
Pulmonary compliance
Encyclopedia
Pulmonary compliance can refer to either dynamic or static lung compliance. Static lung compliance is the change in volume for any given applied pressure. Dynamic lung compliance is the compliance of the lung at any given time during actual movement of air.
The compliance of the lungs demonstrate hysteresis
, that is the compliance is different on inspiration and expiration for identical volumes. See
Hysteresis#Respiratory physiology.
Compliance is greatest at moderate lung volumes
, and much lower at volumes which are very low or very high.
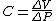
For example if a patient inhales 500 mL of air from a spirometer and intrapleural pressure before inspiration is – 5 cm H2O and -10 cm H2O at the end of inspiration. Then:
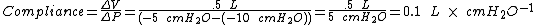
Dynamic lung compliance is ≤ static lung compliance. Dynamic lung compliance is calculated using the following equation, where CD = Dynamic compliance; VT = tidal volume; PIP = Peak inspiratory pressure; PEEP = Positive End Expiratory Pressure):
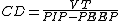
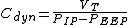
Cdyn — VT / (PIP - P_{EEP}), where PIP = peak inspiratory pressure
(the maximum pressure during inspiration). Alterations in airway resistance, lung compliance and chest wall compliance influence Cdyn.
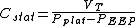
Cstat — Vt / (Pplat - PEEP), where Pplat = plateau pressure. Pplat is measured at the end of inhalation and prior to exhalation using an inspiratory hold maneuver. During this maneuver, airflow is transiently (~0.5 sec) discontinued, which eliminates the effects of airway resistance. Pplat is never > PIP and is typically < 3-5 cmH2O lower than PIP when airway resistance is not elevated.
.
Pulmonary surfactant
increases compliance by decreasing the surface tension of water. The internal surface of the alveolus is covered with a thin coat of fluid. The water in this fluid has a high surface tension, and provides a force that could collapse the alveolus. The presence of surfactant in this fluid breaks up the surface tension of water, making it less likely that the alveolus can collapse inward. If the alveolus were to collapse, a great force would be required to open it, meaning that compliance would decrease drastically.
In a highly compliant lung, as in emphysema, the elastic tissue has been damaged, usually due to their being overstretched by chronic overinflation. Patients with emphysema have a very high lung compliance due to the poor elastic recoil
, they have no problem inflating the lungs but have extreme difficulty exhaling air. In this condition extra work is required to get air out of the lungs.
Compliance decreases in the following cases:
The compliance of the lungs demonstrate hysteresis
Hysteresis
Hysteresis is the dependence of a system not just on its current environment but also on its past. This dependence arises because the system can be in more than one internal state. To predict its future evolution, either its internal state or its history must be known. If a given input alternately...
, that is the compliance is different on inspiration and expiration for identical volumes. See
Hysteresis#Respiratory physiology.
Compliance is greatest at moderate lung volumes
Lung volumes
Lung volumes and lung capacities refer to the volume of air associated with different phases of the respiratory cycle. Lung volumes are directly measured...
, and much lower at volumes which are very low or very high.
Calculation
Static compliance is calculated using the following equation, where ΔV is the change in volume, and ΔP is the change in pleural pressure: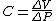
For example if a patient inhales 500 mL of air from a spirometer and intrapleural pressure before inspiration is – 5 cm H2O and -10 cm H2O at the end of inspiration. Then:
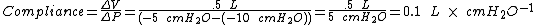
Dynamic lung compliance is ≤ static lung compliance. Dynamic lung compliance is calculated using the following equation, where CD = Dynamic compliance; VT = tidal volume; PIP = Peak inspiratory pressure; PEEP = Positive End Expiratory Pressure):
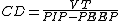
Dynamic Compliance (Cdyn)
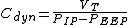
Cdyn — VT / (PIP - P_{EEP}), where PIP = peak inspiratory pressure
Peak inspiratory pressure
Peak inspiratory pressure is the highest level of pressure applied to the lungs during inhalation. In mechanical ventilation the number reflects a positive pressure in centimeters of water pressure . In normal breathing, it may sometimes be referred to as the maximal inspiratory pressure , which...
(the maximum pressure during inspiration). Alterations in airway resistance, lung compliance and chest wall compliance influence Cdyn.
Static Compliance (Cstat)
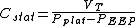
Cstat — Vt / (Pplat - PEEP), where Pplat = plateau pressure. Pplat is measured at the end of inhalation and prior to exhalation using an inspiratory hold maneuver. During this maneuver, airflow is transiently (~0.5 sec) discontinued, which eliminates the effects of airway resistance. Pplat is never > PIP and is typically < 3-5 cmH2O lower than PIP when airway resistance is not elevated.
