
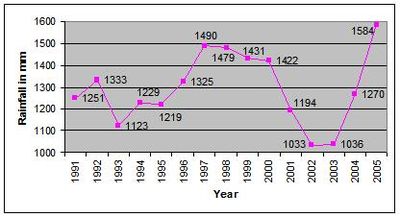
Rainfall in Karnataka
Encyclopedia


Karnataka
Karnataka , the land of the Kannadigas, is a state in South West India. It was created on 1 November 1956, with the passing of the States Reorganisation Act and this day is annually celebrated as Karnataka Rajyotsava...
in India
India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
has a bittersweet relationship with rains. While its regions of Malnad
Malnad
Malenadu is a region of Karnataka state in South India. Malenadu covers the western and eastern slopes of the Western Ghats, roughly 100 kilometers in width. Malenadu covers portions of the Shimoga, Chikmagalur, Uttara Kannada, Kodagu and Hassan districts....
and coastal Karnataka receive copious amount of rainfall; its north Bayaluseemae region in the Deccan Plateau
Deccan Plateau
The Deccan Plateau is a large plateau in India, making up the majority of the southern part of the country. It rises a hundred meters high in the north, rising further to more than a kilometers high in the south, forming a raised triangle nested within the familiar downward-pointing triangle of...
is one of the most arid regions in the country. Most of the rains received in the state is during the monsoon
Monsoon
Monsoon is traditionally defined as a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation, but is now used to describe seasonal changes in atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with the asymmetric heating of land and sea...
season. Being an agrarian economy with a large percentage of its citizens engaged in agriculture, the failure of rains can have a crippling effect on the economy of the state. Apart from the benefits in agriculture, the Government of Karnataka
Government of Karnataka
The Government of Karnataka is a democratically elected body with the Governor as the constitutional head. The Governor who is appointed for a period of five years appoints the Chief Minister and his council of ministers...
has tried to avail other benefits of rainfall using scientific methods. An example of this is the project, Rainwater Harvesting in Rural Karnataka which is initiated by the Karnataka State Council for Science and Technology and is one of the largest rainwater harvesting
Rainwater harvesting
Rainwater harvesting is the accumulating and storing of rainwater for reuse before it reaches the aquifer. It has been used to provide drinking water, water for livestock, water for irrigation, as well as other typical uses. Rainwater collected from the roofs of houses and local institutions can...
projects in the world. Agumbe
Agumbe
Agumbe is a village located in the Shimoga district in the state of Karnataka, India. Lying in the Thirthahalli taluk and the Malnad region, Agumbe is among the places in India that receive very heavy rainfall earning it the sobriquet, "Cherrapunji of the South". It is also the home of the Agumbe...
in the Shimoga district
Shimoga District
Shimoga District is a district in the Karnataka state of India. A major part of Shimoga District lies in the Malnad region of the Western Ghats, a hilly area known for its green forests, plentiful rainfall, and as the source of many of the area's rivers. Shimoga City is the administrative centre...
is known as one of the places with the highest annual rainfall in India.
Importance
The economy of Karnataka is mainly agrarian and most of it is dependent on the rainfall; mainly the southwest monsoon. The extent of arid land in the state is second only to Rajasthan. Only 26.5% of sown area (30,900 km²) is subjected to irrigationIrrigation
Irrigation may be defined as the science of artificial application of water to the land or soil. It is used to assist in the growing of agricultural crops, maintenance of landscapes, and revegetation of disturbed soils in dry areas and during periods of inadequate rainfall...
and hence the rest of the cultivated land is entirely dependent on rainfall. Rainfall also influences the quantity of water available in the rivers which in turn influences the amount of drinking water available to the population and the amount of electricity that can be generated in the hydroelectric power stations in the state. The importance of rainfall is such that Karnataka sometimes had to resort to costly artificial methods like cloud seeding
Cloud seeding
Cloud seeding, a form of intentional weather modification, is the attempt to change the amount or type of precipitation that falls from clouds, by dispersing substances into the air that serve as cloud condensation or ice nuclei, which alter the microphysical processes within the cloud...
in order to induce rain artificially. Rainfall is also crucial to recharge the depleting ground water and Karnataka has come up with innovative methods like rainwater harvesting
Rainwater harvesting
Rainwater harvesting is the accumulating and storing of rainwater for reuse before it reaches the aquifer. It has been used to provide drinking water, water for livestock, water for irrigation, as well as other typical uses. Rainwater collected from the roofs of houses and local institutions can...
in order to solve the drinking water scarcity in the state.
Rainwater harvesting
Karnataka is a pioneer in the concept of rainwater harvestingRainwater harvesting
Rainwater harvesting is the accumulating and storing of rainwater for reuse before it reaches the aquifer. It has been used to provide drinking water, water for livestock, water for irrigation, as well as other typical uses. Rainwater collected from the roofs of houses and local institutions can...
with The Karnataka State Council for Science and Technology (KSCST) implementing one of the largest rainwater harvesting
Rainwater harvesting
Rainwater harvesting is the accumulating and storing of rainwater for reuse before it reaches the aquifer. It has been used to provide drinking water, water for livestock, water for irrigation, as well as other typical uses. Rainwater collected from the roofs of houses and local institutions can...
projects in the world. 23683 schools in rural Karnataka were selected for this project with the main goal of providing drinking water by using the method of rooftop harvesting. In this project, rainwater collected on the rooftop is channeled through a system of PVC
PVC
Polyvinyl chloride is a plastic.PVC may also refer to:*Param Vir Chakra, India's highest military honor*Peripheral venous catheter, a small, flexible tube placed into a peripheral vein in order to administer medication or fluids...
pipes and stored in an enclosed surface tank. The pipeline consists of a first-flush filter which flushes out the first rainfall along with other contaminants that may exist on the roof and then subsequent cleaner rainwater is allowed to pass on to the tank. A sand bed filter is used to further eliminate impurities in the water before it gets collected in the tank. Further precautions are taken to prevent dust and insects from entering the tank.
