Positive psychological capital
Encyclopedia
Positive Psychological Capital is defined as the positive and developmental state of an individual as characterized by high self-efficacy
, optimism
, hope
and resiliency
.
has been dealing mainly with treatment of mental illness. At the very end of the twentieth century a new approach in psychology has emerged: positive psychology
.
Positive psychology, the study of optimal human functioning, is an attempt to respond to the systematic bias inherent in psychology's historical emphasis on mental illness rather than on mental wellness (Seligman ,2002), mainly by focusing on two, forgotten but classical psychological goals:
Since Martin Seligman
, a former head of American Psychological Association
, chose positive psychology as the theme of his presidency term, more empirical research and theoretic development emerged in this field.
Two new branches of positive psychology are being implemented into the industrial-organizational world.
As opposed to positive psychology, organizational positive psychology focuses on situational characteristics that can be developed and improved through intervention in work place and proactive management techniques. Moreover it focuses only on measurable and improvable characteristics. Through POB theories, several concepts were identified including subjective happiness, optimism
, hope
, resiliency
and emotional intelligence
.
Through empirical research it was discovered that different constructs of POB are not conceptually identical. Rather, they differ in their measurement and their combination produces a higher structure. The implications and influences of this structure are bigger than the simple summary of its parts. The name of the construct is positive psychological capital or Psycap. Its components are hope
, self-efficacy
, optimism
and resiliency
.
Hope - Is defined as a positive motivational state where two basic elements - successful feeling of agency (or goal oriented determination) and pathways (or planning to achieve those goals) interact.
Self efficacy – Is defined as people's confidence in their ability to achieve a specific goal in a specific situation.
Optimism – was defined by Seligman by Attribution theory (Fritz Heider
, 1958). An Optimistic person is defined as one that makes "Internal" or "dispositional", fixed and global attributions for positive events and "External" or "situational", not fixed and specific attributions to negative events. Optimism in Psycap is thought as a realistic construct that regards what an employee can or cannot do, as such, optimism reinforces self efficacy and hope.
Resiliency – Is defined in Positive Psychology as a positive way of coping with danger or distress. In organizational aspect, it is defined as an ability to recuperate from stress, conflict, failure, change or increase in responsibility.
Research found that high Psycap employees performed better than low Psycap employees. This difference in performance can be explained by their Psychological constructs which manifest themselves in their cognitions and motivations. The influence on the employees performance is stronger while referring to Psycap than for each of its
Components, meaning, Psycap explains more than its components combined.
Psycap mediates between supportive climate and employee performance - Psycap
Psycap and positive supportive climate are necessary for human resources in order to achieve stable organizational growth. Supportive climate is defined as the total support that an employee receives from their coworkers, other departments and their supervisors which helps them with their job demands.
High Psycap Employees supports effective organizational change
Organizational change is defined as a lack of fit with the environment which intensifies as a result of a gap between the organizational goals and its present outcomes. The employees have the responsibility to adjust and behave according to the new strategy dictated by the management, mostly with fewer resources. During change, different aspects of employees’ Psycap is put to the test – they have to learn new ways of behavior and be confident to do so, recover from the crisis, be motivated to cope efficiently and to believe in a better future. Psycap and positive emotions are examples of how personal factors facilitate organizational change. Positive change is defined as every change that the organization undergoes for its own benefit and has more positive psychological and behavioral consequences than negative ones. The role of positive emotions is that they help workers cope with the organizational change by broadening their point of view, encourage open decision making and giving them essential vitality for their coping.
This interaction means that Psycap, through positive emotions, influences the worker’s attitudes and behavior, which in turn, influences the organizational change.
Psycap decreases absence from work
Psycap has interesting influences on absence from work. Few meta-analyses have shown a connection between personal and organizational climate factors to the level of absenteeism from work. Recently, however, research has shown that attitude variables like satisfaction and commitment cannot explain the significant variance in absenteeism. Psycap can give a new perspective to the understanding and coping with absenteeism. Research has shown that Psycap has a positive influence on levels of involuntary and voluntary absenteeism.
