Protein pKa calculations
Encyclopedia
In computational biology
, protein pKa calculations are used to estimate the pKa values
of amino acid
s as they exist within protein
s. These calculations complement the pKa values reported for amino acids in their free state, and are used frequently within the fields of molecular modeling, structural bioinformatics
, and computational biology
.
of amino acid side chain
s play an important role in defining the pH-dependent characteristics of a protein. The pH-dependence of the activity displayed by enzyme
s and the pH-dependence of protein stability, for example, are properties that are determined by the pKa values of amino acid side chains.
The pKa values of an amino acid side chain in solution is typically inferred from the pKa values of model compounds (compounds that are similar to the side chains of amino acids). (See Amino acid
for the pKa values of all amino acid side chains inferred in such a way.) The table below lists the model pKa values that are normally used in a protein pKa calculation.
Furthermore, in the folded protein the aspartic acid will be closer to other titratable groups in the protein and will also interact with permanent charges (e.g. ions) and dipoles in the protein.
All of these effects alter the pKa value of the amino acid side chain, and pKa calculation methods generally calculate the effect of the protein environment on the model pKa value of an amino acid side chain.
Typically the effects of the protein environment on the amino acid pKa value are divided into pH-independent effects and pH-dependent effects. The pH-independent effects (desolvation, interactions with permanent charges and dipoles) are added to the model pKa value to give the intrinsic pKa value. The pH-dependent effects cannot be added in the same straight-forward way and have to be accounted for using Boltzmann summation, Tanford-Roxby iterations or other methods.
The interplay of the intrinsic pKa values of a system with the electrostatic interaction energies between titratable groups can produce quite spectacular effects such as non-Henderson-Hasselbalch titration curve
s and even back-titration effects . pKaTool provides an easy interactive and instructive way of playing around with these effects.
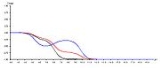
The image below shows a theoretical system consisting of three acidic residues. One group is displaying a back-titration event (blue group).

(PBE), often referred to as FDPB-based methods (FDPB is for "finite difference
Poisson-Boltzmann"). The PBE is a modification of Poisson's equation
that incorporates a description of the effect of solvent ions on the electrostatic field around a molecule.
The H++ web server, the pKD webserver, MCCE and Karlsberg+ use the FDPB method to compute pKa values of amino acid side chains.
FDPB-based methods calculate the change in the pKa value of an amino acid side chain when that side chain is moved from a hypothetical fully solvated state to its position in the protein. To perform such a calculation, one needs theoretical methods that can calculate the effect of the protein interior on a pKa value, and knowledge of the pKa values of amino acid side chains in their fully solvated states.
.
Molecular dynamics is typically a much more computationally expensive way to predict pKa's than using the Poisson-Boltzmann equation
. Currently used molecular force fields do not take polarizability into account, which could be an important property for protonation energies.
. Most pKa calculation methods silently assume that all titration curves are Henderson-Hasselbalch shaped, and pKa values in pKa calculation programs are therefore often determined in this way.
Computational biology
Computational biology involves the development and application of data-analytical and theoretical methods, mathematical modeling and computational simulation techniques to the study of biological, behavioral, and social systems...
, protein pKa calculations are used to estimate the pKa values
Acid dissociation constant
An acid dissociation constant, Ka, is a quantitative measure of the strength of an acid in solution. It is the equilibrium constant for a chemical reaction known as dissociation in the context of acid-base reactions...
of amino acid
Amino acid
Amino acids are molecules containing an amine group, a carboxylic acid group and a side-chain that varies between different amino acids. The key elements of an amino acid are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen...
s as they exist within protein
Protein
Proteins are biochemical compounds consisting of one or more polypeptides typically folded into a globular or fibrous form, facilitating a biological function. A polypeptide is a single linear polymer chain of amino acids bonded together by peptide bonds between the carboxyl and amino groups of...
s. These calculations complement the pKa values reported for amino acids in their free state, and are used frequently within the fields of molecular modeling, structural bioinformatics
Structural bioinformatics
Structural bioinformatics is the branch of bioinformatics which is related to the analysis and prediction of the three-dimensional structure of biological macromolecules such as proteins, RNA, and DNA...
, and computational biology
Computational biology
Computational biology involves the development and application of data-analytical and theoretical methods, mathematical modeling and computational simulation techniques to the study of biological, behavioral, and social systems...
.
Amino acid pKa values
pKa valuesAcid dissociation constant
An acid dissociation constant, Ka, is a quantitative measure of the strength of an acid in solution. It is the equilibrium constant for a chemical reaction known as dissociation in the context of acid-base reactions...
of amino acid side chain
Side chain
In organic chemistry and biochemistry, a side chain is a chemical group that is attached to a core part of the molecule called "main chain" or backbone. The placeholder R is often used as a generic placeholder for alkyl group side chains in chemical structure diagrams. To indicate other non-carbon...
s play an important role in defining the pH-dependent characteristics of a protein. The pH-dependence of the activity displayed by enzyme
Enzyme
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions. In enzymatic reactions, the molecules at the beginning of the process, called substrates, are converted into different molecules, called products. Almost all chemical reactions in a biological cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates...
s and the pH-dependence of protein stability, for example, are properties that are determined by the pKa values of amino acid side chains.
