
Reserve design
Encyclopedia
Reserve Design is the process of planning and creating a nature reserve
in a way that effectively accomplishes the goal of the reserve.
Reserves have a variety of goals and many different factors need to be taken into account in order for a reserve to be successful. These factors include habitat preference, migration, climate change, and public support. In order to fulfil goal of the reserve and accommodate the factors influencing its success, a specific design must be created and implemented.
s) are created with the intent of protecting a flagship species
, usually Charismatic Macrofauna that are well known to the public (such as the Bengal tiger or giant panda). Other times they are created in the interest of protecting biodiversity
.
Ecological communities
that are at high risk and are considered irreplaceable are often selected to be preserved as well .
Also certain species are area sensitive. A study on song birds in Japan showed that certain birds only settle in habitats much larger than the area they actually occupy Knowing species geographic range and preference is essential to determining the size of the reserve needed.
Social factors such as the attitudes of local people should also be taken into account. If a reserve is put up in an area that people depend on for their livelihood the reserve often fails. For example in Bolivia, the Amboró National Park was expanded in 1991 from 1,800 to 6,370 km². While this was celebrated by conservationists, local people who would be displaced by the expansion were angered. They continued to hunt and log within the park and eventually the park size had to be reduced [8]. Because local people were not considered in the design of the reserve, conservation efforts failed. Many conservationists advocate local people must be included in conservation efforts, this is known as an Integrated Conservation and Development Project
.
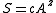 states that the number of species in a habitat is directly proportional to its size. So theoretically if several small reserves have a greater total area than a single large reserve, the small reserves will contain a greater total number of species.
states that the number of species in a habitat is directly proportional to its size. So theoretically if several small reserves have a greater total area than a single large reserve, the small reserves will contain a greater total number of species.
The nested subset theory disagrees with this conclusion. It states that several small reserves will mostly share the same species, because certain species are better adapted to living in smaller habitats and many other species only exist in lager habitats.
A study conducted in Illinois showed that two small forest reserves contained a larger number of bird species than one large forest patch, but the large reserve contained a larger number of migratory birds . http://www.blackwell-synergy.com/links/doi/10.1046/j.1523-1739.2003.01118.x.
Edge effects should also be considered in the creation of reserves.
is an excellent example of this type of conservation effort.
benefit? What are potential barriers to these needed species range shifts? Reserves must be designed with future habitat in mind, perhaps incorporating both the current and future ranges of the species’ of concern.
The fundamental question in determining future species ranges is how the Earth is changing, both in the present and how it will change in the future. According to the United States Environmental Protection Agency
the average surface temperature of the Earth has raised 1.2 – 1.4 °F since 1900. 1 °F of this warming has occurred since the mid 1970s, and at present, the Earth’s surface is heating up about 0.32 °F per decade. http://www.epa.gov/climatechange/science/recenttc.html Predicted increases in global temperature range from 1.4 °C to 5.8 °C by the year 2100 . Large changes in precipitation
are also predicted to occur by both the A1Fl scenario http://www.ipcc.ch/pub/taroldest/wg3/015.htm and the B1 scenario http://www.grida.no/climate/ipcc_tar/wg1/008.htm It is predicted that there will also be large changes in the atmosphere
and in the sea level
. http://www.epa.gov/climatechange/science/recentcc.html.
This rapid, dramatic climate change has affected and will continue to affect species ranges. A well-publicized study by Camille Parmesan and Gary Yohe published in 2003 that drew on data collected on more than 1700 species illustrates this point well. 434 of the species in their study were characterized as having changed their range and abundances in the last 17-1000 years, with a median value of 66 years. Of these species that had seen shifts, 80% of them had shifted in the direction predicted by global climate change. These range shifts averaged 6.1 km per decade toward the poles or upward. Many species colonized regions that had previously been cooler. An example of this was species of sea anemones thriving in Monterey Bay
that had previously had a more southerly distribution. Species of lichen
s , and butterflies in Europe also followed the patterns of species range shifts predicted by models of future climate change.
