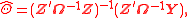Prais–Winsten estimation
Encyclopedia
In econometrics
, Prais–Winsten estimation is a procedure meant to take care of the serial correlation
of type AR(1) in a linear model
. It is a modification of Cochrane–Orcutt estimation in the sense that it does not lose the first observation and leads to more efficiency
as a result.
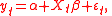
where is the time series
is the time series
of interest at time t,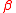 is a vector of coefficients,
is a vector of coefficients,  is a matrix of explanatory variables, and
is a matrix of explanatory variables, and 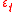 is the error term. The error term can be serially correlated over time:
is the error term. The error term can be serially correlated over time: 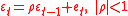 and
and  is a white noise. In addition to the Cochrane–Orcutt procedure transformation, which is
is a white noise. In addition to the Cochrane–Orcutt procedure transformation, which is
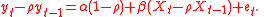
for t=2,3,...,T, Prais-Winsten procedure makes a reasonable transformation for t=1 in the following form
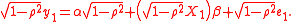
Then the usual least squares
estimation is done.
Now is easy to see that the variance-covariance, , of the model is
, of the model is
Econometrics
Econometrics has been defined as "the application of mathematics and statistical methods to economic data" and described as the branch of economics "that aims to give empirical content to economic relations." More precisely, it is "the quantitative analysis of actual economic phenomena based on...
, Prais–Winsten estimation is a procedure meant to take care of the serial correlation
Autocorrelation
Autocorrelation is the cross-correlation of a signal with itself. Informally, it is the similarity between observations as a function of the time separation between them...
of type AR(1) in a linear model
Linear model
In statistics, the term linear model is used in different ways according to the context. The most common occurrence is in connection with regression models and the term is often taken as synonymous with linear regression model. However the term is also used in time series analysis with a different...
. It is a modification of Cochrane–Orcutt estimation in the sense that it does not lose the first observation and leads to more efficiency
Efficiency (statistics)
In statistics, an efficient estimator is an estimator that estimates the quantity of interest in some “best possible” manner. The notion of “best possible” relies upon the choice of a particular loss function — the function which quantifies the relative degree of undesirability of estimation errors...
as a result.
Theory
Consider the model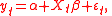
where
 is the time series
is the time seriesTime series
In statistics, signal processing, econometrics and mathematical finance, a time series is a sequence of data points, measured typically at successive times spaced at uniform time intervals. Examples of time series are the daily closing value of the Dow Jones index or the annual flow volume of the...
of interest at time t,
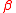 is a vector of coefficients,
is a vector of coefficients,  is a matrix of explanatory variables, and
is a matrix of explanatory variables, and 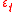 is the error term. The error term can be serially correlated over time:
is the error term. The error term can be serially correlated over time:  and
and  is a white noise. In addition to the Cochrane–Orcutt procedure transformation, which is
is a white noise. In addition to the Cochrane–Orcutt procedure transformation, which is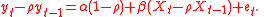
for t=2,3,...,T, Prais-Winsten procedure makes a reasonable transformation for t=1 in the following form
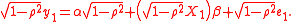
Then the usual least squares
Linear least squares
In statistics and mathematics, linear least squares is an approach to fitting a mathematical or statistical model to data in cases where the idealized value provided by the model for any data point is expressed linearly in terms of the unknown parameters of the model...
estimation is done.
Estimation procedure
To do the estimation in a compact way it is directive to look at the auto-covariance function of the error term considered in the model above:Now is easy to see that the variance-covariance,
 , of the model is
, of the model is-

Now having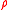 (or an estimate of it), we see that,
(or an estimate of it), we see that,
where is a matrix of observations on the independent variable (Xt, t = 1, 2, ..., T) including a vector of ones,
is a matrix of observations on the independent variable (Xt, t = 1, 2, ..., T) including a vector of ones,  is a vector stacking the observations on the dependent variable (Xt, t = 1, 2, ..., T) and
is a vector stacking the observations on the dependent variable (Xt, t = 1, 2, ..., T) and  includes the model parameters.
includes the model parameters.
Note
To see why the initial observation assumption stated by Prais-Winsten (1954) is reasonable, considering the mechanics of general least square estimation procedure sketched above is helpful. The inverse of can be decomposed as
can be decomposed as  with
with
-

A pre-multiplication of model in a matrix notation with this matrix gives the transformed model of Prais-Winsten.
Restrictions
The error termErrors and residuals in statisticsIn statistics and optimization, statistical errors and residuals are two closely related and easily confused measures of the deviation of a sample from its "theoretical value"...
is still restricted to be of an AR(1) type. If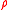 is not known, a recursive procedure maybe used to make the estimation feasible. See Cochrane–Orcutt estimation.
is not known, a recursive procedure maybe used to make the estimation feasible. See Cochrane–Orcutt estimation.
References
http://cowles.econ.yale.edu/P/ccdp/st/s-0383.pdf- Wooldridge, J. (2008) Introductory Econometrics: A Modern Approach, 4th Edition, South-Western Pub. ISBN 0324660545 (p. 435)
-