The pKa values of an amino acid side chain in solution is typically inferred from the pKa values of model compounds (compounds that are similar to the side chains of amino acids). (See Amino acid
Amino acid
Amino acids are molecules containing an amine group, a carboxylic acid group and a side-chain that varies between different amino acids. The key elements of an amino acid are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen...
for the pKa values of all amino acid side chains inferred in such a way.) The table below lists the model pKa values that are normally used in a protein pKa calculation.
| Amino Acid | pKa |
|---|---|
| Asp (D) | 3.9 |
| Glu (E) | 4.3 |
| Arg (R) | 12.0 |
| Lys (K) | 10.5 |
| His (H) | 6.08 |
| Cys (C) | 8.28 (-SH) |
| Tyr (Y) | 10.1 |
The effect of the protein environment
When a protein folds, the titratable amino acids in the protein are transferred from a solution-like environment to an environment determined by the 3-dimensional structure of the protein. For example, in an unfolded protein an aspartic acid typically is in an environment which exposes the titratable side chain to water. When the protein folds the aspartic acid could find itself buried deep in the protein interior with no exposure to solvent.Furthermore, in the folded protein the aspartic acid will be closer to other titratable groups in the protein and will also interact with permanent charges (e.g. ions) and dipoles in the protein.
All of these effects alter the pKa value of the amino acid side chain, and pKa calculation methods generally calculate the effect of the protein environment on the model pKa value of an amino acid side chain.
Typically the effects of the protein environment on the amino acid pKa value are divided into pH-independent effects and pH-dependent effects. The pH-independent effects (desolvation, interactions with permanent charges and dipoles) are added to the model pKa value to give the intrinsic pKa value. The pH-dependent effects cannot be added in the same straight-forward way and have to be accounted for using Boltzmann summation, Tanford-Roxby iterations or other methods.
The interplay of the intrinsic pKa values of a system with the electrostatic interaction energies between titratable groups can produce quite spectacular effects such as non-Henderson-Hasselbalch titration curve
Titration curve
Titrations are often recorded on titration curves, whose compositions are generally identical: the independent variable is the volume of the titrant, while the dependent variable is the pH of the solution...
s and even back-titration effects . pKaTool provides an easy interactive and instructive way of playing around with these effects.
The image below shows a theoretical system consisting of three acidic residues. One group is displaying a back-titration event (blue group).

pKa calculation methods
Several software packages and webserver are available for the calculation of protein pKa values. See links below or this tableUsing the Poisson-Boltzmann equation
Some methods are based on solutions to the Poisson-Boltzmann equationPoisson-Boltzmann equation
The Poisson–Boltzmann equation is a differential equation that describes electrostatic interactions between molecules in ionic solutions. It is the mathematical base for the Gouy–Chapman double layer theory; first proposed by Gouy in 1910 and complemented by Chapman in 1913...
(PBE), often referred to as FDPB-based methods (FDPB is for "finite difference
Finite difference
A finite difference is a mathematical expression of the form f − f. If a finite difference is divided by b − a, one gets a difference quotient...
Poisson-Boltzmann"). The PBE is a modification of Poisson's equation
Poisson's equation
In mathematics, Poisson's equation is a partial differential equation of elliptic type with broad utility in electrostatics, mechanical engineering and theoretical physics...
that incorporates a description of the effect of solvent ions on the electrostatic field around a molecule.
The H++ web server, the pKD webserver, MCCE and Karlsberg+ use the FDPB method to compute pKa values of amino acid side chains.
FDPB-based methods calculate the change in the pKa value of an amino acid side chain when that side chain is moved from a hypothetical fully solvated state to its position in the protein. To perform such a calculation, one needs theoretical methods that can calculate the effect of the protein interior on a pKa value, and knowledge of the pKa values of amino acid side chains in their fully solvated states.
Empirical methods
A set of empirical rules relating the protein structure to the pKa values of ionizable residues have been developed by Li, Robertson, and Jensen. These rules form the basis for the web-accessible program called PROPKA for rapid predictions of pKa values.Molecular dynamics (MD)-based methods
Molecular dynamics methods of calculating pKa values involve computationally measuring the free energy difference between the protonated and deprotonated forms of the molecule. This free energy difference is measured using methods such as free-energy perturbation, thermodynamic integration and the Bennett acceptance ratioBennett acceptance ratio
The Bennett acceptance ratio method is an algorithm for estimating the difference in free energy between two systems .It was suggested by Charles H. Bennett in 1976....
.
Molecular dynamics is typically a much more computationally expensive way to predict pKa's than using the Poisson-Boltzmann equation
Poisson-Boltzmann equation
The Poisson–Boltzmann equation is a differential equation that describes electrostatic interactions between molecules in ionic solutions. It is the mathematical base for the Gouy–Chapman double layer theory; first proposed by Gouy in 1910 and complemented by Chapman in 1913...
. Currently used molecular force fields do not take polarizability into account, which could be an important property for protonation energies.
Using titration curves to determine pKa values
The pH value where the titratable group is half-protonated is equal to the pKa if the titration curve follows the Henderson-Hasselbalch equationHenderson-Hasselbalch equation
In chemistry, the Henderson–Hasselbalch equation describes the derivation of pH as a measure of acidity in biological and chemical systems...
. Most pKa calculation methods silently assume that all titration curves are Henderson-Hasselbalch shaped, and pKa values in pKa calculation programs are therefore often determined in this way.
Software For Protein pKa Calculations
- AccelrysPKA Accelrys CHARMm based pKa calculation
- H++ Poisson-Boltzmann based pKa calculations
- MCCE Multi-Conformation Continuum Electrostatics
- Karlsberg+ pKa computation with multiple pH adapted conformations.
- pKD server pKa calculations and pKa value re-design
- PROPKA Empirical calculation of pKa values
Analysis and teaching software
- pKaTool interactive graphical tool for analysing systems of titratable groups
- H++ webserver

