
RST model
Encyclopedia
The Russo-Susskind-Thorlacius model or RST model in short is a modification of the CGHS model
to take care of conformal anomalies
. In the CGHS model, if we include Faddeev-Popov ghost
s to gauge-fix diffeomorphisms in the conformal gauge, they contribute an anomaly of -24. Each matter field contributes an anomaly of 1. So, unless N=24, we will have gravitational anomalies
.
To the CGHS action , the following term
, the following term
is added, where κ is either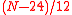 or
or  depending upon whether or not ghosts are considered. The nonlocal term leads to nonlocality
depending upon whether or not ghosts are considered. The nonlocal term leads to nonlocality
.
In the conformal gauge, .
.
It might appear as if the theory is local in the conformal gauge, but this overlooks the fact that the Raychaudhuri equations are still nonlocal.
CGHS model
The Callan-Giddings-Harvey-Strominger model or CGHS in short is a toy model of general relativity in 1 spatial and 1 time dimension. General relativity is a highly nonlinear model, and as such, its 3+1D version is usually too complicated to analyze in detail. In 3+1D and higher, propagating...
to take care of conformal anomalies
Conformal anomaly
Conformal anomaly is an anomaly i.e. a quantum phenomenon that breaks the conformal symmetry of the classical theory.A classically conformal theory is a theory which, when placed on a surface with arbitrary background metric, has an action that is invariant under rescalings of the background metric...
. In the CGHS model, if we include Faddeev-Popov ghost
Faddeev-Popov ghost
In physics, Faddeev–Popov ghosts are additional fields which are introduced into gauge quantum field theories to maintain the consistency of the path integral formulation...
s to gauge-fix diffeomorphisms in the conformal gauge, they contribute an anomaly of -24. Each matter field contributes an anomaly of 1. So, unless N=24, we will have gravitational anomalies
Gravitational anomaly
In theoretical physics, a gravitational anomaly is an example of a gauge anomaly: it is an effect of quantum mechanics–usually a one-loop diagram—that invalidates the general covariance of a theory of general relativity combined with some other fields. The adjective "gravitational" is derived from...
.
To the CGHS action
 , the following term
, the following term
is added, where κ is either
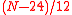 or
or  depending upon whether or not ghosts are considered. The nonlocal term leads to nonlocality
depending upon whether or not ghosts are considered. The nonlocal term leads to nonlocalityNonlocality
In Classical physics, nonlocality is the direct influence of one object on another, distant object. In Quantum mechanics, nonlocality refers to the absence of a local, realist model in agreement with quantum mechanical predictions.Nonlocality may refer to:...
.
In the conformal gauge,
 .
.It might appear as if the theory is local in the conformal gauge, but this overlooks the fact that the Raychaudhuri equations are still nonlocal.

