
Pythagorean addition
Encyclopedia
In mathematics
, Pythagorean addition is the following binary operation
on the real number
s: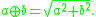
The name recalls the Pythagorean theorem
, which states that the length of the hypotenuse of a right triangle is where a and b are the lengths of the other sides.
This operation provides a simple notation and terminology when the summands are complicated; for example, the energy-momentum relation
in physics becomes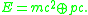
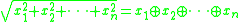 .
.
This is enough to form the real numbers into a commutative semigroup
. However, ⊕ is not a group
operation for the following reasons.
The only element which could potentially act as an identity element
is 0, since an identity e must satisfy e⊕e = e. This yields the equation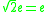 , but if e is nonzero then
, but if e is nonzero then 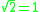 is a contradiction, so e could only be zero. Unfortunately 0 does not work as an identity element after all, since 0⊕(−1) = 1. This does indicate, however, that if the operation ⊕ is restricted to nonnegative real numbers, then 0 does act as an identity. Consequently the operation ⊕ acting on the nonnegative real numbers forms a commutative monoid
is a contradiction, so e could only be zero. Unfortunately 0 does not work as an identity element after all, since 0⊕(−1) = 1. This does indicate, however, that if the operation ⊕ is restricted to nonnegative real numbers, then 0 does act as an identity. Consequently the operation ⊕ acting on the nonnegative real numbers forms a commutative monoid
.
Mathematics
Mathematics is the study of quantity, space, structure, and change. Mathematicians seek out patterns and formulate new conjectures. Mathematicians resolve the truth or falsity of conjectures by mathematical proofs, which are arguments sufficient to convince other mathematicians of their validity...
, Pythagorean addition is the following binary operation
Binary operation
In mathematics, a binary operation is a calculation involving two operands, in other words, an operation whose arity is two. Examples include the familiar arithmetic operations of addition, subtraction, multiplication and division....
on the real number
Real number
In mathematics, a real number is a value that represents a quantity along a continuum, such as -5 , 4/3 , 8.6 , √2 and π...
s:
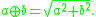
The name recalls the Pythagorean theorem
Pythagorean theorem
In mathematics, the Pythagorean theorem or Pythagoras' theorem is a relation in Euclidean geometry among the three sides of a right triangle...
, which states that the length of the hypotenuse of a right triangle is where a and b are the lengths of the other sides.
This operation provides a simple notation and terminology when the summands are complicated; for example, the energy-momentum relation
Energy-momentum relation
In special relativity, the energy-momentum relation is a relation between the energy, momentum and the mass of a body: E^2 = m^2 c^4 + p^2 c^2 , \;where c is the speed of light, E \; is total energy, m \; is invariant mass, and p = |\vec p|\; is momentum....
in physics becomes
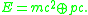
Properties
The operation ⊕ is associative and commutative, and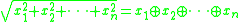 .
.This is enough to form the real numbers into a commutative semigroup
Semigroup
In mathematics, a semigroup is an algebraic structure consisting of a set together with an associative binary operation. A semigroup generalizes a monoid in that there might not exist an identity element...
. However, ⊕ is not a group
Group (mathematics)
In mathematics, a group is an algebraic structure consisting of a set together with an operation that combines any two of its elements to form a third element. To qualify as a group, the set and the operation must satisfy a few conditions called group axioms, namely closure, associativity, identity...
operation for the following reasons.
The only element which could potentially act as an identity element
Identity element
In mathematics, an identity element is a special type of element of a set with respect to a binary operation on that set. It leaves other elements unchanged when combined with them...
is 0, since an identity e must satisfy e⊕e = e. This yields the equation
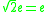 , but if e is nonzero then
, but if e is nonzero then 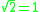 is a contradiction, so e could only be zero. Unfortunately 0 does not work as an identity element after all, since 0⊕(−1) = 1. This does indicate, however, that if the operation ⊕ is restricted to nonnegative real numbers, then 0 does act as an identity. Consequently the operation ⊕ acting on the nonnegative real numbers forms a commutative monoid
is a contradiction, so e could only be zero. Unfortunately 0 does not work as an identity element after all, since 0⊕(−1) = 1. This does indicate, however, that if the operation ⊕ is restricted to nonnegative real numbers, then 0 does act as an identity. Consequently the operation ⊕ acting on the nonnegative real numbers forms a commutative monoidMonoid
In abstract algebra, a branch of mathematics, a monoid is an algebraic structure with a single associative binary operation and an identity element. Monoids are studied in semigroup theory as they are naturally semigroups with identity. Monoids occur in several branches of mathematics; for...
.

