
Power gain
Encyclopedia
The power gain of an electrical network
is the ratio of an output power
to an input power. Unlike other signal gain
s, such as voltage
and current
gain, "power gain" may be ambiguous as the meaning of terms "input power" and "output power" is not always clear. Three important power gains are operating power gain, transducer power gain and available power gain. Note that all these definitions of power gains employ the use of average (as oppose of instantaneous) power quantities and therefore the term "average" is often suppressed, which can be confusing at occasions.
, GP, is defined as:
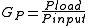
where
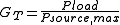
where
In terms of y-parameters this definition can be used to derive:
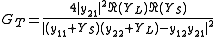
where
This result can be generalized to z, h, g and y-parameters as:
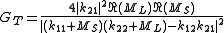
where
Psource,max may only be obtained from the source when the load impedance
connected to it (i.e. the equivalent input impedance
of the two-port network) is the complex conjugate
of the source impedance, a consequence of the maximum power theorem
.
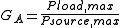
where
Similarly Pload,max may only obtained when the load impedance is the complex conjugate of the output impedance
of the network.
Electrical network
An electrical network is an interconnection of electrical elements such as resistors, inductors, capacitors, transmission lines, voltage sources, current sources and switches. An electrical circuit is a special type of network, one that has a closed loop giving a return path for the current...
is the ratio of an output power
Power (physics)
In physics, power is the rate at which energy is transferred, used, or transformed. For example, the rate at which a light bulb transforms electrical energy into heat and light is measured in watts—the more wattage, the more power, or equivalently the more electrical energy is used per unit...
to an input power. Unlike other signal gain
Gain
In electronics, gain is a measure of the ability of a circuit to increase the power or amplitude of a signal from the input to the output. It is usually defined as the mean ratio of the signal output of a system to the signal input of the same system. It may also be defined on a logarithmic scale,...
s, such as voltage
Voltage
Voltage, otherwise known as electrical potential difference or electric tension is the difference in electric potential between two points — or the difference in electric potential energy per unit charge between two points...
and current
Electric current
Electric current is a flow of electric charge through a medium.This charge is typically carried by moving electrons in a conductor such as wire...
gain, "power gain" may be ambiguous as the meaning of terms "input power" and "output power" is not always clear. Three important power gains are operating power gain, transducer power gain and available power gain. Note that all these definitions of power gains employ the use of average (as oppose of instantaneous) power quantities and therefore the term "average" is often suppressed, which can be confusing at occasions.
Operating power gain
The operating power gain of a two-port networkTwo-port network
A two-port network is an electrical circuit or device with two pairs of terminals connected together internally by an electrical network...
, GP, is defined as:
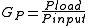
where
- Pload is the maximum power delivered to the load
- Pinput is the average power entering the network
Transducer power gain
The transducer power gain of a two-port network, GT, is defined as: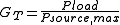
where
- Pload is the average power delivered to the load
- Psource,max is the maximum available average power at the source
In terms of y-parameters this definition can be used to derive:
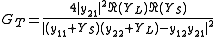
where
- YL is the load admittance
- YS is the source admittance
This result can be generalized to z, h, g and y-parameters as:
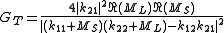
where
- kxx is a z, h, g or y-parameter
- ML is the load value in the corresponding parameter set
- MS is the source value in the corresponding parameter set
Psource,max may only be obtained from the source when the load impedance
Electrical impedance
Electrical impedance, or simply impedance, is the measure of the opposition that an electrical circuit presents to the passage of a current when a voltage is applied. In quantitative terms, it is the complex ratio of the voltage to the current in an alternating current circuit...
connected to it (i.e. the equivalent input impedance
Input impedance
The input impedance of an electrical network is the equivalent impedance "seen" by a power source connected to that network. If the source provides known voltage and current, such impedance can be calculated using Ohm's Law...
of the two-port network) is the complex conjugate
Complex conjugate
In mathematics, complex conjugates are a pair of complex numbers, both having the same real part, but with imaginary parts of equal magnitude and opposite signs...
of the source impedance, a consequence of the maximum power theorem
Maximum power theorem
In electrical engineering, the maximum power transfer theorem states that, to obtain maximum external power from a source with a finite internal resistance, the resistance of the load must be equal to the resistance of the source as viewed from the output terminals...
.
Available power gain
The available power gain of a two-port network, GA, is defined as: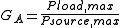
where
- Pload,max is the maximum available average power at the load
- Psource,max is the maximum power available from the source
Similarly Pload,max may only obtained when the load impedance is the complex conjugate of the output impedance
Output impedance
The output impedance, source impedance, or internal impedance of an electronic device is the opposition exhibited by its output terminals to an alternating current of a particular frequency as a result of resistance, inductance and capacitance...
of the network.