Clinical significance
It is an important measurement in respiratory physiologyRespiratory physiology
Respiratory physiology is the branch of human physiology focusing upon respiration.Topics include:-Volumes:* lung volumes* vital capacity* functional residual capacity* dead space* spirometry* body plethysmography* peak flow meter-Mechanics:...
.
- fibrosisFibrosisFibrosis is the formation of excess fibrous connective tissue in an organ or tissue in a reparative or reactive process. This is as opposed to formation of fibrous tissue as a normal constituent of an organ or tissue...
is associated with a decrease in pulmonary compliance. - emphysemaEmphysemaEmphysema is a long-term, progressive disease of the lungs that primarily causes shortness of breath. In people with emphysema, the tissues necessary to support the physical shape and function of the lungs are destroyed. It is included in a group of diseases called chronic obstructive pulmonary...
/COPDChronic obstructive pulmonary diseaseChronic obstructive pulmonary disease , also known as chronic obstructive lung disease , chronic obstructive airway disease , chronic airflow limitation and chronic obstructive respiratory disease , is the co-occurrence of chronic bronchitis and emphysema, a pair of commonly co-existing diseases...
may be associated with an increase in pulmonary compliance due to the loss of alveolar and elastic tissue.
Pulmonary surfactant
Pulmonary surfactant
Pulmonary surfactant is a surface-active lipoprotein complex formed by type II alveolar cells. The proteins and lipids that surfactant comprises have both a hydrophilic region and a hydrophobic region...
increases compliance by decreasing the surface tension of water. The internal surface of the alveolus is covered with a thin coat of fluid. The water in this fluid has a high surface tension, and provides a force that could collapse the alveolus. The presence of surfactant in this fluid breaks up the surface tension of water, making it less likely that the alveolus can collapse inward. If the alveolus were to collapse, a great force would be required to open it, meaning that compliance would decrease drastically.
Functional significance of abnormally high or low compliance
Low compliance indicates a stiff lung and means extra work is required to bring in a normal volume of air. This occurs as the lungs in this case become fibrotic, lose their distensibility and become stiffer.In a highly compliant lung, as in emphysema, the elastic tissue has been damaged, usually due to their being overstretched by chronic overinflation. Patients with emphysema have a very high lung compliance due to the poor elastic recoil
Elastic recoil
Elastic recoil is the rebound of the lungs after having been stretched by inhalation, or rather, the ease with which the lung rebounds. With inhalation, the interpleural pressure of the lungs decreases. Relaxing the diaphragm during expiration allows the lungs to recoil and regain the interpleural...
, they have no problem inflating the lungs but have extreme difficulty exhaling air. In this condition extra work is required to get air out of the lungs.
Compliance decreases in the following cases:
- Elderly peopleOld ageOld age consists of ages nearing or surpassing the average life span of human beings, and thus the end of the human life cycle...
- Supine positionSupine positionThe supine position is a position of the body: lying down with the face up, as opposed to the prone position, which is face down, sometimes with the hands behind the head or neck. When used in surgical procedures, it allows access to the peritoneal, thoracic and pericardial regions; as well as the...
- LaparoscopicLaparoscopic surgeryLaparoscopic surgery, also called minimally invasive surgery , bandaid surgery, or keyhole surgery, is a modern surgical technique in which operations in the abdomen are performed through small incisions as opposed to the larger incisions needed in laparotomy.Keyhole surgery makes use of images...
surgical interventions - Severe restrictiveRestrictive lung diseaseRestrictive lung diseases are a category of extrapulmonary, pleural, or parenchymal respiratory diseases that restrict lung expansion, resulting in a decreased lung volume, an increased work of breathing, and inadequate ventilation and/or oxygenation...
pathologies - Chronic restrictiveRestrictive lung diseaseRestrictive lung diseases are a category of extrapulmonary, pleural, or parenchymal respiratory diseases that restrict lung expansion, resulting in a decreased lung volume, an increased work of breathing, and inadequate ventilation and/or oxygenation...
pathologies - HydrothoraxHydrothoraxA hydrothorax is a condition that results from serous fluid accumulating in the pleural cavity. This specific condition can be related to cirrhosis with ascites in which ascitic fluid leaks into the pleural cavity...
- PneumothoraxPneumothoraxPneumothorax is a collection of air or gas in the pleural cavity of the chest between the lung and the chest wall. It may occur spontaneously in people without chronic lung conditions as well as in those with lung disease , and many pneumothoraces occur after physical trauma to the chest, blast...
- High standing of a diaphragmDiaphragm-Optics and photography:* Diaphragm , a stop in the light path of a lens, having an aperture that regulates the amount of light that passes* Diaphragm shutter, a type of leaf shutter consisting of a number of thin blades in a camera-Acoustics:...

