
Religious symbolism of unity of opposites
Encyclopedia
Religious symbolism of unity of opposites
is the use of symbols, to express that the dualistic nature of the material
, having a oneness in its self.
The predominant opposites depicted are those of male
/female
, but can also be light
/darkness
, heaven
/earth
, warm
/cold
.
Each symbol may also contain several of these aspects or suggest a sinonym of these aspects.
Unity of opposites
The unity of opposites was first suggested by Heraclitus a pre-Socratic Greek philosopher.Philosophers had for some time been contemplating the notion of opposites. Anaximander posited that every element was an opposite, or connected to an opposite...
is the use of symbols, to express that the dualistic nature of the material
Material
Material is anything made of matter, constituted of one or more substances. Wood, cement, hydrogen, air and water are all examples of materials. Sometimes the term "material" is used more narrowly to refer to substances or components with certain physical properties that are used as inputs to...
, having a oneness in its self.
The predominant opposites depicted are those of male
Male
Male refers to the biological sex of an organism, or part of an organism, which produces small mobile gametes, called spermatozoa. Each spermatozoon can fuse with a larger female gamete or ovum, in the process of fertilization...
/female
Female
Female is the sex of an organism, or a part of an organism, which produces non-mobile ova .- Defining characteristics :The ova are defined as the larger gametes in a heterogamous reproduction system, while the smaller, usually motile gamete, the spermatozoon, is produced by the male...
, but can also be light
Light
Light or visible light is electromagnetic radiation that is visible to the human eye, and is responsible for the sense of sight. Visible light has wavelength in a range from about 380 nanometres to about 740 nm, with a frequency range of about 405 THz to 790 THz...
/darkness
Darkness
Darkness, in contrast with brightness, is a relative absence of visible light. It is the appearance of black in a color space. When light is not present, rod and cone cells within the eye are not stimulated. This lack of stimulation means photoreceptor cells are unable to distinguish color...
, heaven
Heaven
Heaven, the Heavens or Seven Heavens, is a common religious cosmological or metaphysical term for the physical or transcendent place from which heavenly beings originate, are enthroned or inhabit...
/earth
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun, and the densest and fifth-largest of the eight planets in the Solar System. It is also the largest of the Solar System's four terrestrial planets...
, warm
Warm
Warm or WARM can refer to:* A somewhat high temperature.* WARM , a radio station licensed to Scranton, Pennsylvania, United States* WARM-FM, a radio station licensed to York, Pennsylvania, United States...
/cold
Cold
Cold describes the condition of low temperature.Cold may also refer to:*Common cold, a contagious viral infectious disease of the upper respiratory system*Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease...
.
Each symbol may also contain several of these aspects or suggest a sinonym of these aspects.
| Religion or philosophy | Name | Symbol |
|---|---|---|
| Buddhism Buddhism Buddhism is a religion and philosophy encompassing a variety of traditions, beliefs and practices, largely based on teachings attributed to Siddhartha Gautama, commonly known as the Buddha . The Buddha lived and taught in the northeastern Indian subcontinent some time between the 6th and 4th... |
Golden fish pair |  |
| Yab-Yum Yab-Yum Yab-yum is a common symbol in the Buddhist art of India, Bhutan, Nepal, and Tibet representing the male deity in sexual union with his female consort... |
||
| Gnosticism Gnosticism Gnosticism is a scholarly term for a set of religious beliefs and spiritual practices common to early Christianity, Hellenistic Judaism, Greco-Roman mystery religions, Zoroastrianism , and Neoplatonism.A common characteristic of some of these groups was the teaching that the realisation of Gnosis... |
Gnostic Ankh Ankh The ankh , also known as key of life, the key of the Nile or crux ansata, was the ancient Egyptian hieroglyphic character that read "eternal life", a triliteral sign for the consonants ʻ-n-ḫ... |
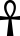 |
| Caduceus Caduceus The caduceus is the staff carried by Hermes in Greek mythology. The same staff was also borne by heralds in general, for example by Iris, the messenger of Hera. It is a short staff entwined by two serpents, sometimes surmounted by wings... (also a symbol of Alchemy Alchemy Alchemy is an influential philosophical tradition whose early practitioners’ claims to profound powers were known from antiquity. The defining objectives of alchemy are varied; these include the creation of the fabled philosopher's stone possessing powers including the capability of turning base... and Hermeticism Hermeticism Hermeticism or the Western Hermetic Tradition is a set of philosophical and religious beliefs based primarily upon the pseudepigraphical writings attributed to Hermes Trismegistus... ) |
 |
|