Deficient rainfall
An year of deficient rainfall leads to the following consequences:- Agricultural output will be impacted: While this has a direct impact on the economy of the state, it also leads to other social issues like the suicide of farmers. Due to the crop failure, the farmers would not be in a position to repay the loans they had taken for agriculture and few of them take an extreme step of suicide.
- Drinking water scarcity: A lot of towns and cities in Karnataka are dependent on rivers for the supply of drinking water and any deficiency in rainfall leads to lesser amount of drinking water being supplied to the homes.
- Shortage of electricity: Deficient rainfall leads to a drop in the amount of electricity produced by hydroelectric projects and hence drastic measures like compulsory power cuts have to be employed to counter this shortage.
Excess rainfall
Heavy rains can lead to a significant loss of life and property and also cause damage to the crops. Excess rains also cause an impact in major cities with inundated roads causing traffic jams. An example of this was in the year 2005 when the Madivala lake overflowed on to the Hosur RoadHosur Road
Hosur Road is the part of National Highway 7 which connects the city of Bangalore capital of Karnataka, and the Tamil Nadu border town of Hosur. It is a four to eight-lane highway which also has service lanes on either sides at the busier parts. Apart from being a part of the National Highway, the...
in Bangalore
Bangalore
Bengaluru , formerly called Bengaluru is the capital of the Indian state of Karnataka. Bangalore is nicknamed the Garden City and was once called a pensioner's paradise. Located on the Deccan Plateau in the south-eastern part of Karnataka, Bangalore is India's third most populous city and...
forcing many schools and offices to close.
Rainfall distribution
The average annual rainfall in Karnataka is 1248 mm. The state is divided into three meteorological zones viz. North Interior Karnataka, South Interior Karnataka and Coastal Karnataka. Coastal Karnataka with an average annual rainfall of 3456 mm is one of the most rainy regions in the country. Contrasting this, the region of South Interior Karnataka and North Interior Karnataka receive only 1286 and 731 mm of average annual rainfall.Districts
The average annual rainfall in the districts of Karnataka varies from 562 mm in the Bagalkot districtBagalkot district
Bāgalkot district is an administrative district in the Indian state of Karnataka. The district headquarters is located in the town of Bagalkot. The district is located in northern Karnataka and borders Belgaum, Gadag, Koppal, Raichur and Bijapur...
to 4119 mm in the Udupi district
Udupi district
Udupi district , ಉಡುಪಿ ಜಿಲ್ಲೆ) in the Karnataka state of India was created in August 1997. The three northern taluks, Udupi, Kundapur and Karkal, were separated from Dakshina Kannada District to form Udupi district. Udupi district is surrounded by Uttara Kannada district in north, Dakshina Kannada...
. Bagalkot
Bagalkot district
Bāgalkot district is an administrative district in the Indian state of Karnataka. The district headquarters is located in the town of Bagalkot. The district is located in northern Karnataka and borders Belgaum, Gadag, Koppal, Raichur and Bijapur...
, Chitradurga
Chitradurga district
Chitradurga district is an administrative district of Karnataka state in southern India. The city of Chitradurga is the district headquarters. Chitradurga gets its name from Chitrakaldurga, an umbrella-shaped lofty hill found there. Tradition dates Chitradurga District to the period of the...
and Koppal
Koppal district
Koppal district is an administrative district in the state of Karnataka in India. In the past Koppal was referred to as 'Kopana Nagara'. Hampi, a World heritage center, covers some areas of Koppal District. It is situated approximately 38 km away...
are the districts which receive the least rainfall whereas Uttara Kannada
Uttara Kannada
Uttara Kannada also known as North Canara or North Kanara, is a district in the southern Indian state of Karnataka. It is bordered by the state of Goa and Belgaum District to the north, Dharwad District and Haveri District to the east, Shimoga District and Udupi District to the south and the...
, Dakshina Kannada
Dakshina Kannada
- Geography :The district geography consists of sea shore in the west and Western Ghats in the east. The major rivers are Netravathi, Kumaradhara, Phalguni, Shambhavi, Nandini or Pavanje and Payaswini which all join Arabian sea. Vast areas of evergreen forests which once covered this district, have...
and Udupi
Udupi district
Udupi district , ಉಡುಪಿ ಜಿಲ್ಲೆ) in the Karnataka state of India was created in August 1997. The three northern taluks, Udupi, Kundapur and Karkal, were separated from Dakshina Kannada District to form Udupi district. Udupi district is surrounded by Uttara Kannada district in north, Dakshina Kannada...
districts receive the heaviest rainfall.
| Average annual rainfall in the districts of Karnataka | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|

