
Project Delivery Method
Encyclopedia
A project delivery method is a system used by an agency or owner for organizing and financing design, construction, operations, and maintenance services for a structure
or facility by entering into legal agreements with one or more entities or parties.
Design-Bid-Build
(DBB) or Design-Award-Build (DAB)
DBB with Construction Management
(DBB with CM)
Design-Build
(DB) or Design-Construct
Design-Build-Operate-Maintain (DBOM)
Build-Operate-Transfer (BOT)
Integrated Project Delivery
(IPD)
s of centuries past acted both as designers and constructors for both public and private clients. In the United States
, Zane's Post Road in Ohio
and the IRT
in New York City
were both originally developed under more integrated delivery methods, as were most infrastructure projects until 1933. Integrated Project Delivery offers a new delivery method to remove considerable waste from the construction process while improving quality and a return to more collaborative methods from the past.
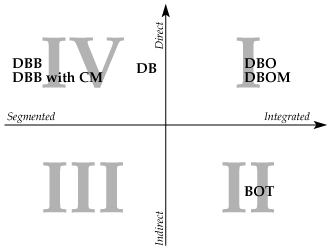 There are two key variables which account for the bulk of the variation between delivery methods:
There are two key variables which account for the bulk of the variation between delivery methods:
When the various service providers are segmented, the owner has the most amount of control, but this control is costly and doesn't give each provider an incentive to optimize its contribution for the next service. When there is tight integration amongst providers, each step of the delivery is undertaken with future activities in mind, resulting in cost savings, but limiting the owner's influence throughout the project.
The owner's direct financing of a project simply means that the owner directly pays the providers for their services. In the case of a facility with a consistent revenue stream, indirect financing becomes possible: rather than be paid by the owner, the providers are paid with the revenue collected from the facility's operation.
Indirect financing risks being mistaken for privatization
. Though the providers do have a concession to operate and collect revenue from a facility that they built and financed, the structure itself remains the property of the owner (usually a government agency in the case of public infrastructure).
Structure
Structure is a fundamental, tangible or intangible notion referring to the recognition, observation, nature, and permanence of patterns and relationships of entities. This notion may itself be an object, such as a built structure, or an attribute, such as the structure of society...
or facility by entering into legal agreements with one or more entities or parties.
Types of Project Delivery Methods
Common project delivery methods include:Design-Bid-Build
Design-Bid-Build
Design–bid–build , also known as Design–tender and traditional method, is a project delivery method in which the agency or owner contracts with separate entities for each the design and construction of a project.Design–bid–build is the traditional method for project...
(DBB) or Design-Award-Build (DAB)
- An owner develops contract documents with an architectArchitectAn architect is a person trained in the planning, design and oversight of the construction of buildings. To practice architecture means to offer or render services in connection with the design and construction of a building, or group of buildings and the space within the site surrounding the...
or engineer consisting of a set of blueprintBlueprintA blueprint is a type of paper-based reproduction usually of a technical drawing, documenting an architecture or an engineering design. More generally, the term "blueprint" has come to be used to refer to any detailed plan....
s and a detailed specification. Bids are solicited from contractorIndependent contractorAn independent contractor is a natural person, business, or corporation that provides goods or services to another entity under terms specified in a contract or within a verbal agreement. Unlike an employee, an independent contractor does not work regularly for an employer but works as and when...
s based on these documents; a contract is then awarded to the lowest responsive and responsible bidder.
DBB with Construction Management
Construction management
Construction Project Management is the overall planning, coordination and control of a project from inception to completion aimed at meeting a client’s requirements in order to produce a functionally and financially viable project that will be complete mingement is project management that applies...
(DBB with CM)
- With partially completed contract documents, an owner will hire a construction manager to act as an agent. As substantial portions of the documents are completed, the construction manager will solicit bids from suitable subcontractors. This allows construction to proceed more quickly and allows the owner to share some of the risk inherent in the project with the construction manager.
