
Radial nerve
Encyclopedia
The radial nerve is a nerve
in the human body that supplies the upper limb. It supplies the medial and lateral heads of the triceps brachii muscle
of the arm, as well as all 12 muscles in the posterior osteofascial compartment of the forearm and the associated joints and overlying skin.
It originates from the posterior cord of the brachial plexus
, carrying fibers from the ventral roots of spinal nerves C5, C6, C7, C8 & T1.
The radial nerve and its branches provide motor innervation to the dorsal arm muscles (the triceps brachii and the anconeus) and the extrinsic extensors of the wrists and hands; it also provides cutaneous sensory innervation to most of the back of the hand. The ulnar nerve
provides cutaneous sensory innervation to the back of the little finger and adjacent half of the ring finger.
The radial nerve divides into a deep branch, which becomes the posterior interosseous nerve
, and a superficial branch, which goes on to innervate the dorsum (back) of the hand.
of the brachial plexus
. It goes through the arm, first in the posterior compartment of the arm
, and later in the anterior compartment of the arm
, and continues in the posterior compartment of the forearm
.
(US), the lower triangular space of the axilla (UK) or the triceps hiatus (medical terminology).
Having passed through this inter muscular gap, the radial nerve continues posteriorly in a medial to lateral fashion on the arm while in conjunction with the axillary artery
/brachial artery
.
The nerve will first give off branches to the medial head of the triceps brachii and then enter a groove on the humerus, the radial sulcus
(AKA spiral groove), where it innervates the lateral head of the triceps. It is commonly believed that the radial nerve also provided motor innervation to the long head of the triceps. However, a study conducted in 2004 determined that, in 20 cadaveric specimens and 15 surgical dissections on participants, the long head was innervated by a branch of the axillary nerve
in all cases.
With the lateral and medial heads of the triceps intervated, the radial nerve emerges from the radial groove on the lateral aspect of the humerus.
At this point, it pierces the lateral intermuscular septum and enters the anterior compartment of the arm
.
It continues its journey inferiorly between the brachialis and brachioradialis
muscles.
When the radial nerve reaches the distal part of the humerus, it passes anterior to the lateral epicondyle
and continues in the forearm.
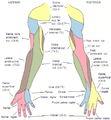 Cutaneous innervation
Cutaneous innervation
by the radial nerve is provided by the following nerve branches:
The superficial branch of the radial nerve
provides sensory innervation to much of the back of the hand, including the web of skin between the thumb and index finger.
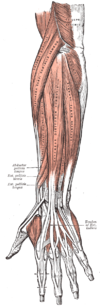 Muscular branches of the radial nerve
Muscular branches of the radial nerve
:
Deep branch of the radial nerve
:
Posterior interosseous nerve
(a continuation of the deep branch after the supinator):
The radial nerve (and its deep branch) provides motor innervation to the muscles in the posterior compartment of the arm
and forearm
, which are mostly extensors.
Nerve
A peripheral nerve, or simply nerve, is an enclosed, cable-like bundle of peripheral axons . A nerve provides a common pathway for the electrochemical nerve impulses that are transmitted along each of the axons. Nerves are found only in the peripheral nervous system...
in the human body that supplies the upper limb. It supplies the medial and lateral heads of the triceps brachii muscle
Triceps brachii muscle
The triceps brachii muscle is the large muscle on the back of the upper limb of many vertebrates. It is the muscle principally responsible for extension of the elbow joint .-Terminology:...
of the arm, as well as all 12 muscles in the posterior osteofascial compartment of the forearm and the associated joints and overlying skin.
It originates from the posterior cord of the brachial plexus
Brachial plexus
The brachial plexus is a network of nerve fibers, running from the spine, formed by the ventral rami of the lower four cervical and first thoracic nerve roots...
, carrying fibers from the ventral roots of spinal nerves C5, C6, C7, C8 & T1.
The radial nerve and its branches provide motor innervation to the dorsal arm muscles (the triceps brachii and the anconeus) and the extrinsic extensors of the wrists and hands; it also provides cutaneous sensory innervation to most of the back of the hand. The ulnar nerve
Ulnar nerve
In human anatomy, the ulnar nerve is a nerve which runs near the ulna bone. The ulnar collateral ligament of elbow joint is in relation with the ulnar nerve. The nerve is the largest unprotected nerve in the human body , so injury is common...
provides cutaneous sensory innervation to the back of the little finger and adjacent half of the ring finger.
The radial nerve divides into a deep branch, which becomes the posterior interosseous nerve
Posterior interosseous nerve
The posterior interosseous nerve is a nerve in the forearm. It is the continuation of the deep branch of the radial nerve, after this has crossed the supinator muscle. It is considerably diminished in size compared to the deep branch of the radial nerve...
, and a superficial branch, which goes on to innervate the dorsum (back) of the hand.
