
Refrigeration plant
Encyclopedia
Gas
Gas is one of the three classical states of matter . Near absolute zero, a substance exists as a solid. As heat is added to this substance it melts into a liquid at its melting point , boils into a gas at its boiling point, and if heated high enough would enter a plasma state in which the electrons...
, liquid
Liquid
Liquid is one of the three classical states of matter . Like a gas, a liquid is able to flow and take the shape of a container. Some liquids resist compression, while others can be compressed. Unlike a gas, a liquid does not disperse to fill every space of a container, and maintains a fairly...
, and mechanical energy
Mechanical energy
In physics, mechanical energy is the sum of potential energy and kinetic energy present in the components of a mechanical system. It is the energy associated with the motion and position of an object. The law of conservation of energy states that in an isolated system that is only subject to...
to move heat
Heat
In physics and thermodynamics, heat is energy transferred from one body, region, or thermodynamic system to another due to thermal contact or thermal radiation when the systems are at different temperatures. It is often described as one of the fundamental processes of energy transfer between...
from one place to another. A liquid, such as ammonia
Ammonia
Ammonia is a compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula . It is a colourless gas with a characteristic pungent odour. Ammonia contributes significantly to the nutritional needs of terrestrial organisms by serving as a precursor to food and fertilizers. Ammonia, either directly or...
, which has a low boiling
Boiling
Boiling is the rapid vaporization of a liquid, which occurs when a liquid is heated to its boiling point, the temperature at which the vapor pressure of the liquid is equal to the pressure exerted on the liquid by the surrounding environmental pressure. While below the boiling point a liquid...
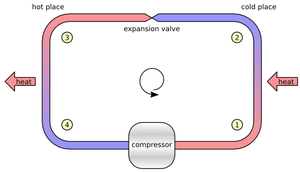
temperature is allowed to pass into a space via tubing. As the pressure in the ammonia drops, the liquid begins to boil, and enter a phase change from liquid to gas. In doing so, there is a great absorption of heat energy by the liquid in the tubing to create this phase change. The heat energy is absorbed from the space, and as the liquid boils off, it forms a gas. The gas is pulled through the tubing in the space into a suction header outside the space to the suction of a compressor
Gas compressor
A gas compressor is a mechanical device that increases the pressure of a gas by reducing its volume.Compressors are similar to pumps: both increase the pressure on a fluid and both can transport the fluid through a pipe. As gases are compressible, the compressor also reduces the volume of a gas...
. The compressor repressurises the gas, and discharges the liquid through cold water heat exchangers or cooling fans, exhausting the heat absorbed from the space, into the outside atmosphere. By pressurising and cooling the gas, the gas returns to a liquid stage, where it is stored and reintroduced to the space to be cooled.

