Quasinormal mode
Encyclopedia
Wave Mechanics
Quasinormal modes (QNM) are the modes of energyEnergy
In physics, energy is an indirectly observed quantity. It is often understood as the ability a physical system has to do work on other physical systems...
dissipation of a
perturbed object or field. A familiar example is the
perturbation (gentle tap) of a wine glass with a knife: the glass begins to
ring, it rings with a set, or superposition, of its natural
frequencies -- its modes of sonic energy
Energy
In physics, energy is an indirectly observed quantity. It is often understood as the ability a physical system has to do work on other physical systems...
dissipation. One could call these modes normal if the glass went
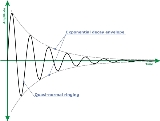
on ringing forever. Here the amplitude of oscillation decays in time, so we call its modes quasi-normal. To a very high degree of
accuracy, quasinormal ringing can be approximated by

where
 is the amplitude of oscillation,
is the amplitude of oscillation, is the frequency, and
is the frequency, and is the decay rate. The quasinormal
is the decay rate. The quasinormalfrequency is described by two numbers,

or, more compactly


where
 stands for the real part. Here,
stands for the real part. Here, is what is commonly referred to as the
is what is commonly referred to as thequasinormal mode frequency. It is a complex number
Complex number
A complex number is a number consisting of a real part and an imaginary part. Complex numbers extend the idea of the one-dimensional number line to the two-dimensional complex plane by using the number line for the real part and adding a vertical axis to plot the imaginary part...
with two pieces of
information: real part is the temporal oscillation; imaginary part is
the temporal, exponential decay.
In certain cases the amplitude of the wave decays quickly, to follow the decay for
a longer time one may plot

-
- The sound of quasinormal ringing
Mathematical Physics
In theoretical physicsTheoretical physics
Theoretical physics is a branch of physics which employs mathematical models and abstractions of physics to rationalize, explain and predict natural phenomena...
, a quasinormal mode is a formal solution of linearized differential equation
Differential equation
A differential equation is a mathematical equation for an unknown function of one or several variables that relates the values of the function itself and its derivatives of various orders...
s (such as the linearized equations of general relativity
General relativity
General relativity or the general theory of relativity is the geometric theory of gravitation published by Albert Einstein in 1916. It is the current description of gravitation in modern physics...
constraining perturbations around a black hole
Black hole
A black hole is a region of spacetime from which nothing, not even light, can escape. The theory of general relativity predicts that a sufficiently compact mass will deform spacetime to form a black hole. Around a black hole there is a mathematically defined surface called an event horizon that...
solution) with a complex eigenvalue (frequency
Frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit time. It is also referred to as temporal frequency.The period is the duration of one cycle in a repeating event, so the period is the reciprocal of the frequency...
).
Black hole
Black hole
A black hole is a region of spacetime from which nothing, not even light, can escape. The theory of general relativity predicts that a sufficiently compact mass will deform spacetime to form a black hole. Around a black hole there is a mathematically defined surface called an event horizon that...
s have many quasinormal modes (also: ringing modes) that describe the exponential decrease of asymmetry of the black hole in time as it evolves towards the perfect spherical shape.
Recently, the properties of quasinormal modes have been tested in the context of the AdS/CFT correspondence
AdS/CFT correspondence
In physics, the AdS/CFT correspondence , sometimes called the Maldacena duality, is the conjectured equivalence between a string theory and gravity defined on one space, and a quantum field theory without gravity defined on the conformal boundary of this space, whose dimension is lower by one or more...
. Also, the asymptotic behavior of quasinormal modes was proposed to be related to the Immirzi parameter
Immirzi parameter
The Immirzi parameter is a numerical coefficient appearing in loop quantum gravity, a nonperturbative theory of quantum gravity. The Immirzi parameter measures the size of the quantum of area in Planck units...
in loop quantum gravity
Loop quantum gravity
Loop quantum gravity , also known as loop gravity and quantum geometry, is a proposed quantum theory of spacetime which attempts to reconcile the theories of quantum mechanics and general relativity...
, but convincing arguments have not been found yet.

