Quantum harmonic oscillator
Overview
Quantum mechanics
Quantum mechanics, also known as quantum physics or quantum theory, is a branch of physics providing a mathematical description of much of the dual particle-like and wave-like behavior and interactions of energy and matter. It departs from classical mechanics primarily at the atomic and subatomic...
analog of the classical harmonic oscillator
Harmonic oscillator
In classical mechanics, a harmonic oscillator is a system that, when displaced from its equilibrium position, experiences a restoring force, F, proportional to the displacement, x: \vec F = -k \vec x \, where k is a positive constant....
. Because an arbitrary potential can be approximated as a harmonic potential at the vicinity of a stable equilibrium point, it is one of the most important model systems in quantum mechanics. Furthermore, it is one of the few quantum-mechanical systems for which an exact, analytical solution is known.
The Hamiltonian
Hamiltonian (quantum mechanics)
In quantum mechanics, the Hamiltonian H, also Ȟ or Ĥ, is the operator corresponding to the total energy of the system. Its spectrum is the set of possible outcomes when one measures the total energy of a system...
of the particle is:
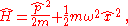
where
 is the position operator
is the position operatorPosition operator
In quantum mechanics, the position operator is the operator that corresponds to the position observable of a particle. Consider, for example, the case of a spinless particle moving on a line. The state space for such a particle is L2, the Hilbert space of complex-valued and square-integrable ...
, and
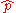 is the momentum operator
is the momentum operatorMomentum operator
In quantum mechanics, momentum is defined as an operator on the wave function. The Heisenberg uncertainty principle defines limits on how accurately the momentum and position of a single observable system can be known at once...
, given by
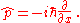
The first term in the Hamiltonian represents the kinetic energy of the particle, and the second term represents the potential energy in which it resides.

