
Polymethylpentene
Encyclopedia
Thermoplastic
Thermoplastic, also known as a thermosoftening plastic, is a polymer that turns to a liquid when heated and freezes to a very glassy state when cooled sufficiently...
polymer
Polymer
A polymer is a large molecule composed of repeating structural units. These subunits are typically connected by covalent chemical bonds...
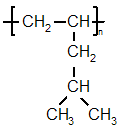
of methylpentene monomer
Monomer
A monomer is an atom or a small molecule that may bind chemically to other monomers to form a polymer; the term "monomeric protein" may also be used to describe one of the proteins making up a multiprotein complex...
units. It is used for gas permeable packaging, autoclavable
Autoclave
An autoclave is an instrument used to sterilize equipment and supplies by subjecting them to high pressure saturated steam at 121 °C for around 15–20 minutes depending on the size of the load and the contents. It was invented by Charles Chamberland in 1879, although a precursor known as the...
medical and laboratory equipment, microwave components, and cookware. It is commonly called TPX, which is a trademark of Mitsui Chemicals
Mitsui Chemicals
is a Japanese Chemicals company listed on the Nikkei. It is a part of the Mitsui conglomerate. The company has a turnover of around 15 billion USD and has business interests in Japan, Europe, China, Southeast Asia and the USA. It employs approximately 13,000 people worldwide. The company mainly...
.
Production
Polymethylpentene is a 4-methyl-1-pentene based linear isotactic polyolefinPolyolefin
A polyolefin is a polymer produced from a simple olefin as a monomer. For example, polyethylene is the polyolefin produced by polymerizing the olefin ethylene. An equivalent term is polyalkene; this is a more modern term, although polyolefin is still used in the petrochemical industry...
and is made by Ziegler-Natta type catalysis
Catalysis
Catalysis is the change in rate of a chemical reaction due to the participation of a substance called a catalyst. Unlike other reagents that participate in the chemical reaction, a catalyst is not consumed by the reaction itself. A catalyst may participate in multiple chemical transformations....
. The commercially available grades are usually copolymers. It can be extruded
Extrusion
Extrusion is a process used to create objects of a fixed cross-sectional profile. A material is pushed or drawn through a die of the desired cross-section...
and molded (by injection molding
Injection molding
Injection molding is a manufacturing process for producing parts from both thermoplastic and thermosetting plastic materials. Material is fed into a heated barrel, mixed, and forced into a mold cavity where it cools and hardens to the configuration of the cavity...
or blow molding
Blow molding
Blow molding is a manufacturing process by which hollow plastic parts are formed. In general, there are three main types of blow molding: extrusion blow molding, injection blow molding, and stretch blow molding. The blow molding process begins with melting down the plastic and forming it into a...
).
Physical properties
Polymethylpentene melts at ≈ 235 °C. It has a very low densityDensity
The mass density or density of a material is defined as its mass per unit volume. The symbol most often used for density is ρ . In some cases , density is also defined as its weight per unit volume; although, this quantity is more properly called specific weight...
(0.84 g·cm³) and is transparent. It has excellent chemical resistance, low moisture absorption, and exceptional acoustical and electrical properties. Its properties are reasonably similar to those of other polyolefins, although it is more brittle
Brittle
A material is brittle if, when subjected to stress, it breaks without significant deformation . Brittle materials absorb relatively little energy prior to fracture, even those of high strength. Breaking is often accompanied by a snapping sound. Brittle materials include most ceramics and glasses ...
and more gas permeable.
In comparison to other materials being used for operating in THz range, TPX shows excellent optical properties with a wavelength independent refractive index of 1.460±0.005 between visible light and 100~GHz.
Applications
- Applications include sonar covers, speaker cones, ultrasonic transducer heads, and lightweight structural parts. It is also FDA compliant for use in food processing machinery. Polymethylpentene is often used in films and coatings for gas permeable packaging.
- Because of its high melting pointMelting pointThe melting point of a solid is the temperature at which it changes state from solid to liquid. At the melting point the solid and liquid phase exist in equilibrium. The melting point of a substance depends on pressure and is usually specified at standard atmospheric pressure...
and good temperature stability, polymethylpentene is used for autoclavable medical and laboratory equipment, microwave components, and cookware.
- It is also often used in electrical components e.g. LEDLEdLEd is a TeX/LaTeX editing software working under Microsoft Windows. It is a freeware product....
molds because it is an excellent electrical insulator.
- TPX is a hard, solid material, which can be mechanically shaped into various optical components like lenses and windows. Also specifically TPX is used in CO2 laser pumped molecular lasers as an output window because it is transparent in the whole terahertz range and totally suppresses the ~10 µm pump radiation.

