.gif)
Reification (computer science)
Encyclopedia
Reification is the process by which an abstract idea about a computer program
is turned into an explicit data model
or other object created in a programming language
. A computable/addressable object — a resource — is created in a system as a proxy for a non computable/addressable object. By means of reification, something that was previously implicit, unexpressed, and possibly inexpressible is explicitly formulated and made available to conceptual (logical or computational) manipulation. Informally, reification is often referred to as "making something a first-class citizen" within the scope of a particular system. Some aspect of a system can be reified at language design time, which is related to reflection
in programming languages. It can be applied as a stepwise refinement at system design time. Reification is one of the most frequently used techniques of conceptual analysis and knowledge representation
.
In linguistics, reification
corresponds to a well-known phenomenon called nominalization
, the transformation of a verb into a noun, e.g. "move" → "movement", "be a member" → "membership". Nominalization often makes it easier to supply additional clause
s to the verb.
s, reification is the process by which a user program or any aspect of a programming language that was implicit in the translated program and the run-time system, are expressed in the language itself. This process makes it available to the program, which can inspect all these aspects as ordinary data
. In reflective languages
, reification data is causally connected to the related reified aspect such that a modification to one of them affects the other. Therefore, the reification data is always a faithful representation of the related reified aspect. Reification data is often said to be made a first class object. Reification, at least partially, has been experienced in many languages to date: in early Lisp dialects and in current Prolog dialects
, programs have been treated as data, although the causal connection has often been left to the responsibility of the programmer. In Smalltalk
-80, the compiler from the source text to bytecode has been part of the run-time system since the very first implementations of the language.
char* buffer = (char*) 0xB800000;
buffer[0] = 10;
s used in a formal specification
.
Data reification is the terminology of the Vienna Development Method
(VDM) that most other people would call data refinement. An example is taking a step towards an implementation by replacing a data representation without a counterpart in the intended implementation language, such as sets, by one that does have a counterpart (such as maps with fixed domains that can be implemented by arrays), or at least one that is closer to having a counterpart, such as sequences. The VDM community prefers the word "reification" over "refinement", as the process has more to do with concretising an idea than with refining it.
For similar usages, see Reification (linguistics)
.
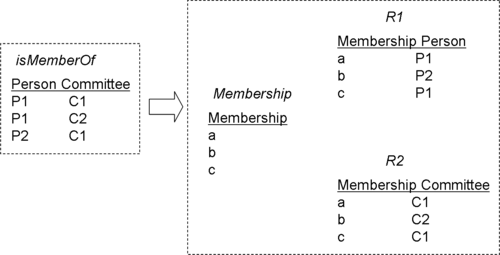 The same fact, however, could also be viewed as an entity. Viewing a relationship as an entity, one can say that the entity reifies the relationship. This is called reification of a relationship. Like any other entity, it must be an instance of an entity type. In the present example, the entity type has been named
The same fact, however, could also be viewed as an entity. Viewing a relationship as an entity, one can say that the entity reifies the relationship. This is called reification of a relationship. Like any other entity, it must be an instance of an entity type. In the present example, the entity type has been named
For related usages see Reification (knowledge representation)
.
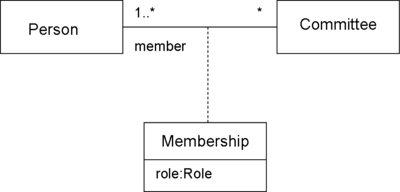 UML
UML
provides an association class construct for defining reified relationship types. The association class is a single model element that is both a kind of association and a kind of a class. The association and the entity type that reifies are both the same model element. Note that attributes cannot be reified.
languages, such as Resource Description Framework
(RDF) and Web Ontology Language
(OWL), a statement is a binary relation. It is used to link two individuals or an individual and a value. Applications sometimes need to describe other RDF statements, for instance, to record information like when statements were made, or who made them, which is sometimes called "provenance
" information. As an example, we may want to represent properties of a relation, such as our certainty about it, severity or strength of a relation, relevance of a relation, and so on.