These species were shown to be migrating northward and upward, to higher latitude
s and sky island
s. The data from this study also indicated “the dynamics at the range boundaries are expected to be more influenced by climate than are dynamics within the interior of a species range…[where] response to global warming predicts that southerly species should outperform northerly species at the same site.”
These findings are of particular interest when considering reserve design. At the edges of a reserve, presuming that the reserve is also the species range if the species is highly threatened, climate change will be far more of a factor. Northern borders and those at higher elevations will become future battlegrounds for the conservation of the species in question, as they migrate northward and upward. The borders of today may not include the habitat of tomorrow, thus defeating the purpose of preservation by instead making the species range smaller and smaller if there are barriers to migration at the Northern and higher elevation boundaries of the reserve. Reserves could be designed to keep Northern migration a possibility, with boundaries farther to the North than might be considered practical looking at the today’s species ranges and abundances. Keeping open corridors between reserves connecting them to reserves to the North and the South is another possibility.
, the term biodiversity hotspot
refers to "the richest and most threatened reservoirs of plant and animal life on Earth... To qualify as a hotspot, a region must meet two strict criteria: it must contain at least 1,500 species of vascular plants (> 0.5 percent of the world’s total) as endemics, and it has to have lost at least 70 percent of its original habitat." http://www.biodiversityhotspots.org/ These hotspots are rapidly disappearing due to human activities, but they still have a chance of being saved if conservation measures are enacted. Biodiversity hotspots could be considered the most important places to put reserves.
Nature reserve
A nature reserve is a protected area of importance for wildlife, flora, fauna or features of geological or other special interest, which is reserved and managed for conservation and to provide special opportunities for study or research...
in a way that effectively accomplishes the goal of the reserve.
Reserves have a variety of goals and many different factors need to be taken into account in order for a reserve to be successful. These factors include habitat preference, migration, climate change, and public support. In order to fulfil goal of the reserve and accommodate the factors influencing its success, a specific design must be created and implemented.
Purpose of Reserves
Often reserves (or protected areaProtected area
Protected areas are locations which receive protection because of their recognised natural, ecological and/or cultural values. There are several kinds of protected areas, which vary by level of protection depending on the enabling laws of each country or the regulations of the international...
s) are created with the intent of protecting a flagship species
Flagship species
The concept of flagship species is a surrogate species concept with its genesis in the field of conservation biology. The flagship species concept holds that by raising the profile of a particular species, it can successfully leverage more support for biodiversity conservation at large in a...
, usually Charismatic Macrofauna that are well known to the public (such as the Bengal tiger or giant panda). Other times they are created in the interest of protecting biodiversity
Biodiversity
Biodiversity is the degree of variation of life forms within a given ecosystem, biome, or an entire planet. Biodiversity is a measure of the health of ecosystems. Biodiversity is in part a function of climate. In terrestrial habitats, tropical regions are typically rich whereas polar regions...
.
Ecological communities
Biocoenosis
A biocoenosis , coined by Karl Möbius in 1877, describes the interacting organisms living together in a habitat . This term is rarely used in English, as this concept has not been popularized in Anglophone countries...
that are at high risk and are considered irreplaceable are often selected to be preserved as well .
Social and ecological factors
Successful reserves incorporate important ecological and social factors into their design. Such factors include the natural range of predators. When a reserve is too small, carnivores have increased contact with humans, resulting in higher mortality rates for the carnivoreAlso certain species are area sensitive. A study on song birds in Japan showed that certain birds only settle in habitats much larger than the area they actually occupy Knowing species geographic range and preference is essential to determining the size of the reserve needed.
