
Protein-Npi-phosphohistidine-sugar phosphotransferase
Encyclopedia
In enzymology, a protein-Npi-phosphohistidine-sugar phosphotransferase is an enzyme
that catalyzes
the chemical reaction
Thus, the two substrates
of this enzyme are protein Npi-phospho-L-histidine and sugar
, whereas its two products
are protein histidine and sugar phosphate.
This enzyme belongs to the family of transferase
s, specifically those transferring phosphorus-containing groups (phosphotransferase
s) with an alcohol group as acceptor. The systematic name of this enzyme class is protein-Npi-phosphohistidine:sugar Npi-phosphotransferase. Other names in common use include glucose permease, PTS permease, phosphotransferase, phosphohistidinoprotein-hexose, enzyme IIl4ac, gene glC proteins, gene bglC RNA formation factors, PEP-dependent phosphotransferase enzyme II, PEP-sugar phosphotransferase enzyme II, phosphoenolpyruvate-sugar phosphotransferase enzyme II, phosphohistidinoprotein-hexose phosphotransferase, phosphohistidinoprotein-hexose phosphoribosyltransferase, phosphoprotein factor-hexose phosophotransferase, protein, specific or class, gene bglC, ribonucleic acid formation factor, gene glC, sucrose phosphotransferase system II, and protein-Npi-phosphohistidine:sugar N-pros-phosphotransferase. This enzyme participates in 7 metabolic pathways
: glycolysis / gluconeogenesis, fructose and mannose metabolism, galactose metabolism, ascorbate and aldarate metabolism, starch and sucrose metabolism, aminosugars metabolism, and phosphotransferase system (pts).
have been solved for this class of enzymes, with PDB
accession codes , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , and .
Enzyme
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions. In enzymatic reactions, the molecules at the beginning of the process, called substrates, are converted into different molecules, called products. Almost all chemical reactions in a biological cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates...
that catalyzes
Catalysis
Catalysis is the change in rate of a chemical reaction due to the participation of a substance called a catalyst. Unlike other reagents that participate in the chemical reaction, a catalyst is not consumed by the reaction itself. A catalyst may participate in multiple chemical transformations....
the chemical reaction
Chemical reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Chemical reactions can be either spontaneous, requiring no input of energy, or non-spontaneous, typically following the input of some type of energy, such as heat, light or electricity...
- protein Npi-phospho-L-histidine + sugar
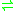 protein histidine + sugar phosphate
protein histidine + sugar phosphate
Thus, the two substrates
Substrate (biochemistry)
In biochemistry, a substrate is a molecule upon which an enzyme acts. Enzymes catalyze chemical reactions involving the substrate. In the case of a single substrate, the substrate binds with the enzyme active site, and an enzyme-substrate complex is formed. The substrate is transformed into one or...
of this enzyme are protein Npi-phospho-L-histidine and sugar
Sugar
Sugar is a class of edible crystalline carbohydrates, mainly sucrose, lactose, and fructose, characterized by a sweet flavor.Sucrose in its refined form primarily comes from sugar cane and sugar beet...
, whereas its two products
Product (chemistry)
Product are formed during chemical reactions as reagents are consumed. Products have lower energy than the reagents and are produced during the reaction according to the second law of thermodynamics. The released energy comes from changes in chemical bonds between atoms in reagent molecules and...
are protein histidine and sugar phosphate.
This enzyme belongs to the family of transferase
Transferase
In biochemistry, a transferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of a functional group from one molecule to another . For example, an enzyme that catalyzed this reaction would be a transferase:In this example, A would be the donor, and B would be the acceptor...
s, specifically those transferring phosphorus-containing groups (phosphotransferase
Phosphotransferase
Phosphotransferases are a category of enzymes that catalyze phosphorylation reactions. The general form of the reactions they catalyze is: A—P + B ⇔ B—P + A...
s) with an alcohol group as acceptor. The systematic name of this enzyme class is protein-Npi-phosphohistidine:sugar Npi-phosphotransferase. Other names in common use include glucose permease, PTS permease, phosphotransferase, phosphohistidinoprotein-hexose, enzyme IIl4ac, gene glC proteins, gene bglC RNA formation factors, PEP-dependent phosphotransferase enzyme II, PEP-sugar phosphotransferase enzyme II, phosphoenolpyruvate-sugar phosphotransferase enzyme II, phosphohistidinoprotein-hexose phosphotransferase, phosphohistidinoprotein-hexose phosphoribosyltransferase, phosphoprotein factor-hexose phosophotransferase, protein, specific or class, gene bglC, ribonucleic acid formation factor, gene glC, sucrose phosphotransferase system II, and protein-Npi-phosphohistidine:sugar N-pros-phosphotransferase. This enzyme participates in 7 metabolic pathways
Metabolism
Metabolism is the set of chemical reactions that happen in the cells of living organisms to sustain life. These processes allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. Metabolism is usually divided into two categories...
: glycolysis / gluconeogenesis, fructose and mannose metabolism, galactose metabolism, ascorbate and aldarate metabolism, starch and sucrose metabolism, aminosugars metabolism, and phosphotransferase system (pts).
Structural studies
As of late 2007, 29 structuresTertiary structure
In biochemistry and molecular biology, the tertiary structure of a protein or any other macromolecule is its three-dimensional structure, as defined by the atomic coordinates.-Relationship to primary structure:...
have been solved for this class of enzymes, with PDB
Protein Data Bank
The Protein Data Bank is a repository for the 3-D structural data of large biological molecules, such as proteins and nucleic acids....
accession codes , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , and .

