Rel homology domain
Encyclopedia
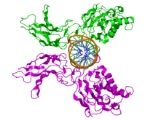
The Rel homology domain (RHD) is a protein domain
found in a family of eukaryotic transcription factor
s, which includes NF-κB, NFAT
, among others. Some of these transcription factors appear to form multi-protein DNA
-bound complexes. Phosphorylation
of the RHD appears to play a role in the regulation of some of these transcription factors, acting to modulate the expression of their target genes. The RHD is composed of two immunoglobulin-like beta barrel
subdomains that grip the DNA in the major groove. The N-terminal specificity domain resembles the core domain of the p53
transcription factor, and contains a recognition loop that interacts with DNA bases. The C-terminal dimerization domain contains the site for interaction with I-kappaB.
Protein domain
A protein domain is a part of protein sequence and structure that can evolve, function, and exist independently of the rest of the protein chain. Each domain forms a compact three-dimensional structure and often can be independently stable and folded. Many proteins consist of several structural...
found in a family of eukaryotic transcription factor
Transcription factor
In molecular biology and genetics, a transcription factor is a protein that binds to specific DNA sequences, thereby controlling the flow of genetic information from DNA to mRNA...
s, which includes NF-κB, NFAT
NFAT
Nuclear factor of activated T-cells is a general name applied to a family of transcription factors shown to be important in immune response. One or more members of the NFAT family is expressed in most cells of the immune system...
, among others. Some of these transcription factors appear to form multi-protein DNA
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid is a nucleic acid that contains the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all known living organisms . The DNA segments that carry this genetic information are called genes, but other DNA sequences have structural purposes, or are involved in...
-bound complexes. Phosphorylation
Phosphorylation
Phosphorylation is the addition of a phosphate group to a protein or other organic molecule. Phosphorylation activates or deactivates many protein enzymes....
of the RHD appears to play a role in the regulation of some of these transcription factors, acting to modulate the expression of their target genes. The RHD is composed of two immunoglobulin-like beta barrel
Beta barrel
A beta barrel is a large beta-sheet that twists and coils to form a closed structure in which the first strand is hydrogen bonded to the last.Beta-strands in beta-barrels are typically arranged in an antiparallel fashion...
subdomains that grip the DNA in the major groove. The N-terminal specificity domain resembles the core domain of the p53
P53
p53 , is a tumor suppressor protein that in humans is encoded by the TP53 gene. p53 is crucial in multicellular organisms, where it regulates the cell cycle and, thus, functions as a tumor suppressor that is involved in preventing cancer...
transcription factor, and contains a recognition loop that interacts with DNA bases. The C-terminal dimerization domain contains the site for interaction with I-kappaB.