Course
The radial nerve originates as a terminal branch of the posterior cordPosterior cord
The posterior cord is a part of the brachial plexus. It consists of contributions from all of the roots of the brachial plexus.The posterior cord gives rise to the following nerves:...
of the brachial plexus
Brachial plexus
The brachial plexus is a network of nerve fibers, running from the spine, formed by the ventral rami of the lower four cervical and first thoracic nerve roots...
. It goes through the arm, first in the posterior compartment of the arm
Posterior compartment of the arm
The posterior compartment of the arm is an anatomic compartment which contains muscles which are all supplied by the radial nerve. This compartment is also known as the "extensor compartment", extension being its main action.-Contents:...
, and later in the anterior compartment of the arm
Anterior compartment of the arm
The anterior compartment of the arm is known as the "flexor compartment" as flexion is its main action.The muscles contained therein are the biceps brachii, brachialis, and coracobrachialis....
, and continues in the posterior compartment of the forearm
Posterior compartment of the forearm
The posterior compartment of the forearm contains the following muscles:-Muscles:* "E/I" refers to "extrinsic" or "intrinsic"....
.
In arm
From the brachial plexus, it travels posteriorly through what is often called the triangular intervalTriangular interval
The triangular interval is a space found in the axilla.-Borders:Two of its borders are as follows:* teres major - superior* long head of the triceps brachii - medial...
(US), the lower triangular space of the axilla (UK) or the triceps hiatus (medical terminology).
Having passed through this inter muscular gap, the radial nerve continues posteriorly in a medial to lateral fashion on the arm while in conjunction with the axillary artery
Axillary artery
In human anatomy, the axillary artery is a large blood vessel that conveys oxygenated blood to the lateral aspect of the thorax, the axilla and the upper limb...
/brachial artery
Brachial artery
The brachial artery is the major blood vessel of the arm.It is the continuation of the axillary artery beyond the lower margin of teres major muscle. It continues down the ventral surface of the arm until it reaches the cubital fossa at the elbow. It then divides into the radial and ulnar arteries...
.
The nerve will first give off branches to the medial head of the triceps brachii and then enter a groove on the humerus, the radial sulcus
Radial sulcus
The radial sulcus is a broad but shallow oblique depression for the radial nerve and deep brachial artery. It is located on the center of the lateral border of the humerus bone....
(AKA spiral groove), where it innervates the lateral head of the triceps. It is commonly believed that the radial nerve also provided motor innervation to the long head of the triceps. However, a study conducted in 2004 determined that, in 20 cadaveric specimens and 15 surgical dissections on participants, the long head was innervated by a branch of the axillary nerve
Axillary nerve
The axillary nerve or the circumflex nerve is a nerve of the human body, that comes off the of the brachial plexus at the level of the axilla and carries nerve fibers from C5 and C6...
in all cases.
With the lateral and medial heads of the triceps intervated, the radial nerve emerges from the radial groove on the lateral aspect of the humerus.
At this point, it pierces the lateral intermuscular septum and enters the anterior compartment of the arm
Anterior compartment of the arm
The anterior compartment of the arm is known as the "flexor compartment" as flexion is its main action.The muscles contained therein are the biceps brachii, brachialis, and coracobrachialis....
.
It continues its journey inferiorly between the brachialis and brachioradialis
Brachioradialis
Brachioradialis is a muscle of the forearm that acts to flex the forearm at the elbow. It is also capable of both pronation and supination, depending on the position of the forearm...
muscles.
When the radial nerve reaches the distal part of the humerus, it passes anterior to the lateral epicondyle
Lateral epicondyle of the humerus
The lateral epicondyle of the humerus is a small, tuberculated eminence, curved a little forward, and giving attachment to the radial collateral ligament of the elbow-joint, and to a tendon common to the origin of the Supinator and some of the Extensor muscles. In birds, where the arm is somewhat...
and continues in the forearm.
In forearm
In the forearm, it branches into a superficial branch (primarily sensory) and a deep branch (primarily motor).- The superficial branch of the radial nerveSuperficial branch of the radial nerveThe superficial branch of the radial nerve passes along the front of the radial side of the forearm to the commencement of its lower third.It lies at first slightly lateral to the radial artery, concealed beneath the Brachioradialis. In the middle third of the forearm, it lies behind the same...
descends in the forearm under the brachioradialisBrachioradialisBrachioradialis is a muscle of the forearm that acts to flex the forearm at the elbow. It is also capable of both pronation and supination, depending on the position of the forearm...
. It eventually pierces the deep fascia near the back of the wrist.
- The deep branch of the radial nerveDeep branch of the radial nerveThe deep branch of the radial nerve winds to the back of the forearm around the lateral side of the radius between the two planes of fibers of the Supinator, and is prolonged downward between the superficial and deep layers of muscles, to the middle of the forearm.Considerably diminished in size,...
pierces the supinator muscle, after which it is known as the posterior interosseous nervePosterior interosseous nerveThe posterior interosseous nerve is a nerve in the forearm. It is the continuation of the deep branch of the radial nerve, after this has crossed the supinator muscle. It is considerably diminished in size compared to the deep branch of the radial nerve...