Social factors such as the attitudes of local people should also be taken into account. If a reserve is put up in an area that people depend on for their livelihood the reserve often fails. For example in Bolivia, the Amboró National Park was expanded in 1991 from 1,800 to 6,370 km². While this was celebrated by conservationists, local people who would be displaced by the expansion were angered. They continued to hunt and log within the park and eventually the park size had to be reduced [8]. Because local people were not considered in the design of the reserve, conservation efforts failed. Many conservationists advocate local people must be included in conservation efforts, this is known as an Integrated Conservation and Development Project
Integrated Conservation and Development Project
Integrated conservation and development projects are biodiversity conservation projects with rural development components. This is an approach that aspires to combine social development with conservation goals. These projects look to deal with biodiversity conservation objectives through the use...
.
Big or small?
A large debate among conservation biologist is whether it is better to create several small reserves or one large reserve. The species area relationship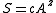 states that the number of species in a habitat is directly proportional to its size. So theoretically if several small reserves have a greater total area than a single large reserve, the small reserves will contain a greater total number of species.
states that the number of species in a habitat is directly proportional to its size. So theoretically if several small reserves have a greater total area than a single large reserve, the small reserves will contain a greater total number of species.The nested subset theory disagrees with this conclusion. It states that several small reserves will mostly share the same species, because certain species are better adapted to living in smaller habitats and many other species only exist in lager habitats.
A study conducted in Illinois showed that two small forest reserves contained a larger number of bird species than one large forest patch, but the large reserve contained a larger number of migratory birds . http://www.blackwell-synergy.com/links/doi/10.1046/j.1523-1739.2003.01118.x.
Edge effects should also be considered in the creation of reserves.
Reserve systems
Protecting species in a confined area sometimes isn’t enough to protect the biodiversity of an entire region. Life within a nature reserve does not function as an isolated unit, separate from its surroundings. Many animals engage in migration and are not guaranteed to stay within fixed reserve boundaries. So in order to protect biodiversity over wide geographic range reserve systems are established. Reserve systems are a series of strategically placed reserves designed to connect habitats. This allows animals to travel between protected areas through wildlife corridors, A wildlife corridor is a protected passageway where it is known that fauna migrate. The Yellowstone to Yukon Conservation InitiativeYellowstone to Yukon Conservation Initiative
The Yellowstone to Yukon Conservation Initiative or Y2Y is a joint Canada-US charitable organization that seeks to preserve and maintain the wildlife, native plants...
is an excellent example of this type of conservation effort.
Future habitat
Future habitat of the species we wish to protect is of utmost importance when designing reserves. There are many questions to think about when determining future species ranges: How will the climate shift in the future? Where will species move? What species will climate changeClimate change
Climate change is a significant and lasting change in the statistical distribution of weather patterns over periods ranging from decades to millions of years. It may be a change in average weather conditions or the distribution of events around that average...
benefit? What are potential barriers to these needed species range shifts? Reserves must be designed with future habitat in mind, perhaps incorporating both the current and future ranges of the species’ of concern.
The fundamental question in determining future species ranges is how the Earth is changing, both in the present and how it will change in the future. According to the United States Environmental Protection Agency
United States Environmental Protection Agency
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency is an agency of the federal government of the United States charged with protecting human health and the environment, by writing and enforcing regulations based on laws passed by Congress...
the average surface temperature of the Earth has raised 1.2 – 1.4 °F since 1900. 1 °F of this warming has occurred since the mid 1970s, and at present, the Earth’s surface is heating up about 0.32 °F per decade. http://www.epa.gov/climatechange/science/recenttc.html Predicted increases in global temperature range from 1.4 °C to 5.8 °C by the year 2100 . Large changes in precipitation
Precipitation (meteorology)
In meteorology, precipitation In meteorology, precipitation In meteorology, precipitation (also known as one of the classes of hydrometeors, which are atmospheric water phenomena is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls under gravity. The main forms of precipitation...
are also predicted to occur by both the A1Fl scenario http://www.ipcc.ch/pub/taroldest/wg3/015.htm and the B1 scenario http://www.grida.no/climate/ipcc_tar/wg1/008.htm It is predicted that there will also be large changes in the atmosphere
Atmosphere
An atmosphere is a layer of gases that may surround a material body of sufficient mass, and that is held in place by the gravity of the body. An atmosphere may be retained for a longer duration, if the gravity is high and the atmosphere's temperature is low...
and in the sea level
Sea level
Mean sea level is a measure of the average height of the ocean's surface ; used as a standard in reckoning land elevation...