The example from the conceptual modeling section describes a particular person with
person:p1 committee:isMemberOf committee:c1 .
It might be useful to record who nominated this particular person to this committee.
RDF provides a built-in vocabulary intended for describing RDF statements. A description of a statement using this vocabulary is called a reification of the statement. The RDF reification vocabulary consists of the type
Using the reification vocabulary, a reification of the statement about the person's membership would be given by assigning the statement a URIref such as
committee:membership12345 rdf:type rdf:Statement .
committee:membership12345 rdf:subject person:p1 .
committee:membership12345 rdf:predicate committee:isMemberOf .
committee:membership12345 rdf:object committee:c1 .
These statements say that the resource identified by the
Using reification according to this convention, we could record the fact that
person:p2 committee:nominated committee:membership12345
It is important to note that in the conventional use of reification, the subject of the reification triples is assumed to identify a particular instance of a triple in a particular RDF document, rather than some arbitrary triple having the same subject, predicate, and object. This particular convention is used because reification is intended for expressing properties such as dates of composition and source information, as in the examples given already, and these properties need to be applied to specific instances of triples.
The power of the reification vocabulary in RDF is restricted by the lack of a built-in means for assigning URIrefs to statements, so in order to express "provenance" information of this kind in RDF, one has to use some mechanism (outside of RDF) to assign URIs to individual RDF statements, then make further statements about those individual statements, using their URIs to identify them.
A more general approach to reification is to create an explicit new class and n new properties to represent an n-ary relation, making an instance of the relation linking the n individuals an instance of this class. This approach can also be used to represent provenance information and other properties for an individual relation instance.
:p1
a :Person ;
:has_membership _:Membership_12345 .
:_Membership_12345
a :Membership ;
:committee :C1;
:nominated_by :p2 .
committee:membership12345 rdf:subject person:p1 .
describing the
Computer program
A computer program is a sequence of instructions written to perform a specified task with a computer. A computer requires programs to function, typically executing the program's instructions in a central processor. The program has an executable form that the computer can use directly to execute...
is turned into an explicit data model
Data model
A data model in software engineering is an abstract model, that documents and organizes the business data for communication between team members and is used as a plan for developing applications, specifically how data is stored and accessed....
or other object created in a programming language
Programming language
A programming language is an artificial language designed to communicate instructions to a machine, particularly a computer. Programming languages can be used to create programs that control the behavior of a machine and/or to express algorithms precisely....
. A computable/addressable object — a resource — is created in a system as a proxy for a non computable/addressable object. By means of reification, something that was previously implicit, unexpressed, and possibly inexpressible is explicitly formulated and made available to conceptual (logical or computational) manipulation. Informally, reification is often referred to as "making something a first-class citizen" within the scope of a particular system. Some aspect of a system can be reified at language design time, which is related to reflection
Reflection (computer science)
In computer science, reflection is the process by which a computer program can observe and modify its own structure and behavior at runtime....
in programming languages. It can be applied as a stepwise refinement at system design time. Reification is one of the most frequently used techniques of conceptual analysis and knowledge representation
Knowledge representation
Knowledge representation is an area of artificial intelligence research aimed at representing knowledge in symbols to facilitate inferencing from those knowledge elements, creating new elements of knowledge...
.
In linguistics, reification
Reification (linguistics)
Reification in natural language processing refers to where a natural language statement is transformed so actions and events in it become quantifiable variables...
corresponds to a well-known phenomenon called nominalization
Nominalization
In linguistics, nominalization or nominalisation is the use of a verb, an adjective, or an adverb as the head of a noun phrase, with or without morphological transformation...