The basis of the interaction between Psycap and absenteeism lies in the already proven connection between the body and the soul and more specifically, a strong connection between stress and physiological factors. Workers who confront similar obstacles in their workplace will react differently according to their Psycap and therefore the influence of such obstacle on them will be different. The nature of workers with high Psycap will contribute to lower levels of sickness or to the ability to recover from sickness and get back to work afterwards, which will result in lower levels of involuntary absenteeism.
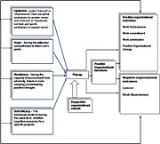
 The model
The model
On the left side of the model you can see the different dimensions of Psycap.
Psycap is influenced by organizational climate and influences several positive and negative outcomes in the organization.
This influence can be direct or mediated by positive feelings in the organization.
Different organizational phenomena have influence on the employee, specifically on the characteristics that assemble his Psycap. For example- while a high Psycap employee observes the good results of his performance, his Psycap grows even more due to the impact of the good performance on self efficacy and hope. From this example we can conclude that Bottom up processes have to do with Psycap. A worker gives feedback not only to himself but for the others observing him as well. Thus, his Psycap affect his surroundings cognitively and affectively ( By his performance outcomes ). For example: A worker which manifests behavior and feelings that show high Psycap and succeeds in his job, not only his Psycap will grow but also the Psycap of the ones around him.
Positive, as well as negative Psycap have a “contagious” aspect that influences groups and generates a Bottom-up process. The model also shows that every one of the four characteristics of Psycap has the possibility to influence organizational outcomes directly as shown widely in past research.
It should be mentioned that Psycap has developed mainly since 2005 and therefore all findings should be considered as preliminary and need further research.
Self-efficacy
Self-efficacy is a term used in psychology, roughly corresponding to a person's belief in their own competence.It has been defined as the belief that one is capable of performing in a certain manner to attain certain set of goals. It is believed that our personalized ideas of self-efficacy affect...
, optimism
Optimism
The Oxford English Dictionary defines optimism as having "hopefulness and confidence about the future or successful outcome of something; a tendency to take a favourable or hopeful view." The word is originally derived from the Latin optimum, meaning "best." Being optimistic, in the typical sense...
, hope
Hope
Hope is the emotional state which promotes the belief in a positive outcome related to events and circumstances in one's life. It is the "feeling that what is wanted can be had or that events will turn out for the best" or the act of "look[ing] forward to with desire and reasonable confidence" or...
and resiliency
Psychological resilience
Resilience in psychology refers to the idea of an individual's tendency to cope with stress and adversity. This coping may result in the individual “bouncing back” to a previous state of normal functioning, or using the experience of exposure to adversity to produce a “steeling effect” and function...
.
Introduction
For decades psychologyPsychology
Psychology is the study of the mind and behavior. Its immediate goal is to understand individuals and groups by both establishing general principles and researching specific cases. For many, the ultimate goal of psychology is to benefit society...
has been dealing mainly with treatment of mental illness. At the very end of the twentieth century a new approach in psychology has emerged: positive psychology
Positive psychology
Positive psychology is a recent branch of psychology whose purpose was summed up in 1998 by Martin Seligman and Mihaly Csikszentmihalyi: "We believe that a psychology of positive human functioning will arise, which achieves a scientific understanding and effective interventions to build thriving in...
.
Positive psychology, the study of optimal human functioning, is an attempt to respond to the systematic bias inherent in psychology's historical emphasis on mental illness rather than on mental wellness (Seligman ,2002), mainly by focusing on two, forgotten but classical psychological goals:
- Help ordinary people to live a more productive and meaningful life.
- A full realization of the potential that exists in the human being.
Since Martin Seligman
Martin Seligman
Martin E. P. "Marty" Seligman is an American psychologist, educator, and author of self-help books. His theory of "learned helplessness" is widely respected among scientific psychologists....
, a former head of American Psychological Association
American Psychological Association
The American Psychological Association is the largest scientific and professional organization of psychologists in the United States. It is the world's largest association of psychologists with around 154,000 members including scientists, educators, clinicians, consultants and students. The APA...
, chose positive psychology as the theme of his presidency term, more empirical research and theoretic development emerged in this field.
