
Plessey Code
Encyclopedia
Plessey Code is a 1D linear barcode
symbology based on pulse width modulation, developed in 1971 by The Plessey Company plc
, a British-based company. It is one of the first barcode symbology, and is still used in some rare libraries and for shelf tags in retail stores, in part as a solution to their internal requirement for stock control. The system was first used in the early 1970s by J.Sainsbury to identify all of its products on supermarket shelves for its product restocking system.
The chief advantages are the relative ease of printing using the dot-matrix printers popular at the time of the code's introduction, and its somewhat higher density than the more common 2 of 5 and 3 of 9 codes. It has latter led several variations as Anker Code by ADS Company, Telxon, and MSI
(also known as Plessey modified). It is difficult to have the specifications for them nowadays and thus hard to tell the differences between them (except for MSI), because is was mainly available as paper document and in discontinued since then.
digits (i.e., the hex digits 0-F) as 4 bars (bits). The LSB
is on the first bar on the left, and the MSB
is the last bar on the right. A "0" bit is represented as a narrow bar, followed by a wide space. The "1" is represented by a wide bar, followed by a narrow space.
The barcode can be read in either direction (left to right or right to left).
The barcode comprises:
, using polynomial
division
. Is uses 2 characters, or 8 bits. The generator polynomial is with n=8, in binary "111101001".
with n=8, in binary "111101001".
 , with b < 0,229mm
, with b < 0,229mm
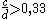 , with c > 0,127mm
, with c > 0,127mm
Bit dimension in mm :
Values are slightly different for Anker Code
Before and after each barcode, there should be margins of 4 bits.
Barcode
A barcode is an optical machine-readable representation of data, which shows data about the object to which it attaches. Originally barcodes represented data by varying the widths and spacings of parallel lines, and may be referred to as linear or 1 dimensional . Later they evolved into rectangles,...
symbology based on pulse width modulation, developed in 1971 by The Plessey Company plc
Plessey
The Plessey Company plc was a British-based international electronics, defence and telecommunications company. It originated in 1917, growing and diversifying into electronics. It expanded after the second world war by acquisition of companies and formed overseas companies...
, a British-based company. It is one of the first barcode symbology, and is still used in some rare libraries and for shelf tags in retail stores, in part as a solution to their internal requirement for stock control. The system was first used in the early 1970s by J.Sainsbury to identify all of its products on supermarket shelves for its product restocking system.
The chief advantages are the relative ease of printing using the dot-matrix printers popular at the time of the code's introduction, and its somewhat higher density than the more common 2 of 5 and 3 of 9 codes. It has latter led several variations as Anker Code by ADS Company, Telxon, and MSI
MSI Barcode
MSI is a barcode symbology developed by the MSI Data Corporation, based on the original Plessey Code symbology. It is a continuous symbology that is not self-checking...
(also known as Plessey modified). It is difficult to have the specifications for them nowadays and thus hard to tell the differences between them (except for MSI), because is was mainly available as paper document and in discontinued since then.
Encoding
The barcode encodes hexadecimalHexadecimal
In mathematics and computer science, hexadecimal is a positional numeral system with a radix, or base, of 16. It uses sixteen distinct symbols, most often the symbols 0–9 to represent values zero to nine, and A, B, C, D, E, F to represent values ten to fifteen...
digits (i.e., the hex digits 0-F) as 4 bars (bits). The LSB
Least significant bit
In computing, the least significant bit is the bit position in a binary integer giving the units value, that is, determining whether the number is even or odd. The lsb is sometimes referred to as the right-most bit, due to the convention in positional notation of writing less significant digits...
is on the first bar on the left, and the MSB
Most significant bit
In computing, the most significant bit is the bit position in a binary number having the greatest value...
is the last bar on the right. A "0" bit is represented as a narrow bar, followed by a wide space. The "1" is represented by a wide bar, followed by a narrow space.
The barcode can be read in either direction (left to right or right to left).
The barcode comprises:
- the forward start code
- the label / data digits
- the check code, for error detection
- the termination bar
- the reverse start code
Forward start code
The forward start code is "1101". It defines the beginning of the encoded text.Label
The character of the text to encode are hexadecimal values encoded as reversed BCD| Value | Encoding | Value | Encoding | Value | Encoding | Value | Encoding |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0000 | 4 | 0010 | 8 | 0001 | C | 0011 |
| 1 | 1000 | 5 | 1010 | 9 | 1001 | D | 1011 |
| 2 | 0100 | 6 | 0110 | A | 0101 | E | 0111 |
| 3 | 1100 | 7 | 1110 | B | 1101 | F | 1111 |
Check code
The check code for error detection and correction is as CRCCyclic redundancy check
A cyclic redundancy check is an error-detecting code commonly used in digital networks and storage devices to detect accidental changes to raw data...
, using polynomial
Polynomial
In mathematics, a polynomial is an expression of finite length constructed from variables and constants, using only the operations of addition, subtraction, multiplication, and non-negative integer exponents...
division
Mathematics of CRC
The cyclic redundancy check is based on division in the ring of polynomials over the finite field GF , that is, the set of polynomials where each coefficient is either zero or one, and arithmetic operations wrap around .Any string of bits can be interpreted as the coefficients of a message...
. Is uses 2 characters, or 8 bits. The generator polynomial is
 with n=8, in binary "111101001".
with n=8, in binary "111101001".Reverse start code
The reverse start code, with the forward start code, are used to detect the direction of reading : from left to right or right to left. It's encoded as a reversed "0011". Reversed because the "0" is represented by a wide space and simple bar, and "1" as a simple space and wide bar.Dimensions
The dimensions of the bars and spaces are defined by the following rules : , with b < 0,229mm
, with b < 0,229mm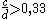 , with c > 0,127mm
, with c > 0,127mmBit dimension in mm :
| | "1" | | "0" | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| bit/inch | pitch 'p' | width | min | nom | max | width | min | nom | max |
| 40 | 0.635 | bar 'a' | 0.305 | 0.343 | 0.381 | bar 'c' | 0.114 | 0.127 | 0.152 |
| space 'b' | 0.254 | 0.292 | 0.305 | space 'd' | 0.471 | 0.508 | 0.533 | ||
| 32 | 0.787 | bar 'a' | 0.394 | 0.432 | 0.470 | bar 'c' | 0.127 | 0.152 | 0.173 |
| space 'b' | 0.318 | 0.356 | 0.394 | space 'd' | 0.584 | 0.635 | 0.685 | ||
| 25 (std.) | 1.020 | bar 'a' | 0.533 | 0.584 | 0.635 | bar 'c' | 0.127 | 0.178 | 0.229 |
| space 'b' | 0.381 | 0.432 | 0.483 | space 'd' | 0.787 | 0.838 | 0.889 |
Values are slightly different for Anker Code
Before and after each barcode, there should be margins of 4 bits.