, the transformation of a verb into a noun, e.g. "move" → "movement", "be a member" → "membership". Nominalization often makes it easier to supply additional clause
Clause
In grammar, a clause is the smallest grammatical unit that can express a complete proposition. In some languages it may be a pair or group of words that consists of a subject and a predicate, although in other languages in certain clauses the subject may not appear explicitly as a noun phrase,...
s to the verb.
Reification and reflective programming languages
In the context of programming languageProgramming language
A programming language is an artificial language designed to communicate instructions to a machine, particularly a computer. Programming languages can be used to create programs that control the behavior of a machine and/or to express algorithms precisely....
s, reification is the process by which a user program or any aspect of a programming language that was implicit in the translated program and the run-time system, are expressed in the language itself. This process makes it available to the program, which can inspect all these aspects as ordinary data
Data
The term data refers to qualitative or quantitative attributes of a variable or set of variables. Data are typically the results of measurements and can be the basis of graphs, images, or observations of a set of variables. Data are often viewed as the lowest level of abstraction from which...
. In reflective languages
Reflection (computer science)
In computer science, reflection is the process by which a computer program can observe and modify its own structure and behavior at runtime....
, reification data is causally connected to the related reified aspect such that a modification to one of them affects the other. Therefore, the reification data is always a faithful representation of the related reified aspect. Reification data is often said to be made a first class object. Reification, at least partially, has been experienced in many languages to date: in early Lisp dialects and in current Prolog dialects
Prolog
Prolog is a general purpose logic programming language associated with artificial intelligence and computational linguistics.Prolog has its roots in first-order logic, a formal logic, and unlike many other programming languages, Prolog is declarative: the program logic is expressed in terms of...
, programs have been treated as data, although the causal connection has often been left to the responsibility of the programmer. In Smalltalk
Smalltalk
Smalltalk is an object-oriented, dynamically typed, reflective programming language. Smalltalk was created as the language to underpin the "new world" of computing exemplified by "human–computer symbiosis." It was designed and created in part for educational use, more so for constructionist...
-80, the compiler from the source text to bytecode has been part of the run-time system since the very first implementations of the language.
- The C programming languageC (programming language)C is a general-purpose computer programming language developed between 1969 and 1973 by Dennis Ritchie at the Bell Telephone Laboratories for use with the Unix operating system....
reifies the low-level detail of memory addressMemory addressA digital computer's memory, more specifically main memory, consists of many memory locations, each having a memory address, a number, analogous to a street address, at which computer programs store and retrieve, machine code or data. Most application programs do not directly read and write to...
es.
-
- Many programming language designs encapsulate the details of memory allocation in the compiler and the run-time system. In the design of the C programming language, the memory address is reified and is available for direct manipulation by other language constructs. For example, the following code may be used when implementing a memory-mapped device driver. The buffer pointer is a proxy for the memory address 0xB800000.
char* buffer = (char*) 0xB800000;
buffer[0] = 10;
- Functional programming languages based on lambda-calculus reify the concept of a procedure abstraction and procedure application in the form of the Lambda expression.
- The Scheme programming language reifies continuations (approximately, the call stack).
- In C#, reification is used to make parametric polymorphismParametric polymorphismIn programming languages and type theory, parametric polymorphism is a way to make a language more expressive, while still maintaining full static type-safety. Using parametric polymorphism, a function or a data type can be written generically so that it can handle values identically without...
implemented as generics as a first-class feature of the language. - In JavaJava (programming language)Java is a programming language originally developed by James Gosling at Sun Microsystems and released in 1995 as a core component of Sun Microsystems' Java platform. The language derives much of its syntax from C and C++ but has a simpler object model and fewer low-level facilities...
programming language, there exist "reifiable types" that are "completely available at run time" (i.e. their information is not erased during compilation). - REBOLREBOLREBOL is a cross-platform data exchange language and a multi-paradigm dynamic programming language originally designed by Carl Sassenrath for network communications and distributed computing. The language and its official implementation, which is a proprietary freely redistributable software are...
reifies code as data and vice-versa. - Many languages, such as Curl, JavaScriptJavaScriptJavaScript is a prototype-based scripting language that is dynamic, weakly typed and has first-class functions. It is a multi-paradigm language, supporting object-oriented, imperative, and functional programming styles....
