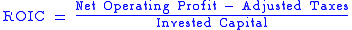Return on capital
Encyclopedia
Return on capital is a ratio used in finance, valuation, and accounting. The ratio is estimated by dividing the after-tax operating income (NOPAT
) by the book value
of invested capital
.
This differs from ROIC. Return on invested capital (ROIC) is a financial measure that quantifies how well a company generates cash flow relative to the capital it has invested in its business. It is defined as net operating profit less adjusted taxes
divided by invested capital
and is usually expressed as a percentage
. In this calculation, capital invested includes all monetary capital invested: long-term debt, common and preferred shares.
When the return on capital is greater than the cost of capital
(usually measured as the weighted average cost of capital
), the company is creating value; when it is less than the cost of capital, value is destroyed.
Note that the numerator in the ROIC fraction does not subtract interest expense
, because denominator includes debt capital.
NOPAT
In corporate finance, net operating profit after tax or NOPAT is a company's after-tax operating profit for all investors, including shareholders and debt holders. It is equal to NOPLAT and is defined as follows:An alternative formula is as follows...
) by the book value
Book value
In accounting, book value or carrying value is the value of an asset according to its balance sheet account balance. For assets, the value is based on the original cost of the asset less any depreciation, amortization or Impairment costs made against the asset. Traditionally, a company's book value...
of invested capital
Invested Capital
Invested Capital represents the total cash investment that shareholders and debtholders have made in a company. There are two different but completely equivalent methods for calculating invested capital...
.
Formula
This differs from ROIC. Return on invested capital (ROIC) is a financial measure that quantifies how well a company generates cash flow relative to the capital it has invested in its business. It is defined as net operating profit less adjusted taxes
NOPLAT
NOPLAT = Net Operating Profit Less Adjusted Taxes.It means Total operating profits for a firm with adjustments made for taxes. It represents the profits generated from a company's core operations after subtracting the income taxes related to the core operations...
divided by invested capital
Invested Capital
Invested Capital represents the total cash investment that shareholders and debtholders have made in a company. There are two different but completely equivalent methods for calculating invested capital...
and is usually expressed as a percentage
Percentage
In mathematics, a percentage is a way of expressing a number as a fraction of 100 . It is often denoted using the percent sign, “%”, or the abbreviation “pct”. For example, 45% is equal to 45/100, or 0.45.Percentages are used to express how large/small one quantity is, relative to another quantity...
. In this calculation, capital invested includes all monetary capital invested: long-term debt, common and preferred shares.
When the return on capital is greater than the cost of capital
Cost of capital
The cost of capital is a term used in the field of financial investment to refer to the cost of a company's funds , or, from an investor's point of view "the shareholder's required return on a portfolio of all the company's existing securities"...
(usually measured as the weighted average cost of capital
Weighted average cost of capital
The weighted average cost of capital is the rate that a company is expected to pay on average to all its security holders to finance its assets....
), the company is creating value; when it is less than the cost of capital, value is destroyed.
ROIC formula
Note that the numerator in the ROIC fraction does not subtract interest expense
Interest expense
Interest expense relates to the cost of borrowing money. It is the price that a lender charges a borrower for the use of the lender's money. Interest expense is different from OPEX and CAPEX, for it relates to the capital structure of a company. Interest expense is usually tax-deductible....
, because denominator includes debt capital.
See also
- Cash flow return on investmentCash flow return on investmentCash flow return on investment is a valuation model that assumes the stock market sets prices based on cash flow, not on corporate performance and earnings.CFROI = Cash Flow / Market Recapitalization...
(CFROI) - ProfitabilityProfit (accounting)In accounting, profit can be considered to be the difference between the purchase price and the costs of bringing to market whatever it is that is accounted as an enterprise in terms of the component costs of delivered goods and/or services and any operating or other expenses.-Definition:There are...
- Rate of profitRate of profitIn economics and finance, the profit rate is the relative profitability of an investment project, of a capitalist enterprise, or of the capitalist economy as a whole...
- Rate of return on a portfolioRate of return on a portfolioThe rate of return on a portfolio is "a weighted average of the rates of return on the various assets with the weights being equal to the fractions of the individual's wealth held in these assets" This equates to an average of the average returns on a portfolio taking into account what portion of...
- Profit maximizationProfit maximizationIn economics, profit maximization is the process by which a firm determines the price and output level that returns the greatest profit. There are several approaches to this problem...
- Tendency of the rate of profit to fallTendency of the rate of profit to fallThe tendency of the rate of profit to fall is a hypothesis in economics and political economy, most famously expounded by Karl Marx in chapter 13 of Das Kapital Vol. 3. It was generally accepted in the 19th century...
- Return on investmentReturn on investmentReturn on investment is one way of considering profits in relation to capital invested. Return on assets , return on net assets , return on capital and return on invested capital are similar measures with variations on how “investment” is defined.Marketing not only influences net profits but also...
(ROI) - Return on net assetsReturn on net assetsThe return on net assets is a measure of financial performance of a company which takes the use of assets into account.-Formula:Return on net assets = Profit after tax /...
(RONA) - Return on revenue (ROR), also Return on sales (ROS)
- Risk adjusted return on capitalRisk adjusted return on capitalRisk adjusted return on capital is a risk-based profitability measurement framework for analysing risk-adjusted financial performance and providing a consistent view of profitability across businesses. The concept was developed by Bankers Trust and principal designer Dan Borge in the late 1970s...
(RAROC)