| Gold and Silver or Sun and Moon (mostly a symbol of Alchemy Alchemy Alchemy is an influential philosophical tradition whose early practitioners’ claims to profound powers were known from antiquity. The defining objectives of alchemy are varied; these include the creation of the fabled philosopher's stone possessing powers including the capability of turning base... and Hermeticism Hermeticism Hermeticism or the Western Hermetic Tradition is a set of philosophical and religious beliefs based primarily upon the pseudepigraphical writings attributed to Hermes Trismegistus... ) |
  |
|
| Double Ouroboros Ouroboros The Ouroboros is an ancient symbol depicting a serpent or dragon eating its own tail. The name originates from within Greek language; οὐρά meaning "tail" and βόρος meaning "eating", thus "he who eats the tail".... Ouroboros on about.com (also a symbol of Alchemy Alchemy Alchemy is an influential philosophical tradition whose early practitioners’ claims to profound powers were known from antiquity. The defining objectives of alchemy are varied; these include the creation of the fabled philosopher's stone possessing powers including the capability of turning base... and Hermeticism Hermeticism Hermeticism or the Western Hermetic Tradition is a set of philosophical and religious beliefs based primarily upon the pseudepigraphical writings attributed to Hermes Trismegistus... ) |
 |
|
| Hinduism Hinduism Hinduism is the predominant and indigenous religious tradition of the Indian Subcontinent. Hinduism is known to its followers as , amongst many other expressions... |
Ardhanari Ardhanari Ardhanarishvara , is a composite androgynous form of the Hindu god Shiva and his consort Parvati . Ardhanarishvara is depicted as half male and half female, split down the middle... |
|
| Connection of nadis at chakra Chakra Chakra is a concept originating in Hindu texts, featured in tantric and yogic traditions of Hinduism and Buddhism. Its name derives from the Sanskrit word for "wheel" or "turning" .Chakra is a concept referring to wheel-like vortices... s (more specifically solar nadi pingala and lunar nadi ida) |
||
| Linga Lingam The Lingam is a representation of the Hindu deity Shiva used for worship in temples.... -Yoni Yoni Yoni is the Sanskrit word for the vagina. Its counterpart is the lingam as interpreted by some, the phallus.It is also the divine passage, womb or sacred temple... |
||
| Union of Bhairava Bhairava Bhairava , sometimes known as Bhairo or Bhairon or Bhairadya or Bheruji , Kaala Bhairavar or Vairavar , is the fierce manifestation of Lord Shiva associated with annihilation... (Shiva Shiva Shiva is a major Hindu deity, and is the destroyer god or transformer among the Trimurti, the Hindu Trinity of the primary aspects of the divine. God Shiva is a yogi who has notice of everything that happens in the world and is the main aspect of life. Yet one with great power lives a life of a... in his terrible form) and Kali Kali ' , also known as ' , is the Hindu goddess associated with power, shakti. The name Kali comes from kāla, which means black, time, death, lord of death, Shiva. Kali means "the black one". Since Shiva is called Kāla - the eternal time, Kālī, his consort, also means "Time" or "Death" . Hence, Kāli is... |
 |
|
| Yantra Yantra Yantra is the Sanskrit word for "instrument" or "machine". Much like the word "instrument" itself, it can stand for symbols, processes, automata, machinery or anything that has structure and organization, depending on context.... |
 |
|
| Judaism Judaism Judaism ) is the "religion, philosophy, and way of life" of the Jewish people... |
Star of David Star of David The Star of David, known in Hebrew as the Shield of David or Magen David is a generally recognized symbol of Jewish identity and Judaism.Its shape is that of a hexagram, the compound of two equilateral triangles... |
 |
| Mayas | Hunab Ku Hunab Ku Hunab Ku is the name of a supposed Maya deity, described as "the supreme god" whose name appears in only two colonial sources: the Motul Dictionary and the Chilam Balam of Chumayel... |
|
| Taoism (Daoism) Taoism Taoism refers to a philosophical or religious tradition in which the basic concept is to establish harmony with the Tao , which is the mechanism of everything that exists... |
Yin and yang Yin and yang In Asian philosophy, the concept of yin yang , which is often referred to in the West as "yin and yang", is used to describe how polar opposites or seemingly contrary forces are interconnected and interdependent in the natural world, and how they give rise to each other in turn. Opposites thus only... (Taiji Taiji Taiji 太極 is a Chinese cosmological term for the "Supreme Ultimate" state of undifferentiated absolute and infinite potentiality, contrasted with the Wuji 無極 "Without Ultimate"... ) |
 |
| Thelema Thelema Thelema is a religious philosophy that was established, defined and developed by the early 20th century British writer and ceremonial magician, Aleister Crowley. He believed himself to be the prophet of a new age, the Æon of Horus, based upon a religious experience that he had in Egypt in 1904... |
Unicursal Hexagram Unicursal Hexagram The unicursal hexagram is a hexagram or six-pointed star that can be traced or drawn unicursally, in one continuous line rather than by two overlaid triangles... |
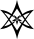 |