, and Lisp provide anevalorevaluateprocedure that effectively reifies the language interpreter. - The LogtalkLogtalkLogtalk is an object-oriented logic programming language that extends the Prolog language with a feature set suitable for programming in the large. It provides support for encapsulation and data hiding, separation of concerns and enhanced code reuse...
framework for PrologPrologProlog is a general purpose logic programming language associated with artificial intelligence and computational linguistics.Prolog has its roots in first-order logic, a formal logic, and unlike many other programming languages, Prolog is declarative: the program logic is expressed in terms of...
offers a means to explore reification in the context of logic programmingLogic programmingLogic programming is, in its broadest sense, the use of mathematical logic for computer programming. In this view of logic programming, which can be traced at least as far back as John McCarthy's [1958] advice-taker proposal, logic is used as a purely declarative representation language, and a...
. - SmalltalkSmalltalkSmalltalk is an object-oriented, dynamically typed, reflective programming language. Smalltalk was created as the language to underpin the "new world" of computing exemplified by "human–computer symbiosis." It was designed and created in part for educational use, more so for constructionist...
and Actor languagesActor modelIn computer science, the Actor model is a mathematical model of concurrent computation that treats "actors" as the universal primitives of concurrent digital computation: in response to a message that it receives, an actor can make local decisions, create more actors, send more messages, and...
permit the reification of blocks and messagesMessage passingMessage passing in computer science is a form of communication used in parallel computing, object-oriented programming, and interprocess communication. In this model, processes or objects can send and receive messages to other processes...
, which are equivalent of lambda expressions in Lisp, and thisContext which is a reification of the current executing block.
Data reification vs. data refinement
Data reification (stepwise refinement) involves finding a more concrete representation of the abstract data typeAbstract data type
In computing, an abstract data type is a mathematical model for a certain class of data structures that have similar behavior; or for certain data types of one or more programming languages that have similar semantics...
s used in a formal specification
Formal specification
In computer science, a formal specification is a mathematical description of software or hardware that may be used to develop an implementation. It describes what the system should do, not how the system should do it...
.
Data reification is the terminology of the Vienna Development Method
Vienna Development Method
The Vienna Development Method is one of the longest-established Formal Methods for the development of computer-based systems. Originating in work done at IBM's Vienna Laboratory in the 1970s, it has grown to include a group of techniques and tools based on a formal specification language - the VDM...
(VDM) that most other people would call data refinement. An example is taking a step towards an implementation by replacing a data representation without a counterpart in the intended implementation language, such as sets, by one that does have a counterpart (such as maps with fixed domains that can be implemented by arrays), or at least one that is closer to having a counterpart, such as sequences. The VDM community prefers the word "reification" over "refinement", as the process has more to do with concretising an idea than with refining it.
For similar usages, see Reification (linguistics)
Reification (linguistics)
Reification in natural language processing refers to where a natural language statement is transformed so actions and events in it become quantifiable variables...
.
Reification in conceptual modeling
Reification is widely used in conceptual modeling. Reifying a relationship means viewing it as an entity. The purpose of reifying a relationship is to make it explicit, when additional information needs to be added to it. Consider the relationship typeIsMemberOf(member:Person, Committee). An instance of IsMemberOf is a relationship that represents the fact that a person is a member of a committee. The figure below shows an example population of IsMemberOf relationship in tabular form. Person P1 is a member of committees C1 and C2. Person P2 is a member of committee C1 only. 