Design-Build
Design-Build
Design-build is a project delivery system used in the construction industry. It is a method to deliver a project in which the design and construction services are contracted by a single entity known as the design–builder or design–build contractor...
(DB) or Design-Construct
- An owner develops a conceptual plan for a project, then solicits bids from joint ventureJoint ventureA joint venture is a business agreement in which parties agree to develop, for a finite time, a new entity and new assets by contributing equity. They exercise control over the enterprise and consequently share revenues, expenses and assets...
s of architects and/or engineer and builders for the design and construction of the project.
Design-Build-Operate-Maintain (DBOM)
- DBOM takes DB one step further by including the operations and maintenance of the completed project in the same original contract.
Build-Operate-Transfer (BOT)
- BOT represents complete integration of the project delivery: the same contract governs the design, construction, operations, maintenance and financing of the project. After some concessionaryConcession (contract)A concession is a business operated under a contract or license associated with a degree of exclusivity in business within a certain geographical area. For example, sports arenas or public parks may have concession stands. Many department stores contain numerous concessions operated by other...
period, the facility is transferred back to the owner.
Integrated Project Delivery
Integrated Project Delivery
Integrated project delivery , is a collaborative alliance of people, systems, business structures and practices into a process that harnesses the talents and insights of all participants to optimize project results, increase value to the owner, reduce waste, and maximize efficiency through all...
(IPD)
- A project delivery method in which the interests of the primary team members are aligned in such a way that the members can be integrated for optimal project performance resulting in a collaborative, value-based process delivering high-outcome results to the entire building team.
Trends in Delivery Method Prevalence
Though DBB is presently used for most private projects and the majority of public projects, it has not historically been the predominant delivery method of choice. The master builderMaster Builder
Master Builder can refer to:* Master builder, also "master mason", a central figure leading construction projects in pre-modern times .* The Master Builder, a play by Henrik Ibsen....
s of centuries past acted both as designers and constructors for both public and private clients. In the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
, Zane's Post Road in Ohio
Ohio
Ohio is a Midwestern state in the United States. The 34th largest state by area in the U.S.,it is the 7th‑most populous with over 11.5 million residents, containing several major American cities and seven metropolitan areas with populations of 500,000 or more.The state's capital is Columbus...
and the IRT
Interborough Rapid Transit Company
The Interborough Rapid Transit Company was the private operator of the original underground New York City Subway line that opened in 1904, as well as earlier elevated railways and additional rapid transit lines in New York City. The IRT was purchased by the City in June 1940...
in New York City
New York City
New York is the most populous city in the United States and the center of the New York Metropolitan Area, one of the most populous metropolitan areas in the world. New York exerts a significant impact upon global commerce, finance, media, art, fashion, research, technology, education, and...
were both originally developed under more integrated delivery methods, as were most infrastructure projects until 1933. Integrated Project Delivery offers a new delivery method to remove considerable waste from the construction process while improving quality and a return to more collaborative methods from the past.
Conceptual Differences between Delivery Methods

- The extent of the integration of the various service providers.
- The extent to which the owner is directly financing the project.
When the various service providers are segmented, the owner has the most amount of control, but this control is costly and doesn't give each provider an incentive to optimize its contribution for the next service. When there is tight integration amongst providers, each step of the delivery is undertaken with future activities in mind, resulting in cost savings, but limiting the owner's influence throughout the project.
The owner's direct financing of a project simply means that the owner directly pays the providers for their services. In the case of a facility with a consistent revenue stream, indirect financing becomes possible: rather than be paid by the owner, the providers are paid with the revenue collected from the facility's operation.
Indirect financing risks being mistaken for privatization
Privatization
Privatization is the incidence or process of transferring ownership of a business, enterprise, agency or public service from the public sector to the private sector or to private non-profit organizations...
. Though the providers do have a concession to operate and collect revenue from a facility that they built and financed, the structure itself remains the property of the owner (usually a government agency in the case of public infrastructure).

