Purine nucleoside phosphorylase deficiency
Encyclopedia
Purine nucleoside phosphorylase deficiency, often called PNP-deficiency, is a rare autosomal
recessive metabolic disorder which results in severe combined immunodeficiency
.
activity, and an abrupt proliferation of both benign and opportunistic infections, PNP-deficiency is often characterized by the development of autoimmune disorders. Lupus
-erythematosis, autoimmune hemolytic anemia
, and idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura
have been reported with PNP-deficiency.
Neurological symptoms, such as developmental decline, hypotonia
, and mental retardation
have also been reported.
 The disorder is caused by a mutation of the purine nucleoside phosphorylase
The disorder is caused by a mutation of the purine nucleoside phosphorylase
(PNP) gene, located at chromosome
14q13.1
. PNP is a key enzyme
in the purine salvage pathway, and is required for purine
degradation. Specifically, it catalyzes the conversion of inosine and guanosine to hypoxanthine
. A deficiency of it leads to build up of elevated deoxy-GTP (dGTP) levels resulting in T-cell toxicity and deficiency. In contrast to adenosine deaminase deficiency
(another deficiency of purine metabolism
), there is minimal disruption to B cell
s.
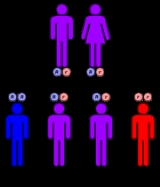
PNP deficiency is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner. This means the defective gene responsible for the disorder is located on an autosome
(chromosome 14 is an autosome), and two copies of the defective gene (one inherited from each parent) are required in order to be born with the disorder. The parents of an individual with an autosomal recessive disorder both carry
one copy of the defective gene, but usually do not experience any signs or symptoms of the disorder.
have been documented. In the United Kingdom only one child has been diagnosed with this disorder.
Autosome
An autosome is a chromosome that is not a sex chromosome, or allosome; that is to say, there is an equal number of copies of the chromosome in males and females. For example, in humans, there are 22 pairs of autosomes. In addition to autosomes, there are sex chromosomes, to be specific: X and Y...
recessive metabolic disorder which results in severe combined immunodeficiency
Severe combined immunodeficiency
Severe combined immunodeficiency , is a genetic disorder in which both "arms" of the adaptive immune system are impaired due to a defect in one of several possible genes. SCID is a severe form of heritable immunodeficiency...
.
Signs and symptoms
In addition to the symptoms associated with immunodeficiency, such as depletion of T-cells, decline of lymphocyteLymphocyte
A lymphocyte is a type of white blood cell in the vertebrate immune system.Under the microscope, lymphocytes can be divided into large lymphocytes and small lymphocytes. Large granular lymphocytes include natural killer cells...
activity, and an abrupt proliferation of both benign and opportunistic infections, PNP-deficiency is often characterized by the development of autoimmune disorders. Lupus
Lupus erythematosus
Lupus erythematosus is a category for a collection of diseases with similar underlying problems with immunity . Symptoms of these diseases can affect many different body systems, including joints, skin, kidneys, blood cells, heart, and lungs...
-erythematosis, autoimmune hemolytic anemia
Hemolytic anemia
Hemolytic anemia is a form of anemia due to hemolysis, the abnormal breakdown of red blood cells , either in the blood vessels or elsewhere in the human body . It has numerous possible causes, ranging from relatively harmless to life-threatening...
, and idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura
Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura
Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura is the condition of having an abnormally low platelet count of no known cause . As most incidents of ITP appear to be related to the production of antibodies against platelets, immune thrombocytopenic purpura or immune thrombocytopenia are terms also used to...
have been reported with PNP-deficiency.
Neurological symptoms, such as developmental decline, hypotonia
Hypotonia
Hypotonia is a state of low muscle tone , often involving reduced muscle strength. Hypotonia is not a specific medical disorder, but a potential manifestation of many different diseases and disorders that affect motor nerve control by the brain or muscle strength...