Membership. For each instance of IsMemberOf, there is one and only one instance of Membership, and vice versa. Now, it becomes possible to add more information to the original relationship. As an example, we can express the fact that "person p1 was nominated to be the member of committee c1 by person p2". Reified relationship Membership can be used as the source of a new relationship IsNominatedBy(Membership, Person).For related usages see Reification (knowledge representation)
Reification (knowledge representation)
Reification in knowledge representation involves the representation of factual assertions, that are referred to by other assertions; which might then be manipulated in some way...
.
Reification in Unified Modeling Language (UML)

Unified Modeling Language
Unified Modeling Language is a standardized general-purpose modeling language in the field of object-oriented software engineering. The standard is managed, and was created, by the Object Management Group...
provides an association class construct for defining reified relationship types. The association class is a single model element that is both a kind of association and a kind of a class. The association and the entity type that reifies are both the same model element. Note that attributes cannot be reified.
RDF and OWL
In Semantic WebSemantic Web
The Semantic Web is a collaborative movement led by the World Wide Web Consortium that promotes common formats for data on the World Wide Web. By encouraging the inclusion of semantic content in web pages, the Semantic Web aims at converting the current web of unstructured documents into a "web of...
languages, such as Resource Description Framework
Resource Description Framework
The Resource Description Framework is a family of World Wide Web Consortium specifications originally designed as a metadata data model...
(RDF) and Web Ontology Language
Web Ontology Language
The Web Ontology Language is a family of knowledge representation languages for authoring ontologies.The languages are characterised by formal semantics and RDF/XML-based serializations for the Semantic Web...
(OWL), a statement is a binary relation. It is used to link two individuals or an individual and a value. Applications sometimes need to describe other RDF statements, for instance, to record information like when statements were made, or who made them, which is sometimes called "provenance
Provenance
Provenance, from the French provenir, "to come from", refers to the chronology of the ownership or location of an historical object. The term was originally mostly used for works of art, but is now used in similar senses in a wide range of fields, including science and computing...
" information. As an example, we may want to represent properties of a relation, such as our certainty about it, severity or strength of a relation, relevance of a relation, and so on.
The example from the conceptual modeling section describes a particular person with
URIref person:p1, who is a member of the committee:c1. The RDF triple from that description isperson:p1 committee:isMemberOf committee:c1 .
It might be useful to record who nominated this particular person to this committee.
RDF provides a built-in vocabulary intended for describing RDF statements. A description of a statement using this vocabulary is called a reification of the statement. The RDF reification vocabulary consists of the type
rdf:Statement, and the properties rdf:subject, rdf:predicate, and rdf:object.Using the reification vocabulary, a reification of the statement about the person's membership would be given by assigning the statement a URIref such as
committee:membership12345 so that describing statements can be written as follows:committee:membership12345 rdf:type rdf:Statement .
committee:membership12345 rdf:subject person:p1 .
committee:membership12345 rdf:predicate committee:isMemberOf .
committee:membership12345 rdf:object committee:c1 .
These statements say that the resource identified by the
URIref committee:membership12345 is an RDF statement, that the subject of the statement refers to the resource identified by person:p1, the predicate of the statement refers to the resource identified by committee:isMemberOf, and the object of the statement refers to the resource committee:c1. Assuming that the original statement is actually identified by committee:membership12345, it should be clear by comparing the original statement with the reification that the reification actually does describe it. The conventional use of the RDF reification vocabulary always involves describing a statement using four statements in this pattern. Therefore, they are sometimes referred to as the "reification quad".Using reification according to this convention, we could record the fact that
person:p2 made the nomination described by the original statement by adding the statementperson:p2 committee:nominated committee:membership12345
It is important to note that in the conventional use of reification, the subject of the reification triples is assumed to identify a particular instance of a triple in a particular RDF document, rather than some arbitrary triple having the same subject, predicate, and object. This particular convention is used because reification is intended for expressing properties such as dates of composition and source information, as in the examples given already, and these properties need to be applied to specific instances of triples.
