Raci
Encyclopedia
Serbs
The Serbs are a South Slavic ethnic group of the Balkans and southern Central Europe. Serbs are located mainly in Serbia, Montenegro and Bosnia and Herzegovina, and form a sizable minority in Croatia, the Republic of Macedonia and Slovenia. Likewise, Serbs are an officially recognized minority in...
, or sometimes, in a wider perspective, all South Slavs
South Slavs
The South Slavs are the southern branch of the Slavic peoples and speak South Slavic languages. Geographically, the South Slavs are native to the Balkan peninsula, the southern Pannonian Plain and the eastern Alps...
(especially Bunjevci
Bunjevci
Bunjevci are a South Slavic community and ethnic group living mostly in the Bačka region of Serbia and southern Hungary...
and Šokci), in the Middle Ages and the early modern times. The name was primary used by Hungarians and Germans
Germans
The Germans are a Germanic ethnic group native to Central Europe. The English term Germans has referred to the German-speaking population of the Holy Roman Empire since the Late Middle Ages....
and it derived from the name of medieval Serbian principality – Rascia
Raška (state)
Principality of Serbia or Serbian Principality was an early medieval state of the Serbs ruled by the Vlastimirović dynasty, that existed from ca 768 to 969 in Southeastern Europe. It was established through an unification of several provincial chiefs under the supreme rule of a certain Višeslav,...
. Because of the large number of Serbs who migrated from Rascia to the Pannonian Plain since the 14th century, the southern parts of the Pannonian Plain were also named Rascia (Raška or Рашка in Serbian, Ráczság or Ráczország in Hungarian and Ratzenland or Rezenland in German).
History of usage
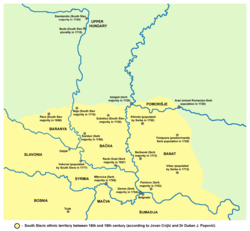
Since the 15th century, the Serbs made up a large percentage of the population on the territory of present-day VojvodinaVojvodina
Vojvodina, officially called Autonomous Province of Vojvodina is an autonomous province of Serbia. Its capital and largest city is Novi Sad...
. Because of this, many historical sources and maps, which were written and drawn between 15th and 18th centuries, mention the territory of present-day Vojvodina under the names of Rascia (Raška, Serbia) and Little Rascia (Mala Raška, Little Serbia). The name Rascia was also used to designate parts of Slavonia
Slavonia
Slavonia is a geographical and historical region in eastern Croatia...
populated by Serbs.
One sixteenth-century Italian account of the Ottoman Empire said that "the Rascians were people from Serbia and Rascia who had fled from the Turks and now lived to the north of the Danube".
According to one historical record from 1543, Timişoara
Timisoara
Timișoara is the capital city of Timiș County, in western Romania. One of the largest Romanian cities, with an estimated population of 311,586 inhabitants , and considered the informal capital city of the historical region of Banat, Timișoara is the main social, economic and cultural center in the...
and Arad
Arad, Romania
Arad is the capital city of Arad County, in western Romania, in the Crişana region, on the river Mureş.An important industrial center and transportation hub, Arad is also the seat of a Romanian Orthodox archbishop and features two universities, a Romanian Orthodox theological seminary, a training...
were located in the middle of Rascia (in medio Rascionarum). According to the same record, the main language spoken in Banat
Banat
The Banat is a geographical and historical region in Central Europe currently divided between three countries: the eastern part lies in western Romania , the western part in northeastern Serbia , and a small...
in that time was Serbian
Serbian language
Serbian is a form of Serbo-Croatian, a South Slavic language, spoken by Serbs in Serbia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Montenegro, Croatia and neighbouring countries....
and Banat was named the Little Rascia, while 17 Serbian monasteries existed in Banat in that time.
In seventeenth-century Habsburg usage, the term "Rascian" referred most commonly to the Serbs who lived in Habsburg territory, then more generally to Orthodox Serbs, wherever they lived, and then more generally still to speakers of Serbian or Serbo-Croat. The Emperor's so-called "Invitatorium" in April 1690, for example, was addressed to Arsenije as "Patriarch of the Rascians", but Austrian court style also distinguished between "Catholic Rascians" and "Orthodox Rascians".
In official Habsburg documents from the 18th century the Serbs of Habsburg Monarchy were mentioned as Rasciani ("Rascians"), Natio Rasciana ("Rascian nation"), Illyri ("Illyrians") and Natio Illyrica ("Illyrian nation").
During the Kuruc
Kuruc
The kuruc was a term used to denote the armed anti-Habsburg rebels in Royal Hungary between 1671 and 1711....