, and mental retardation
Mental retardation
Mental retardation is a generalized disorder appearing before adulthood, characterized by significantly impaired cognitive functioning and deficits in two or more adaptive behaviors...
have also been reported.
Cause, Pathophysiology and Genetics

Purine nucleoside phosphorylase
Purine nucleoside phosphorylase also known as PNPase and inosine phosphorylase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the NP gene.- Function :Purine nucleoside phosphorylase is an enzyme involved in purine metabolism...
(PNP) gene, located at chromosome
Chromosome
A chromosome is an organized structure of DNA and protein found in cells. It is a single piece of coiled DNA containing many genes, regulatory elements and other nucleotide sequences. Chromosomes also contain DNA-bound proteins, which serve to package the DNA and control its functions.Chromosomes...
14q13.1
Chromosome 14 (human)
rightChromosome14 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. People normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 14 spans about 109 million base pairs and represents between 3 and 3.5% of the total DNA in cells....
. PNP is a key enzyme
Enzyme
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions. In enzymatic reactions, the molecules at the beginning of the process, called substrates, are converted into different molecules, called products. Almost all chemical reactions in a biological cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates...
in the purine salvage pathway, and is required for purine
Purine
A purine is a heterocyclic aromatic organic compound, consisting of a pyrimidine ring fused to an imidazole ring. Purines, including substituted purines and their tautomers, are the most widely distributed kind of nitrogen-containing heterocycle in nature....
degradation. Specifically, it catalyzes the conversion of inosine and guanosine to hypoxanthine
Hypoxanthine
Hypoxanthine is a naturally occurring purine derivative. It is occasionally found as a constituent of nucleic acids where it is present in the anticodon of tRNA in the form of its nucleoside inosine. It has a tautomer known as 6-Hydroxypurine. Hypoxanthine is a necessary additive in certain cell,...
. A deficiency of it leads to build up of elevated deoxy-GTP (dGTP) levels resulting in T-cell toxicity and deficiency. In contrast to adenosine deaminase deficiency
Adenosine deaminase deficiency
Adenosine deaminase deficiency, also called ADA deficiency or ADA-SCID, is an autosomal recessive metabolic disorder that causes immunodeficiency. It occurs in fewer than one in 100,000 live births worldwide....
(another deficiency of purine metabolism
Purine metabolism
-Biosynthesis:Purines are biologically synthesized as nucleotides and in particular as ribotides, i.e. bases attached to ribose 5-phosphate. A key regulatory step is the production of 5-phospho-α-D-ribosyl 1-pyrophosphate by PRPP synthetase, which is activated by inorganic phosphate and...
), there is minimal disruption to B cell
B cell
B cells are lymphocytes that play a large role in the humoral immune response . The principal functions of B cells are to make antibodies against antigens, perform the role of antigen-presenting cells and eventually develop into memory B cells after activation by antigen interaction...
s.
PNP deficiency is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner. This means the defective gene responsible for the disorder is located on an autosome
Autosome
An autosome is a chromosome that is not a sex chromosome, or allosome; that is to say, there is an equal number of copies of the chromosome in males and females. For example, in humans, there are 22 pairs of autosomes. In addition to autosomes, there are sex chromosomes, to be specific: X and Y...
(chromosome 14 is an autosome), and two copies of the defective gene (one inherited from each parent) are required in order to be born with the disorder. The parents of an individual with an autosomal recessive disorder both carry
Genetic carrier
A genetic carrier , is a person or other organism that has inherited a genetic trait or mutation, but who does not display that trait or show symptoms of the disease. They are, however, able to pass the gene onto their offspring, who may then express the gene...
one copy of the defective gene, but usually do not experience any signs or symptoms of the disorder.
Epidemiology
PNP-deficiency is extremely rare. Only 33 patients with the disorder in the United StatesUnited States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
have been documented. In the United Kingdom only one child has been diagnosed with this disorder.

