
Nucleotidyltransferase
Encyclopedia
Nucleotidyltransferases are transferase
enzymes of phosphorus-containing groups, e.g., substituent
s of nucleotidylic acids or simply nucleoside monophosphates. The general reaction of transferring a nucleoside monophosphate moiety from A to B, can be written as:
For example, in the case of polymerases, A is pyrophosphate and B is the nascent polynucleotide.
They are classified under EC number
2.7.7 and they can be categorised into:
. This repair mechanism begins when a single nucleotide is recognized by DNA glycosylase as incorrectly matched or has been mutated in some way (UV light, chemical mutagen, etc.), and is removed. Later, a nucleotidyl tranferase is used to fill in the gap with the correct base, using the template strand as the reference.
Transferase
In biochemistry, a transferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of a functional group from one molecule to another . For example, an enzyme that catalyzed this reaction would be a transferase:In this example, A would be the donor, and B would be the acceptor...
enzymes of phosphorus-containing groups, e.g., substituent
Substituent
In organic chemistry and biochemistry, a substituent is an atom or group of atoms substituted in place of a hydrogen atom on the parent chain of a hydrocarbon...
s of nucleotidylic acids or simply nucleoside monophosphates. The general reaction of transferring a nucleoside monophosphate moiety from A to B, can be written as:
- A-P-N + B
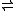 A + B-P-N
A + B-P-N
For example, in the case of polymerases, A is pyrophosphate and B is the nascent polynucleotide.
They are classified under EC number
EC number
The Enzyme Commission number is a numerical classification scheme for enzymes, based on the chemical reactions they catalyze....
2.7.7 and they can be categorised into:
- Uridylyltransferases, which transfer uridylyl- groups
- Adenylyltransferases, which transfer adenylyl- groups
- Guanylyltransferases, which transfer guanylyl- groups
- Cytitidylyltransferases, which transfer cytidylyl- groups
- Thymidylyltransferases, which transfer thymidylyl- groups
Role DNA repair mechanisms
Nucleotidyl transferase is a component of the repair pathway for single nucleotide base excision repairBase excision repair
In biochemistry and genetics, base excision repair is a cellular mechanism that repairs damaged DNA throughout the cell cycle. It is responsible primarily for removing small, non-helix-distorting base lesions from the genome. The related nucleotide excision repair pathway repairs bulky...
. This repair mechanism begins when a single nucleotide is recognized by DNA glycosylase as incorrectly matched or has been mutated in some way (UV light, chemical mutagen, etc.), and is removed. Later, a nucleotidyl tranferase is used to fill in the gap with the correct base, using the template strand as the reference.

