexity in the risk loving case has the effect of causing a mean-preserving spread
of any probability distribution
of wealth outcomes to be preferred over the unspread distribution.
Economics
Economics is the social science that analyzes the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services. The term economics comes from the Ancient Greek from + , hence "rules of the house"...
and finance
Finance
"Finance" is often defined simply as the management of money or “funds” management Modern finance, however, is a family of business activity that includes the origination, marketing, and management of cash and money surrogates through a variety of capital accounts, instruments, and markets created...
, a risk lover is a person who has a preference for risk
Risk
Risk is the potential that a chosen action or activity will lead to a loss . The notion implies that a choice having an influence on the outcome exists . Potential losses themselves may also be called "risks"...
. While most investors
Investment
Investment has different meanings in finance and economics. Finance investment is putting money into something with the expectation of gain, that upon thorough analysis, has a high degree of security for the principal amount, as well as security of return, within an expected period of time...
are considered risk averse, one could view casino goers as risk loving. If offered either €50 or a 50% chance of each of €100 and nothing, a risk seeking person would prefer the gamble even though the gamble and the sure thing both have the same expected value
Expected value
In probability theory, the expected value of a random variable is the weighted average of all possible values that this random variable can take on...
; in fact, the risk lover would be indifferent to accepting a less than 50% chance of €100 versus the sure €50 (how much less would depend on how risk loving the person is). The risk lover would also be indifferent to a 50% chance of each of €X and nothing versus the sure €50, where €X is some amount less than €100 (again, how much less would depend on how risk loving the person is).
The risk-loving behavior can be observed in the negative domain
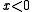 for Prospect theory
for Prospect theoryProspect theory
Prospect theory is a theory that describes decisions between alternatives that involve risk i.e. where the probabilities of outcomes are known. The model is descriptive: it tries to model real-life choices, rather than optimal decisions.-Model:...
value functions, where the functions are convex for
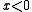 ; while the functions are concave for
; while the functions are concave for  .
.The risk loving utility function
Choice under uncertainty is often characterized as the maximization of expected utility. Utility is often assumed to be a function of profit or final portfolio wealth, with a positive first derivativeDerivative
In calculus, a branch of mathematics, the derivative is a measure of how a function changes as its input changes. Loosely speaking, a derivative can be thought of as how much one quantity is changing in response to changes in some other quantity; for example, the derivative of the position of a...
. The utility function whose expected value is maximized is convex
Convex function
In mathematics, a real-valued function f defined on an interval is called convex if the graph of the function lies below the line segment joining any two points of the graph. Equivalently, a function is convex if its epigraph is a convex set...
for a risk lover, concave
Concave function
In mathematics, a concave function is the negative of a convex function. A concave function is also synonymously called concave downwards, concave down, convex upwards, convex cap or upper convex.-Definition:...
for a risk averse agent, and linear for a risk neutral
Risk neutral
In economics and finance, risk neutral behavior is between risk aversion and risk seeking. If offered either €50 or a 50% chance of each of €100 and nothing, a risk neutral person would have no preference between the two options...
agent. Its convexity in the risk loving case has the effect of causing a mean-preserving spread
Mean-preserving spread
In probability and statistics, a mean-preserving spread is a change from one probability distribution A to another probability distribution B, where B is formed by spreading out one or more portions of A's probability density function while leaving the mean unchanged...
of any probability distribution
Probability distribution
In probability theory, a probability mass, probability density, or probability distribution is a function that describes the probability of a random variable taking certain values....
of wealth outcomes to be preferred over the unspread distribution.

