Prolidase deficiency
Encyclopedia
Prolidase deficiency is a rare autosomal
recessive
inborn error of metabolism
.
Although metabolism of the amino acid
proline
is affected by the enzyme
prolidase, this disorder is not to be confused with hyperprolinemia
, which involves different enzymatyic pathways related to proline metabolism.
called prolidase, affected individuals may also excrete large amounts of iminodipeptides in the urine, a condition called iminodipeptiduria.
 Mutations in the PEPD
Mutations in the PEPD
gene on chromosome
19q13.11
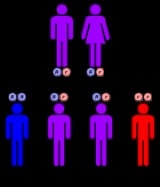
have been observed to cause prolidase deficiency. The disorder is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner. This means the defective gene responsible for the disorder is located on an autosome
(chromosome 19 is an autosome), and two copies of the defective gene (one inherited from each parent) are required in order to be born with the disorder. The parents of an individual with an autosomal recessive disorder both carry
one copy of the defective gene, but usually do not experience any signs or symptoms of the disorder.
Autosome
An autosome is a chromosome that is not a sex chromosome, or allosome; that is to say, there is an equal number of copies of the chromosome in males and females. For example, in humans, there are 22 pairs of autosomes. In addition to autosomes, there are sex chromosomes, to be specific: X and Y...
recessive
inborn error of metabolism
Inborn error of metabolism
Inborn errors of metabolism comprise a large class of genetic diseases involving disorders of metabolism. The majority are due to defects of single genes that code for enzymes that facilitate conversion of various substances into others...
.
Although metabolism of the amino acid
Amino acid
Amino acids are molecules containing an amine group, a carboxylic acid group and a side-chain that varies between different amino acids. The key elements of an amino acid are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen...
proline
Proline
Proline is an α-amino acid, one of the twenty DNA-encoded amino acids. Its codons are CCU, CCC, CCA, and CCG. It is not an essential amino acid, which means that the human body can synthesize it. It is unique among the 20 protein-forming amino acids in that the α-amino group is secondary...
is affected by the enzyme
Enzyme
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions. In enzymatic reactions, the molecules at the beginning of the process, called substrates, are converted into different molecules, called products. Almost all chemical reactions in a biological cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates...
prolidase, this disorder is not to be confused with hyperprolinemia
Hyperprolinemia
Hyperprolinemia, also referred to as prolinemia or prolinuria, is a condition which occurs when the amino acid proline is not broken down properly by the enzymes proline oxidase or pyrroline-5-carboxylate dehydrogense, causing a build up of proline in the body.-Hyperprolinemia type I:It is...
, which involves different enzymatyic pathways related to proline metabolism.
Characteristics
Prolidase deficiency is characterized by severe skin ulcers, facial abnormalities, chronic joint dislocations, bacterial infections, and mental retardation. Asymptomatic individuals with the disorder, though rare, have also been recognized.. Due to this deficiency of the exopeptidaseExopeptidase
An exopeptidase is an enzyme produced in the pancreas that catalyses the removal of an amino acid from the end of a polypeptide chain. Exopeptidase cleaves the end of a polypeptide chain....
called prolidase, affected individuals may also excrete large amounts of iminodipeptides in the urine, a condition called iminodipeptiduria.
Cause and Genetics

PEPD
Xaa-Pro dipeptidase, also known as prolidase, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PEPD gene.-Further reading:...
gene on chromosome
Chromosome
A chromosome is an organized structure of DNA and protein found in cells. It is a single piece of coiled DNA containing many genes, regulatory elements and other nucleotide sequences. Chromosomes also contain DNA-bound proteins, which serve to package the DNA and control its functions.Chromosomes...
19q13.11
Chromosome 19 (human)
125px|rightChromosome 19 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. People normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 19 spans more than 63 million base pairs and represents between 2 and 2.5 percent of the total DNA in cells.Identifying genes on each chromosome is an active...
have been observed to cause prolidase deficiency. The disorder is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner. This means the defective gene responsible for the disorder is located on an autosome
Autosome
An autosome is a chromosome that is not a sex chromosome, or allosome; that is to say, there is an equal number of copies of the chromosome in males and females. For example, in humans, there are 22 pairs of autosomes. In addition to autosomes, there are sex chromosomes, to be specific: X and Y...
(chromosome 19 is an autosome), and two copies of the defective gene (one inherited from each parent) are required in order to be born with the disorder. The parents of an individual with an autosomal recessive disorder both carry
Genetic carrier
A genetic carrier , is a person or other organism that has inherited a genetic trait or mutation, but who does not display that trait or show symptoms of the disease. They are, however, able to pass the gene onto their offspring, who may then express the gene...
one copy of the defective gene, but usually do not experience any signs or symptoms of the disorder.
External links
- Prolidase deficiency on OrphaNetOrphanetOrphanet is a European website providing information about orphan drugs and rare diseases. It contains content both for physicians and for patients. Its administrative office is in Paris. The organisation also publishes the open-access online journal Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases.-External...