. http://www.epa.gov/climatechange/science/recentcc.html.
This rapid, dramatic climate change has affected and will continue to affect species ranges. A well-publicized study by Camille Parmesan and Gary Yohe published in 2003 that drew on data collected on more than 1700 species illustrates this point well. 434 of the species in their study were characterized as having changed their range and abundances in the last 17-1000 years, with a median value of 66 years. Of these species that had seen shifts, 80% of them had shifted in the direction predicted by global climate change. These range shifts averaged 6.1 km per decade toward the poles or upward. Many species colonized regions that had previously been cooler. An example of this was species of sea anemones thriving in Monterey Bay
Monterey Bay
Monterey Bay is a bay of the Pacific Ocean, along the central coast of California. The bay is south of San Francisco and San Jose, between the cities of Santa Cruz and Monterey....
that had previously had a more southerly distribution. Species of lichen
Lichen
Lichens are composite organisms consisting of a symbiotic organism composed of a fungus with a photosynthetic partner , usually either a green alga or cyanobacterium...
s , and butterflies in Europe also followed the patterns of species range shifts predicted by models of future climate change.
These species were shown to be migrating northward and upward, to higher latitude
Latitude
In geography, the latitude of a location on the Earth is the angular distance of that location south or north of the Equator. The latitude is an angle, and is usually measured in degrees . The equator has a latitude of 0°, the North pole has a latitude of 90° north , and the South pole has a...
s and sky island
Sky island
Sky islands are mountains that are isolated by surrounding lowlands of a dramatically different environment, a situation which, in combination with the altitudinal zonation of ecosystems, has significant implications for natural habitats. Endemism, vertical migration, and relict populations are...
s. The data from this study also indicated “the dynamics at the range boundaries are expected to be more influenced by climate than are dynamics within the interior of a species range…[where] response to global warming predicts that southerly species should outperform northerly species at the same site.”
These findings are of particular interest when considering reserve design. At the edges of a reserve, presuming that the reserve is also the species range if the species is highly threatened, climate change will be far more of a factor. Northern borders and those at higher elevations will become future battlegrounds for the conservation of the species in question, as they migrate northward and upward. The borders of today may not include the habitat of tomorrow, thus defeating the purpose of preservation by instead making the species range smaller and smaller if there are barriers to migration at the Northern and higher elevation boundaries of the reserve. Reserves could be designed to keep Northern migration a possibility, with boundaries farther to the North than might be considered practical looking at the today’s species ranges and abundances. Keeping open corridors between reserves connecting them to reserves to the North and the South is another possibility.
Biodiversity hotspots
According to Conservation InternationalConservation International
Conservation International is a nonprofit organization headquartered in Arlington, Virginia, which seeks to ensure the health of humanity by protecting Earth's ecosystems and biodiversity. CI’s work focuses on six key initiatives that affect human well-being: climate, food security, freshwater...
, the term biodiversity hotspot
Biodiversity hotspot
A biodiversity hotspot is a biogeographic region with a significant reservoir of biodiversity that is under threat from humans.The concept of biodiversity hotspots was originated by Norman Myers in two articles in “The Environmentalist” , revised after thorough analysis by Myers and others in...
refers to "the richest and most threatened reservoirs of plant and animal life on Earth... To qualify as a hotspot, a region must meet two strict criteria: it must contain at least 1,500 species of vascular plants (> 0.5 percent of the world’s total) as endemics, and it has to have lost at least 70 percent of its original habitat." http://www.biodiversityhotspots.org/ These hotspots are rapidly disappearing due to human activities, but they still have a chance of being saved if conservation measures are enacted. Biodiversity hotspots could be considered the most important places to put reserves.

