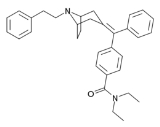
RWJ-394,674
Encyclopedia
RWJ-394674 is a drug which is used in scientific research. It is a potent, orally active analgesic
drug, which produces little respiratory depression. RWJ-394674 itself is a potent and selective agonist
for δ-opioid
receptors
, with a Ki
of 0.24 nM at δ and 72 nM at μ. However once inside the body, RWJ-394674 is dealkylated to its monodesethyl metabolite RWJ-413216 which is a potent agonist at the μ-opioid receptor
and has less affinity for δ (Ki 0.26 nM at μ, 46.7 nM at δ). The effect of RWJ-394674 when administered in vivo thus produces potent agonist effects at both μ and δ receptors through the combined actions of the parent drug and its active metabolite, with the δ-agonist effects counteracting the respiratory depression from the μ-opioid effects, and the only prominent side effect being sedation
.
Analgesic
An analgesic is any member of the group of drugs used to relieve pain . The word analgesic derives from Greek an- and algos ....
drug, which produces little respiratory depression. RWJ-394674 itself is a potent and selective agonist
Agonist
An agonist is a chemical that binds to a receptor of a cell and triggers a response by that cell. Agonists often mimic the action of a naturally occurring substance...
for δ-opioid
Delta Opioid receptor
The δ-opioid receptors, also known as delta opioid receptor or simply delta receptor, abbreviated DOR, is an opioid receptor that has enkephalins as its endogenous ligands.-Function:...
receptors
Receptor (biochemistry)
In biochemistry, a receptor is a molecule found on the surface of a cell, which receives specific chemical signals from neighbouring cells or the wider environment within an organism...
, with a Ki
Dissociation constant
In chemistry, biochemistry, and pharmacology, a dissociation constant is a specific type of equilibrium constant that measures the propensity of a larger object to separate reversibly into smaller components, as when a complex falls apart into its component molecules, or when a salt splits up into...
of 0.24 nM at δ and 72 nM at μ. However once inside the body, RWJ-394674 is dealkylated to its monodesethyl metabolite RWJ-413216 which is a potent agonist at the μ-opioid receptor
Mu Opioid receptor
The μ-opioid receptors are a class of opioid receptors with high affinity for enkephalins and beta-endorphin but low affinity for dynorphins. They are also referred to as μ opioid peptide receptors. The prototypical μ receptor agonist is the opium alkaloid morphine; μ refers to morphine...
and has less affinity for δ (Ki 0.26 nM at μ, 46.7 nM at δ). The effect of RWJ-394674 when administered in vivo thus produces potent agonist effects at both μ and δ receptors through the combined actions of the parent drug and its active metabolite, with the δ-agonist effects counteracting the respiratory depression from the μ-opioid effects, and the only prominent side effect being sedation
Sedation
Sedation is the reduction of irritability or agitation by administration of sedative drugs, generally to facilitate a medical procedure or diagnostic procedure...
.

