Plastoquinone
Encyclopedia
Plastoquinone is a quinone
molecule involved in the electron transport chain in the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis
. Plastoquinone is reduced (accepts two protons (H+) from the stromal matrix of the chloroplast, coupled to two electrons (e-) from photosystem II
), forming plastoquinol. It transports the protons to the lumen of thylakoid discs
, while the electrons continue through the electron transport chain
into the cytochrome b6f
protein complex.
The prefix plasto means either plastid
or chloroplast
, alluding to its location within the cell.
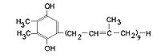
Structurally it is a 2,3-dimethyl-1,4-benzoquinone molecule with a side chain of nine isoprenyl units.
(plastoquinonyl-decyl-triphenylphosphonium), SkQR1
(the rhodamine
-containing analog of SkQ1), SkQ3) have anti-oxidant and protonophore
activity.
SkQ1 is proposed as an anti-aging treatment.
SkQ1
is starting clinical trials for glaucoma
in Russia.
Quinone
A quinone is a class of organic compounds that are formally "derived from aromatic compounds [such as benzene or naphthalene] by conversion of an even number of –CH= groups into –C– groups with any necessary rearrangement of double bonds," resulting in "a fully conjugated cyclic dione structure."...
molecule involved in the electron transport chain in the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a chemical process that converts carbon dioxide into organic compounds, especially sugars, using the energy from sunlight. Photosynthesis occurs in plants, algae, and many species of bacteria, but not in archaea. Photosynthetic organisms are called photoautotrophs, since they can...
. Plastoquinone is reduced (accepts two protons (H+) from the stromal matrix of the chloroplast, coupled to two electrons (e-) from photosystem II
Photosystem II
Photosystem II is the first protein complex in the Light-dependent reactions. It is located in the thylakoid membrane of plants, algae, and cyanobacteria. The enzyme uses photons of light to energize electrons that are then transferred through a variety of coenzymes and cofactors to reduce...
), forming plastoquinol. It transports the protons to the lumen of thylakoid discs
Thylakoid
A thylakoid is a membrane-bound compartment inside chloroplasts and cyanobacteria. They are the site of the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis. Thylakoids consist of a thylakoid membrane surrounding a thylakoid lumen. Chloroplast thylakoids frequently form stacks of disks referred to as...
, while the electrons continue through the electron transport chain
Electron transport chain
An electron transport chain couples electron transfer between an electron donor and an electron acceptor with the transfer of H+ ions across a membrane. The resulting electrochemical proton gradient is used to generate chemical energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate...
into the cytochrome b6f
Cytochrome b6f complex
The cytochrome b6f complex is an enzyme found in the thylakoid membrane in chloroplasts of plants, cyanobacteria, and green algae, catalyzing the transfer of electrons from plastoquinol to plastocyanin...
protein complex.
The prefix plasto means either plastid
Plastid
Plastids are major organelles found in the cells of plants and algae. Plastids are the site of manufacture and storage of important chemical compounds used by the cell...
or chloroplast
Chloroplast
Chloroplasts are organelles found in plant cells and other eukaryotic organisms that conduct photosynthesis. Chloroplasts capture light energy to conserve free energy in the form of ATP and reduce NADP to NADPH through a complex set of processes called photosynthesis.Chloroplasts are green...
, alluding to its location within the cell.
Structurally it is a 2,3-dimethyl-1,4-benzoquinone molecule with a side chain of nine isoprenyl units.
Derivatives
Some derivatives designed to penetrate cell membranes (SkQ1SkQ
SkQ stands for a class of organic molecules composed of a large organic cation with antioxidant plastoquinone attached to it. When added to a living cell, penetrating cations are distributed according to the transmembrane electrical potential difference...
(plastoquinonyl-decyl-triphenylphosphonium), SkQR1
SkQ
SkQ stands for a class of organic molecules composed of a large organic cation with antioxidant plastoquinone attached to it. When added to a living cell, penetrating cations are distributed according to the transmembrane electrical potential difference...
(the rhodamine
Rhodamine
Rhodamine is a family of related chemical compounds, fluorone dyes. Examples are Rhodamine 6G and Rhodamine B. They are used as a dye and as a dye laser gain medium. They are often used as a tracer dye within water to determine the rate and direction of flow and transport...
-containing analog of SkQ1), SkQ3) have anti-oxidant and protonophore
Protonophore
A protonophore, also known as a proton translocator, is an ionophore that allows protons to cross lipid bilayers. This would otherwise not occur as protons have positive charge and hydrophilic properties, making them unable to cross without a channel or transporter...
activity.
SkQ1 is proposed as an anti-aging treatment.
SkQ1
SkQ
SkQ stands for a class of organic molecules composed of a large organic cation with antioxidant plastoquinone attached to it. When added to a living cell, penetrating cations are distributed according to the transmembrane electrical potential difference...
is starting clinical trials for glaucoma
Glaucoma
Glaucoma is an eye disorder in which the optic nerve suffers damage, permanently damaging vision in the affected eye and progressing to complete blindness if untreated. It is often, but not always, associated with increased pressure of the fluid in the eye...
in Russia.
External links
- Plastoquinones History, absorption specta, and analogs.

