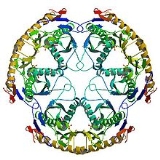
RNase PH
Encyclopedia
RNase PH is an 3'-5' exoribonuclease
and nucleotidyltransferase
, present in archaea
and bacteria
, that is involved in tRNA processing. Contrary to hydrolytic enzymes, it is a phosphorolytic
enzyme, meaning that it uses inorganic phosphate as a cofactor to cleave nucleotide-nucleotide bonds, releasing diphosphate nucleotides. The active structure of the proteins is actually a homohexameric complex, consisting of three RNase PH dimers. RNase PH has homologues
in many other organisms, which are referred to as RNase PH-like proteins. The part of another larger protein with a domain
that is very similar to RNase PH is called an RNase PH domain (RPD).
Exoribonuclease
An exoribonuclease is an exonuclease ribonuclease, which are enzymes that degrade RNA by removing terminal nucleotides from either the 5' end or the 3' end of the RNA molecule...
and nucleotidyltransferase
Nucleotidyltransferase
Nucleotidyltransferases are transferase enzymes of phosphorus-containing groups, e.g., substituents of nucleotidylic acids or simply nucleoside monophosphates...
, present in archaea
Archaea
The Archaea are a group of single-celled microorganisms. A single individual or species from this domain is called an archaeon...
and bacteria
Bacteria
Bacteria are a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria have a wide range of shapes, ranging from spheres to rods and spirals...
, that is involved in tRNA processing. Contrary to hydrolytic enzymes, it is a phosphorolytic
Phosphorolysis
Phosphorolysis is the cleavage of a compound in which inorganic phosphate is the attacking group. It is analogous to hydrolysis.An example of this is glycogen breakdown by glycogen phosphorylase, which catalyzes attack by inorganic phosphate on the terminal glycosyl residue at the nonreducing end...
enzyme, meaning that it uses inorganic phosphate as a cofactor to cleave nucleotide-nucleotide bonds, releasing diphosphate nucleotides. The active structure of the proteins is actually a homohexameric complex, consisting of three RNase PH dimers. RNase PH has homologues
Homology (biology)
Homology forms the basis of organization for comparative biology. In 1843, Richard Owen defined homology as "the same organ in different animals under every variety of form and function". Organs as different as a bat's wing, a seal's flipper, a cat's paw and a human hand have a common underlying...
in many other organisms, which are referred to as RNase PH-like proteins. The part of another larger protein with a domain
Protein domain
A protein domain is a part of protein sequence and structure that can evolve, function, and exist independently of the rest of the protein chain. Each domain forms a compact three-dimensional structure and often can be independently stable and folded. Many proteins consist of several structural...
that is very similar to RNase PH is called an RNase PH domain (RPD).
See also
Two highly related exoribonuclease complexes:- Polynucleotide phosphorylasePolynucleotide phosphorylasePolynucleotide Phosphorylase is a bifunctional enzyme with a phosphorolytic 3' to 5' exoribonuclease activity and a 3'-terminal oligonucleotide polymerase activity. It is involved on mRNA processing and degradation in bacteria, plants, and in humans.In humans, the enzyme is encoded by the gene...
- Exosome complexExosome complexThe exosome complex is a multi-protein complex capable of degrading various types of RNA molecules...