Two new branches of positive psychology are being implemented into the industrial-organizational world.
- Positive organizational scholarship- a research field that emphasizes the positive characteristics of the organization that facilitates its ability to function during periods of crisis.
- Positive organizational behaviorPositive organizational behaviorPositive Organizational Behavior is defined as "the study and application of positively oriented human resource strengths and psychological capacities that can be measured, developed, and effectively managed for performance improvement in today’s workplace" .For a positive psychological capacity...
(POB) – focuses on measurable positive- psychological abilities of the employee. The research is trying to discover and develop those abilities in order to improve job performance.
As opposed to positive psychology, organizational positive psychology focuses on situational characteristics that can be developed and improved through intervention in work place and proactive management techniques. Moreover it focuses only on measurable and improvable characteristics. Through POB theories, several concepts were identified including subjective happiness, optimism
Optimism
The Oxford English Dictionary defines optimism as having "hopefulness and confidence about the future or successful outcome of something; a tendency to take a favourable or hopeful view." The word is originally derived from the Latin optimum, meaning "best." Being optimistic, in the typical sense...
, hope
Hope
Hope is the emotional state which promotes the belief in a positive outcome related to events and circumstances in one's life. It is the "feeling that what is wanted can be had or that events will turn out for the best" or the act of "look[ing] forward to with desire and reasonable confidence" or...
, resiliency
Psychological resilience
Resilience in psychology refers to the idea of an individual's tendency to cope with stress and adversity. This coping may result in the individual “bouncing back” to a previous state of normal functioning, or using the experience of exposure to adversity to produce a “steeling effect” and function...
and emotional intelligence
Emotional intelligence
Emotional intelligence is a skill or ability in the case of the trait EI model, a self-perceived ability to identify, assess, and control the emotions of oneself, of others, and of groups. Various models and definitions have been proposed of which the ability and trait EI models are the most...
.
Through empirical research it was discovered that different constructs of POB are not conceptually identical. Rather, they differ in their measurement and their combination produces a higher structure. The implications and influences of this structure are bigger than the simple summary of its parts. The name of the construct is positive psychological capital or Psycap. Its components are hope
Hope
Hope is the emotional state which promotes the belief in a positive outcome related to events and circumstances in one's life. It is the "feeling that what is wanted can be had or that events will turn out for the best" or the act of "look[ing] forward to with desire and reasonable confidence" or...
, self-efficacy
Self-efficacy
Self-efficacy is a term used in psychology, roughly corresponding to a person's belief in their own competence.It has been defined as the belief that one is capable of performing in a certain manner to attain certain set of goals. It is believed that our personalized ideas of self-efficacy affect...
, optimism
Optimism
The Oxford English Dictionary defines optimism as having "hopefulness and confidence about the future or successful outcome of something; a tendency to take a favourable or hopeful view." The word is originally derived from the Latin optimum, meaning "best." Being optimistic, in the typical sense...
and resiliency
Psychological resilience
Resilience in psychology refers to the idea of an individual's tendency to cope with stress and adversity. This coping may result in the individual “bouncing back” to a previous state of normal functioning, or using the experience of exposure to adversity to produce a “steeling effect” and function...
.
Hope - Is defined as a positive motivational state where two basic elements - successful feeling of agency (or goal oriented determination) and pathways (or planning to achieve those goals) interact.
Self efficacy – Is defined as people's confidence in their ability to achieve a specific goal in a specific situation.
Optimism – was defined by Seligman by Attribution theory (Fritz Heider
Fritz Heider
Fritz Heider was an Austrian psychologist whose work was related to the Gestalt school. In 1958 he published The Psychology of Interpersonal Relations, which expanded upon his creation of balance theory and marked the starting point of attribution theory...
, 1958). An Optimistic person is defined as one that makes "Internal" or "dispositional", fixed and global attributions for positive events and "External" or "situational", not fixed and specific attributions to negative events. Optimism in Psycap is thought as a realistic construct that regards what an employee can or cannot do, as such, optimism reinforces self efficacy and hope.