The power of the reification vocabulary in RDF is restricted by the lack of a built-in means for assigning URIrefs to statements, so in order to express "provenance" information of this kind in RDF, one has to use some mechanism (outside of RDF) to assign URIs to individual RDF statements, then make further statements about those individual statements, using their URIs to identify them.
Reification in Topic Maps
In an XML Topic Map (XTM), only a topic can have a name or play a role in an association. One may use an association to make an assertion about a topic, but one cannot directly make assertions about that assertion. However, it is possible to create a topic that reifies a non-topic construct in a map, thus enabling the association to be named and treated as a topic itself.Reification and n-ary relations
In Semantic Web languages, such as RDF and OWL, a property is a binary relation used to link two individuals or an individual and a value. However, in some cases, the natural and convenient way to represent certain concepts is to use relations to link an individual to more than just one individual or value. These relations are called n-ary relations. Examples are representing relations among multiple individuals, such as a committee, a person who is a committee member and another person who has nominated the first person to become the committee member, or a buyer, a seller, and an object that was bought when describing a purchase of a book.A more general approach to reification is to create an explicit new class and n new properties to represent an n-ary relation, making an instance of the relation linking the n individuals an instance of this class. This approach can also be used to represent provenance information and other properties for an individual relation instance.
:p1
a :Person ;
:has_membership _:Membership_12345 .
:_Membership_12345
a :Membership ;
:committee :C1;
:nominated_by :p2 .
Reification vs. quotation
It is also important to note that the reification described here is not the same as "quotation" found in other languages. Instead, the reification describes the relationship between a particular instance of a triple and the resources the triple refers to. The reification can be read intuitively as saying "this RDF triple talks about these things", rather than (as in quotation) "this RDF triple has this form." For instance, in the reification example used in this section, the triple:committee:membership12345 rdf:subject person:p1 .
describing the
rdf:subject of the original statement says that the subject of the statement is the resource (the person) identified by the URIref person:p1. It does not state that the subject of the statement is the URIref itself (i.e., a string beginning with certain characters), as quotation would.See also
- Denotational semanticsDenotational semanticsIn computer science, denotational semantics is an approach to formalizing the meanings of programming languages by constructing mathematical objects which describe the meanings of expressions from the languages...
- Formal semantics of programming languagesFormal semantics of programming languagesIn programming language theory, semantics is the field concerned with the rigorous mathematical study of the meaning of programming languages and models of computation...
- Meta-circular evaluatorMeta-circular evaluatorA meta-circular evaluator is a special case of a self-interpreter in which the existing facilities of the parent interpreter are directly applied to the source code being interpreted, without any need for additional implementation...
- MetamodelingMetamodelingMetamodeling, or meta-modeling in software engineering and systems engineering among other disciplines, is the analysis, construction and development of the frames, rules, constraints, models and theories applicable and useful for modeling a predefined class of problems...
- MetaobjectMetaobjectIn computer science, a metaobject or meta-object is any entity that manipulates, creates, describes, or implements other objects. The object that the metaobject is about is called the base object...
- MetaprogrammingMetaprogrammingMetaprogramming is the writing of computer programs that write or manipulate other programs as their data, or that do part of the work at compile time that would otherwise be done at runtime...
- Normalization by evaluation
- Operational semanticsOperational semanticsIn computer science, operational semantics is a way to give meaning to computer programs in a mathematically rigorous way. Operational semantics are classified into two categories: structural operational semantics formally describe how the individual steps of a computation take place in a...
- Reflection (computer science)Reflection (computer science)In computer science, reflection is the process by which a computer program can observe and modify its own structure and behavior at runtime....
- Resource Description FrameworkResource Description FrameworkThe Resource Description Framework is a family of World Wide Web Consortium specifications originally designed as a metadata data model...
- Self-interpreterSelf-interpreterA self-interpreter, or metainterpreter, is a programming language interpreter written in the language it interprets. An example would be a BASIC interpreter written in BASIC...
- Topic Maps

