Polypectomy
Encyclopedia
The method used to perform colonic polypectomies during colonoscopy
depends on the size, shape and histological type of the polyp to be removed. Prior to performing polypectomy, polyps can be biopsied and examined histologically to determine the need to perform polypectomy.
Gastrointestinal polyps can be removed endoscopically through colonoscopy
or esophagogastroduodenoscopy
, or surgically if the polyp is too large to be removed endoscopically.
Very small polyps (up to 3mm) can be removed by cold biopsy, where biopsy forceps alone are used to remove the polyp, without electrocautery; but risks incomplete removal of the polyp, but reduces the risk of colonic perforation
. These polyps may also be removed by fulguration
using Argon plasma coagulation
to destroy the polyp; the disadvantage of this technique is that no tissue is obtained for histological analysis.
Slightly larger polyps (4-8mm) may be removed by snare cautery (see below).
and colonic perforation
.
Colonoscopy
Colonoscopy is the endoscopic examination of the large bowel and the distal part of the small bowel with a CCD camera or a fiber optic camera on a flexible tube passed through the anus. It may provide a visual diagnosis and grants the opportunity for biopsy or removal of suspected...
depends on the size, shape and histological type of the polyp to be removed. Prior to performing polypectomy, polyps can be biopsied and examined histologically to determine the need to perform polypectomy.
Gastrointestinal polyps can be removed endoscopically through colonoscopy
Colonoscopy
Colonoscopy is the endoscopic examination of the large bowel and the distal part of the small bowel with a CCD camera or a fiber optic camera on a flexible tube passed through the anus. It may provide a visual diagnosis and grants the opportunity for biopsy or removal of suspected...
or esophagogastroduodenoscopy
Esophagogastroduodenoscopy
For other expansions of the initialism "OGD", see the disambiguation page.In medicine , esophagogastroduodenoscopy is a diagnostic endoscopic procedure that visualizes the upper part of the gastrointestinal tract up to the duodenum...
, or surgically if the polyp is too large to be removed endoscopically.
Small polyps (less than 5mm)
Small polyps can removed by hot biopsy: biopsy forceps are closed over the polyp, and electric current is passed through the forceps to provide electrocautery. This reduces the chances of bleeding from the polyp base, and improves the chance of complete removal of the polyp by destroying the tissue at the base of the polyp.Very small polyps (up to 3mm) can be removed by cold biopsy, where biopsy forceps alone are used to remove the polyp, without electrocautery; but risks incomplete removal of the polyp, but reduces the risk of colonic perforation
Gastrointestinal perforation
Gastrointestinal perforation is a complete penetration of the wall of the stomach, small intestine or large bowel, resulting in intestinal contents flowing into the abdominal cavity. Perforation of the intestines results in the potential for bacterial contamination of the abdominal cavity...
. These polyps may also be removed by fulguration
Fulguration
Fulguration, also called electrofulguration, is a procedure to destroy tissue using a high-frequency electric current applied with a needlelike electrode.- External links :...
using Argon plasma coagulation
Argon plasma coagulation
Argon plasma coagulation or APC is a medical endoscopic procedure used primarily to control bleeding from certain lesions in the gastrointestinal tract, and also sometimes to debulk tumours in the case of patients for whom surgery is not recommended...
to destroy the polyp; the disadvantage of this technique is that no tissue is obtained for histological analysis.
Slightly larger polyps (4-8mm) may be removed by snare cautery (see below).


Larger, sessile polyps
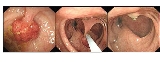
These polyps are more difficult to remove endoscopically, and polypectomy in these cases has a higher risk of complication. Sessile polyps up to 10mm can often be removed by snare polypectomy. Polyps over 10mm may have to be removed piecemeal by snare polypectomy. The use of electrocautery over a large area has a significant risk of causing colonic perforation; to reduce this chance, and to facilitate the polypectomy, sterile fluid (saline or colloid, with methylene blue dye added) can be injected under the base of the polyp to raise it away from the muscular layers of the colon.Larger, pedunculated polyps
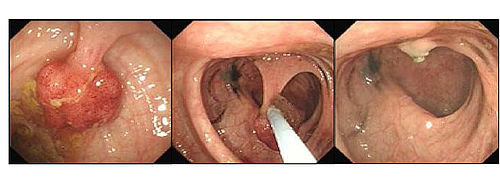
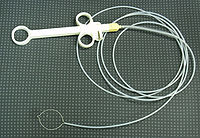
Pedunculated polyps can be removed by snare polypectomy. When the polyp is identified, a polypectomy snare is passed over the polyp and around the stalk of the polyp. The loop of the snare is then tightened to grip the polyp stalk, and the polyp is pulled away from the wall of the colon. An electric current is then passed through the snare loop to cut through the polyp stalk, while providing electrocautery at the same time. The polyp can then be retrieved using the snare, or an endoscopy basket, and removed by withdrawing the colonoscope.Complications
The commonest complications of colonic polypectomy are bleedingBleeding
Bleeding, technically known as hemorrhaging or haemorrhaging is the loss of blood or blood escape from the circulatory system...
and colonic perforation
Gastrointestinal perforation
Gastrointestinal perforation is a complete penetration of the wall of the stomach, small intestine or large bowel, resulting in intestinal contents flowing into the abdominal cavity. Perforation of the intestines results in the potential for bacterial contamination of the abdominal cavity...
.
External links
- DAVE Project videos of polypectomy. Retrieved March 26, 2010.
- "How I Do It" — Removing large or sessile colonic polyps.