War (1703–1711) of Francis II Rakoczi
Francis II Rákóczi
Francis II Rákóczi Hungarian aristocrat, he was the leader of the Hungarian uprising against the Habsburgs in 1703-11 as the prince of the Estates Confederated for Liberty of the Kingdom of Hungary. He was also Prince of Transylvania, an Imperial Prince, and a member of the Order of the Golden...
, the territory of present-day Vojvodina was a battlefield between Hungarian rebels and local Serbs who fought on the side of the Habsburg Emperor. Darvas, the prime military commander of the Hungarian rebels, which fought against Serbs in Bačka, wrote: We burned all large places of Rascia, on the both banks of the rivers Danube
Danube
The Danube is a river in the Central Europe and the Europe's second longest river after the Volga. It is classified as an international waterway....
and Tisa
Tisá
Tisá is a village and municipality in Ústí nad Labem District in the Ústí nad Labem Region of the Czech Republic.The municipality covers an area of , and has a population of 786 ....
.
When the representatives of the Vojvodinian Serbs negotiated with the Hungarian leader Lajos Kossuth
Lajos Kossuth
Lajos Kossuth de Udvard et Kossuthfalva was a Hungarian lawyer, journalist, politician and Regent-President of Hungary in 1849. He was widely honored during his lifetime, including in the United Kingdom and the United States, as a freedom fighter and bellwether of democracy in Europe.-Family:Lajos...
in 1848, they asked him not to call them Raci, because they regard this name insulting, since they have their national and historical endonym – Serbs
Serbs
The Serbs are a South Slavic ethnic group of the Balkans and southern Central Europe. Serbs are located mainly in Serbia, Montenegro and Bosnia and Herzegovina, and form a sizable minority in Croatia, the Republic of Macedonia and Slovenia. Likewise, Serbs are an officially recognized minority in...
.
The initial name of the city of Novi Sad
Novi Sad
Novi Sad is the capital of the northern Serbian province of Vojvodina, and the administrative centre of the South Bačka District. The city is located in the southern part of Pannonian Plain on the Danube river....
(Ratzen Stadt - Rascian City, Serb City) has also derived from the name Rascians. The Tabán
Tabán
Tabán usually refers to an area within the 1st district of Budapest, the capital of Hungary. It lies on the Buda side of the Danube, to the south of György Dózsa Square, on the northern side of Elisabeth Bridge and to the east of Naphegy...
quarter of Budapest
Budapest
Budapest is the capital of Hungary. As the largest city of Hungary, it is the country's principal political, cultural, commercial, industrial, and transportation centre. In 2011, Budapest had 1,733,685 inhabitants, down from its 1989 peak of 2,113,645 due to suburbanization. The Budapest Commuter...
was also called Rácváros in the 18th-19th centuries because of its significant Serb population.
Since the 19th century, the term Rascians is no longer widely used.
Literature
- Drago Njegovan, Prisajedinjenje Vojvodine Srbiji, Novi Sad, 2004.
- Milan Tutorov, Mala Raška a u Banatu, Zrenjanin, 1991.
- Rascia, Časopis o Srbima u Vojvodini, godina I, broj 1, Vršac, Maj 1996.
- Lazo M. Kostić, Srpska Vojvodina i njene manjine, Novi Sad, 1999.
- Noel Malcolm, Kosovo - A Short History, Pan Books, London, 2002.
See also
- SerbsSerbsThe Serbs are a South Slavic ethnic group of the Balkans and southern Central Europe. Serbs are located mainly in Serbia, Montenegro and Bosnia and Herzegovina, and form a sizable minority in Croatia, the Republic of Macedonia and Slovenia. Likewise, Serbs are an officially recognized minority in...
- Serbs in Vojvodina
- RasciaRaška (state)Principality of Serbia or Serbian Principality was an early medieval state of the Serbs ruled by the Vlastimirović dynasty, that existed from ca 768 to 969 in Southeastern Europe. It was established through an unification of several provincial chiefs under the supreme rule of a certain Višeslav,...
- History of SerbiaHistory of SerbiaThe history of Serbia, as a country, begins with the Slavic settlements in the Balkans, established in the 6th century in territories governed by the Byzantine Empire. Through centuries, the Serbian realm evolved into a Kingdom , then an Empire , before the Ottomans annexed it in 1540...
- History of VojvodinaHistory of VojvodinaThis is a history of Vojvodina.Vojvodina is the Serbian name for the territory in the Northern Serbia, consisting of the southern part of the Pannonian Plain, mostly located north from the Danube and Sava rivers...

