
Planar laser-induced fluorescence
Encyclopedia
Flow visualization
Flow visualization in fluid dynamics is used to make the flow patterns visible, in order to get a qualitative or quantitative information on them.- Overview :...
and quantitative measurements. PLIF has been shown to be used for velocity, concentration, temperature and pressure measurements.
Working
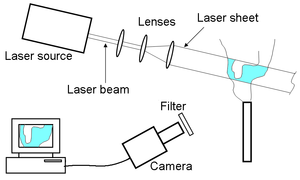
A typical PLIF setup consists a source of light (usually a laserLaser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of photons. The term "laser" originated as an acronym for Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation...
), an arrangement of lenses to form a sheet, fluorescent medium, collection optics and a detector. The light from the source, illuminates the medium, which then fluoresces. This signal is captured by the detector and can be related to the various properties of the medium.
The typical lasers used as light sources are pulsed, which provide a higher peak power than the continuous-wave lasers. Also the short pulse time is useful for good temporal resolution
Temporal resolution
Temporal resolution refers to the precision of a measurement with respect to time. Often there is a tradeoff between temporal resolution of a measurement and its spatial resolution. This trade-off can be attributed to the finite speed of light and the fact that it takes a certain period of time...
. Some of the widely used laser sources are Nd:YAG laser
Nd:YAG laser
Nd:YAG is a crystal that is used as a lasing medium for solid-state lasers. The dopant, triply ionized neodymium, typically replaces yttrium in the crystal structure of the yttrium aluminium garnet , since they are of similar size...
, dye laser
Dye laser
A dye laser is a laser which uses an organic dye as the lasing medium, usually as a liquid solution. Compared to gases and most solid state lasing media, a dye can usually be used for a much wider range of wavelengths. The wide bandwidth makes them particularly suitable for tunable lasers and...
s, excimer laser
Excimer laser
An excimer laser is a form of ultraviolet laser which is commonly used in the production of microelectronic devices , eye surgery, and micromachining....
s, and ion laser
Ion laser
An ion laser is a gas laser which uses an ionized gas as its lasing medium.Like other gas lasers, ion lasers feature a sealed cavity containing the laser medium and mirrors forming a Fabry–Pérot resonator. Unlike HeNe lasers, the energy level transitions that contribute to laser action come from ions...
s. The light from the laser (usually a beam) is passed through a set of lenses and/or mirrors to form a sheet, which is then used to illuminate the medium. This medium is either made up of fluorescent material or can be seeded
Seeded
In fluid dynamics, seeding a flow, or a seeded flow, means to introduce particulates or other foreign substances into an otherwise transparent stream of fluid. These particulates are generally small enough to be carried by the fluid but large enough to be picked up using a flow visualization...
with a fluorescent substance. The signal is usually captured by a CCD
Charge-coupled device
A charge-coupled device is a device for the movement of electrical charge, usually from within the device to an area where the charge can be manipulated, for example conversion into a digital value. This is achieved by "shifting" the signals between stages within the device one at a time...
or CMOS
Active pixel sensor
An active-pixel sensor is an image sensor consisting of an integrated circuit containing an array of pixel sensors, each pixel containing a photodetector and an active amplifier. There are many types of active pixel sensors including the CMOS APS used most commonly in cell phone cameras, web...
camera
Camera
A camera is a device that records and stores images. These images may be still photographs or moving images such as videos or movies. The term camera comes from the camera obscura , an early mechanism for projecting images...
(sometimes intensified cameras are also used). Timing electronics is often used to synchronize pulsed light sources with intensified cameras.
Basic principles

Advantages
- Unlike several other flow imaging techniques, PLIF may be combined with particle image velocimetry (PIV). The allows for the simultaneous measurement of a fluid velocity field and species concentration.See also
- FluorescenceFluorescenceFluorescence is the emission of light by a substance that has absorbed light or other electromagnetic radiation of a different wavelength. It is a form of luminescence. In most cases, emitted light has a longer wavelength, and therefore lower energy, than the absorbed radiation...
- Laser-induced fluorescenceLaser-induced fluorescenceLaser-induced fluorescence is a spectroscopic method used for studying structure of molecules, detection of selective species and flow visualization and measurements....
- Flow visualizationFlow visualizationFlow visualization in fluid dynamics is used to make the flow patterns visible, in order to get a qualitative or quantitative information on them.- Overview :...
- Particle image velocimetry (PIV)Particle image velocimetryParticle image velocimetry is an optical method of flow visualization used in education and research. It is used to obtain instantaneous velocity measurements and related properties in fluids...