Resiliency – Is defined in Positive Psychology as a positive way of coping with danger or distress. In organizational aspect, it is defined as an ability to recuperate from stress, conflict, failure, change or increase in responsibility.
The Relationship Between Positive Psychological Capital And Different Organizational Outcomes
Psycap has positive correlation with performance and satisfactionResearch found that high Psycap employees performed better than low Psycap employees. This difference in performance can be explained by their Psychological constructs which manifest themselves in their cognitions and motivations. The influence on the employees performance is stronger while referring to Psycap than for each of its
Components, meaning, Psycap explains more than its components combined.
Psycap mediates between supportive climate and employee performance - Psycap
Psycap and positive supportive climate are necessary for human resources in order to achieve stable organizational growth. Supportive climate is defined as the total support that an employee receives from their coworkers, other departments and their supervisors which helps them with their job demands.
High Psycap Employees supports effective organizational change
Organizational change is defined as a lack of fit with the environment which intensifies as a result of a gap between the organizational goals and its present outcomes. The employees have the responsibility to adjust and behave according to the new strategy dictated by the management, mostly with fewer resources. During change, different aspects of employees’ Psycap is put to the test – they have to learn new ways of behavior and be confident to do so, recover from the crisis, be motivated to cope efficiently and to believe in a better future. Psycap and positive emotions are examples of how personal factors facilitate organizational change. Positive change is defined as every change that the organization undergoes for its own benefit and has more positive psychological and behavioral consequences than negative ones. The role of positive emotions is that they help workers cope with the organizational change by broadening their point of view, encourage open decision making and giving them essential vitality for their coping.
This interaction means that Psycap, through positive emotions, influences the worker’s attitudes and behavior, which in turn, influences the organizational change.
Psycap decreases absence from work
Psycap has interesting influences on absence from work. Few meta-analyses have shown a connection between personal and organizational climate factors to the level of absenteeism from work. Recently, however, research has shown that attitude variables like satisfaction and commitment cannot explain the significant variance in absenteeism. Psycap can give a new perspective to the understanding and coping with absenteeism. Research has shown that Psycap has a positive influence on levels of involuntary and voluntary absenteeism.
The basis of the interaction between Psycap and absenteeism lies in the already proven connection between the body and the soul and more specifically, a strong connection between stress and physiological factors. Workers who confront similar obstacles in their workplace will react differently according to their Psycap and therefore the influence of such obstacle on them will be different. The nature of workers with high Psycap will contribute to lower levels of sickness or to the ability to recover from sickness and get back to work afterwards, which will result in lower levels of involuntary absenteeism.
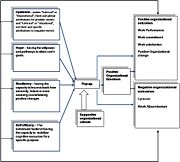
An Integrated Model: The Role of Positive Psychological Capital In The Organization

On the left side of the model you can see the different dimensions of Psycap.
Psycap is influenced by organizational climate and influences several positive and negative outcomes in the organization.
This influence can be direct or mediated by positive feelings in the organization.
Different organizational phenomena have influence on the employee, specifically on the characteristics that assemble his Psycap. For example- while a high Psycap employee observes the good results of his performance, his Psycap grows even more due to the impact of the good performance on self efficacy and hope. From this example we can conclude that Bottom up processes have to do with Psycap. A worker gives feedback not only to himself but for the others observing him as well. Thus, his Psycap affect his surroundings cognitively and affectively ( By his performance outcomes ). For example: A worker which manifests behavior and feelings that show high Psycap and succeeds in his job, not only his Psycap will grow but also the Psycap of the ones around him.
Positive, as well as negative Psycap have a “contagious” aspect that influences groups and generates a Bottom-up process. The model also shows that every one of the four characteristics of Psycap has the possibility to influence organizational outcomes directly as shown widely in past research.
It should be mentioned that Psycap has developed mainly since 2005 and therefore all findings should be considered as preliminary and need further research.
External links
- Liam F. Page and Ross Donohue, Positive Psychological Capital: A Preliminary Exploration of the Construct, Monash University
- Institute of Applied Positive Psychology (IAPPI) - A not-for-profit, research based, educational institution dedicated to advancing the use of positive psychology in organizations.

