
Primum Mobile
Encyclopedia
In medieval and Renaissance astronomy, the Primum Mobile, or "first moved," was the outermost moving sphere in the geocentric model
of the universe
. The primum mobile was thought to be responsible for the apparent daily movement of the heavens around the Earth, producing the east-to-west rising and setting of the sun and stars. This apparent motion is now known to be due to the rotation of the Earth on its polar axis—a concept that, though known since ancient times (generally ascribed to Aristarchus
), was not
widely accepted prior to Copernicus. Astronomers believed that the seven naked-eye planets (including the Moon and the Sun) were carried around the spherical Earth
on invisible orbs. Beyond them was the sphere of fixed star
s, the Primum Mobile, and the Empyrean
.
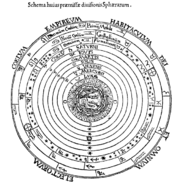 The total number of celestial spheres
The total number of celestial spheres
was not fixed. In this 16th-century illustration, the firmament
(sphere of fixed stars) is eighth, a "crystalline" sphere (posited to account for the reference to "waters . . . above the firmament" in Genesis 1:7) is ninth, and the Primum Mobile is tenth. Outside all is the Empyrean, the "habitation of God and all the elect."
Geocentric model
In astronomy, the geocentric model , is the superseded theory that the Earth is the center of the universe, and that all other objects orbit around it. This geocentric model served as the predominant cosmological system in many ancient civilizations such as ancient Greece...
of the universe
Universe
The Universe is commonly defined as the totality of everything that exists, including all matter and energy, the planets, stars, galaxies, and the contents of intergalactic space. Definitions and usage vary and similar terms include the cosmos, the world and nature...
. The primum mobile was thought to be responsible for the apparent daily movement of the heavens around the Earth, producing the east-to-west rising and setting of the sun and stars. This apparent motion is now known to be due to the rotation of the Earth on its polar axis—a concept that, though known since ancient times (generally ascribed to Aristarchus
Aristarchus
-People:* Aristarchus of Samos , Greek astronomer and mathematician* Aristarchus of Samothrace , Greek grammarian* Aristarchus of Tegea , Greek writer* Aristarchus of Thessalonica , Eastern saint...
), was not
widely accepted prior to Copernicus. Astronomers believed that the seven naked-eye planets (including the Moon and the Sun) were carried around the spherical Earth
Spherical Earth
The concept of a spherical Earth dates back to ancient Greek philosophy from around the 6th century BC, but remained a matter of philosophical speculation until the 3rd century BC when Hellenistic astronomy established the spherical shape of the earth as a physical given...
on invisible orbs. Beyond them was the sphere of fixed star
Star
A star is a massive, luminous sphere of plasma held together by gravity. At the end of its lifetime, a star can also contain a proportion of degenerate matter. The nearest star to Earth is the Sun, which is the source of most of the energy on Earth...
s, the Primum Mobile, and the Empyrean
Empyrean
Empyrean, from the Medieval Latin empyreus, an adaptation of the Ancient Greek ἔμπυρος empyrus "in or on the fire ", properly Empyrean Heaven, is the place in the highest heaven, which in ancient cosmologies was supposed to be occupied by the element of fire .-Use in literature:The Empyrean was...
.

Celestial spheres
The celestial spheres, or celestial orbs, were the fundamental entities of the cosmological models developed by Plato, Eudoxus, Aristotle, Ptolemy, Copernicus and others...
was not fixed. In this 16th-century illustration, the firmament
Firmament
The firmament is the vault or expanse of the sky. According to Genesis, God created the firmament to separate the oceans from other waters above.-Etymology:...
(sphere of fixed stars) is eighth, a "crystalline" sphere (posited to account for the reference to "waters . . . above the firmament" in Genesis 1:7) is ninth, and the Primum Mobile is tenth. Outside all is the Empyrean, the "habitation of God and all the elect."

