
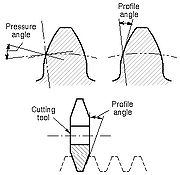
Profile angle
Encyclopedia
Gear
A gear is a rotating machine part having cut teeth, or cogs, which mesh with another toothed part in order to transmit torque. Two or more gears working in tandem are called a transmission and can produce a mechanical advantage through a gear ratio and thus may be considered a simple machine....
is the angle at a specified pitch point between a line tangent to a tooth surface and the line normal to the pitch surface (which is a radial line of a pitch circle). This definition is applicable to every type of gear for which a pitch surface can be defined. The profile angle gives the direction of the tangent to a tooth profile.
In spur gears and straight bevel gears, tooth profiles are considered only in a transverse plane, and the general terms profile angle and pressure angle are customarily used rather than transverse profile angle and transverse pressure angle. In helical teeth, the profiles may be considered in different planes, and in specifications it is essential to use terms that indicate the direction of the plane in which the profile angle or the pressure angle lies, such as transverse profile angle, normal pressure angle, axial profile angle.
Standard profile angles
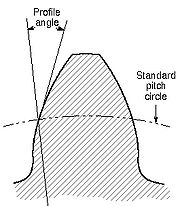
Standard profile angles are established in connection with standard proportions of gear teeth and standard gear cutting tools. Involute gear
Involute gear
The involute gear profile is the most commonly used system for gearing today. In an involute gear, the profiles of the teeth are involutes of a circle. In involute gear design contact between a pair of gear teeth occurs...
s operate together correctly after a change of center distance, and gears designed for a different center distance can be generated correctly by standard tools. A change of center distance is accomplished by changes in operating values for pitch diameter, circular pitch, diametral pitch, pressure angle, and tooth thicknesses or backlash. The same involute gear may be used under conditions that change its operating pitch diameter and pressure angle. Unless there is a good reason for doing otherwise, it is practical to consider that the pitch and the profile angle of a single gear correspond to the pitch and the profile angle of the hob or cutter used to generate its teeth.
Transverse profile angles
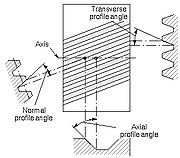
Normal profile angles
Normal pressure angle and normal profile angle are the pressure and profile angles in a normalSurface normal
A surface normal, or simply normal, to a flat surface is a vector that is perpendicular to that surface. A normal to a non-flat surface at a point P on the surface is a vector perpendicular to the tangent plane to that surface at P. The word "normal" is also used as an adjective: a line normal to a...
plane of a helical or a spiral tooth. In a spiral bevel gear
Spiral bevel gear
A spiral bevel gear is a bevel gear with helical teeth. The main application of this is in a vehicle differential, where the direction of drive from the drive shaft must be turned 90 degrees to drive the wheels...
, unless otherwise specified, profile angle means normal profile angle at the mean cone distance.