.
Branches/Innervations
The following are branches/innervations of the radial nerve (including the superficial branch of the radial nerve and the deep branch of the radial nerve/posterior interosseous nerve).Cutaneous

Cutaneous innervation
Cutaneous innervation refers to the area of the skin which is supplied by a specific cutaneous nerve.Dermatomes are similar; however, a dermatome only specifies the area served by a spinal nerve...
by the radial nerve is provided by the following nerve branches:
- Posterior cutaneous nerve of armPosterior cutaneous nerve of armThe posterior cutaneous nerve of arm is a branch of the radial nerve that provides sensory innervation for much of the skin on the back of the arm...
(originates in axilla) - Inferior lateral cutaneous nerve of armInferior lateral cutaneous nerve of armThe inferior lateral cutaneous nerve of arm is a nerve found in humans and other animals. It is also called the inferior lateral brachial cutaneous nerve...
(originates in arm) - Posterior cutaneous nerve of forearmPosterior cutaneous nerve of forearmThe posterior cutaneous nerve of forearm is a nerve found in humans and other animals. It is also known as the dorsal antebrachial cutaneous nerve, the external cutaneous branch of the musculospiral nerve, and the posterior antebrachial cutaneous nerve...
(originates in arm)
The superficial branch of the radial nerve
Superficial branch of the radial nerve
The superficial branch of the radial nerve passes along the front of the radial side of the forearm to the commencement of its lower third.It lies at first slightly lateral to the radial artery, concealed beneath the Brachioradialis. In the middle third of the forearm, it lies behind the same...
provides sensory innervation to much of the back of the hand, including the web of skin between the thumb and index finger.
Motor

Muscular branches of the radial nerve
The muscular branches of the radial nerve supply the Triceps brachii, Anconæus, Brachioradialis, Extensor carpi radialis longus, and Brachialis, and are grouped as medial, posterior, and lateral. -Medial:...
:
- Triceps brachii (lateral and medial heads)
- Anconeus
- BrachioradialisBrachioradialisBrachioradialis is a muscle of the forearm that acts to flex the forearm at the elbow. It is also capable of both pronation and supination, depending on the position of the forearm...
- Extensor carpi radialis longus
Deep branch of the radial nerve
Deep branch of the radial nerve
The deep branch of the radial nerve winds to the back of the forearm around the lateral side of the radius between the two planes of fibers of the Supinator, and is prolonged downward between the superficial and deep layers of muscles, to the middle of the forearm.Considerably diminished in size,...
:
- Extensor carpi radialis brevis
- Supinator
Posterior interosseous nerve
Posterior interosseous nerve
The posterior interosseous nerve is a nerve in the forearm. It is the continuation of the deep branch of the radial nerve, after this has crossed the supinator muscle. It is considerably diminished in size compared to the deep branch of the radial nerve...
(a continuation of the deep branch after the supinator):
- Extensor digitorum
- Extensor digiti minimi
- Extensor carpi ulnaris
- Abductor pollicis longus
- Extensor pollicis brevis
- Extensor pollicis longus
- Extensor indicis
The radial nerve (and its deep branch) provides motor innervation to the muscles in the posterior compartment of the arm
Posterior compartment of the arm
The posterior compartment of the arm is an anatomic compartment which contains muscles which are all supplied by the radial nerve. This compartment is also known as the "extensor compartment", extension being its main action.-Contents:...
and forearm
Posterior compartment of the forearm
The posterior compartment of the forearm contains the following muscles:-Muscles:* "E/I" refers to "extrinsic" or "intrinsic"....
, which are mostly extensors.
See also
- Muscular branches of the radial nerveMuscular branches of the radial nerveThe muscular branches of the radial nerve supply the Triceps brachii, Anconæus, Brachioradialis, Extensor carpi radialis longus, and Brachialis, and are grouped as medial, posterior, and lateral. -Medial:...
- Cutaneous branches of the radial nerveCutaneous branches of the radial nerveThe cutaneous branches of the radial nerve are two in number:* Posterior brachial cutaneous nerve* Dorsal antibrachial cutaneous nerve...
- Superficial branch of the radial nerveSuperficial branch of the radial nerveThe superficial branch of the radial nerve passes along the front of the radial side of the forearm to the commencement of its lower third.It lies at first slightly lateral to the radial artery, concealed beneath the Brachioradialis. In the middle third of the forearm, it lies behind the same...
- Deep branch of the radial nerveDeep branch of the radial nerveThe deep branch of the radial nerve winds to the back of the forearm around the lateral side of the radius between the two planes of fibers of the Supinator, and is prolonged downward between the superficial and deep layers of muscles, to the middle of the forearm.Considerably diminished in size,...
- Radial neuropathy
- Radial tunnel syndromeRadial tunnel syndromeRadial Tunnel Syndrome is a condition proposed to explain lateral elbow pain more distal than typical for enthesopathy of the extensor carpi radialis brevis .-Etiology:...

