Rectilinear scanner
Encyclopedia
A rectilinear scanner is an imaging
device once used in nuclear medicine
.
over different parts of the body, which resulted in a fairly crude determination of the distribution of radioactivity
.
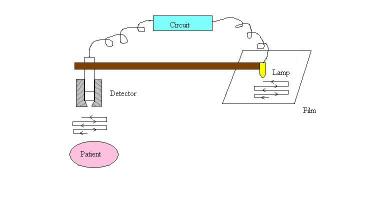
The scanner consists of :
Simultaneously, the light source moves over the photographic film. The intensity of light produced increases with an increase in activity, producing dark areas on the film.
Device can be modified electronically to enhance count rate differences in areas of medical interest.
Data taken during a scan is recorded on a magnetic tape or a disc to be analyzed later by a computer to provide a quantitative image.
Dimensions of scan areas, spacing of scan lines and rate of movement of scanning head is adjusted according to organ size and amount of radioactivity.
Rectilinear scanner can scan the entire body. The image is then minified to fit a standard 36 cm x 43 cm film.
As it uses a focused collimator
, it measures radiation distribution 7.5 - 12.5 cm from the end of the collimator. Thus, a scan from both sides of the patient is often necessary. A few scanners have 2 detectors facing each other to scan simultaneously.
Other types of image
Image can also be made
Because of these defects, the invention of the gamma camera
by Hal Angers in 1956 was indeed a breakthrough.
Medical imaging
Medical imaging is the technique and process used to create images of the human body for clinical purposes or medical science...
device once used in nuclear medicine
Nuclear medicine
In nuclear medicine procedures, elemental radionuclides are combined with other elements to form chemical compounds, or else combined with existing pharmaceutical compounds, to form radiopharmaceuticals. These radiopharmaceuticals, once administered to the patient, can localize to specific organs...
.
History
Before the invention of the rectilinear scanner in 1950 by Benedict Cassen, nuclear medicine pioneers used to move their insensitive Geiger CountersGeiger counter
A Geiger counter, also called a Geiger–Müller counter, is a type of particle detector that measures ionizing radiation. They detect the emission of nuclear radiation: alpha particles, beta particles or gamma rays. A Geiger counter detects radiation by ionization produced in a low-pressure gas in a...
over different parts of the body, which resulted in a fairly crude determination of the distribution of radioactivity
Radioactive decay
Radioactive decay is the process by which an atomic nucleus of an unstable atom loses energy by emitting ionizing particles . The emission is spontaneous, in that the atom decays without any physical interaction with another particle from outside the atom...
.
Components

The scanner consists of :
- A scintillatorScintillatorA scintillator is a special material, which exhibits scintillation—the property of luminescence when excited by ionizing radiation. Luminescent materials, when struck by an incoming particle, absorb its energy and scintillate, i.e., reemit the absorbed energy in the form of light...
which detects the γ radiation emitted by a radiopharmaceuticalRadiopharmacologyRadiopharmacology is the study and preparation of radiopharmaceuticals, which are radioactive pharmaceuticals. Radiopharmaceuticals are used in the field of nuclear medicine as tracers in the diagnosis and treatment of many diseases. Many radiopharmaceuticals use technetium-99m which has many...
located in the organ. The detector consists of a NaISodium iodideSodium iodide is a white, crystalline salt with chemical formula NaI used in radiation detection, treatment of iodine deficiency, and as a reactant in the Finkelstein reaction.-Uses:Sodium iodide is commonly used to treat and prevent iodine deficiency....
(Tl) crystal (12.7 cm in diameter, 5 cm thick) and a photomultiplierPhotomultiplierPhotomultiplier tubes , members of the class of vacuum tubes, and more specifically phototubes, are extremely sensitive detectors of light in the ultraviolet, visible, and near-infrared ranges of the electromagnetic spectrum...
. It is mechanically connected to a light bulb. - An electronic circuit between detector and light bulb.
- A filmPhotographic filmPhotographic film is a sheet of plastic coated with an emulsion containing light-sensitive silver halide salts with variable crystal sizes that determine the sensitivity, contrast and resolution of the film...
.
Mechanism
NaI(Tl) crystal of the detector moves in a raster pattern over studied area of the patient, making a constant count rate.Simultaneously, the light source moves over the photographic film. The intensity of light produced increases with an increase in activity, producing dark areas on the film.
Device can be modified electronically to enhance count rate differences in areas of medical interest.
Data taken during a scan is recorded on a magnetic tape or a disc to be analyzed later by a computer to provide a quantitative image.
Dimensions of scan areas, spacing of scan lines and rate of movement of scanning head is adjusted according to organ size and amount of radioactivity.
Rectilinear scanner can scan the entire body. The image is then minified to fit a standard 36 cm x 43 cm film.
As it uses a focused collimator
Collimator
A collimator is a device that narrows a beam of particles or waves. To "narrow" can mean either to cause the directions of motion to become more aligned in a specific direction or to cause the spatial cross section of the beam to become smaller.- Optical collimators :In optics, a collimator may...
, it measures radiation distribution 7.5 - 12.5 cm from the end of the collimator. Thus, a scan from both sides of the patient is often necessary. A few scanners have 2 detectors facing each other to scan simultaneously.
Other types of image
Image can also be made
- On an oscilloscope.
- By marks tapped on paper. Density or color of marks indicate intensity of activity in corresponding areas of the patient.
Disadvantages
- Time consuming : Scan lasts for over 30 min. Even by reducing time using 2 or more detectors, time is still very long.
- Motion artifacts : The patient may remain motionless, but he can certainly not hold his breath for more than 60 s. Thus, scans of liver for instance include motion artifacts since liver moves up and down 2 cm during normal breathing.
Because of these defects, the invention of the gamma camera
Gamma camera
A gamma camera, also called a scintillation camera or Anger camera, is a device used to image gamma radiation emitting radioisotopes, a technique known as scintigraphy...
by Hal Angers in 1956 was indeed a breakthrough.

