Baseband
Encyclopedia
In telecommunications and signal processing
, baseband is an adjective that describes signals and systems whose range of frequencies is measured from close to 0 hertz to a cut-off frequency, a maximum bandwidth or highest signal frequency; it is sometimes used as a noun for a band of frequencies starting close to zero. Baseband can often be considered as a synonym to lowpass or non-modulated, and antonym to passband
, bandpass, carrier-modulated
or radio frequency (RF) signal.
s (LANs), as opposed to passband
channels such as radio frequency channels and passband filtered wires of the analog telephone network. Frequency division multiplexing (FDM) allows an analog telephone wire to carry a baseband telephone call, concurrently as one or several carrier-modulated telephone calls.
transmission, also known as carrier-modulated transmission. Passband transmission makes communication possible over a bandpass filtered channel, such as the telephone network local-loop or a band-limited wireless channel.
An unfiltered wire is intrinsically a low-pass transmission channel, while a line code is intrinsically a pulse wave signal that occupies a frequency spectrum
of infinite bandwidth. According to the Nyquist theorem
, error-free detection of the line code requires a channel bandwidth of at least the Nyquist rate
, which is half the line code pulse rate.
standards, for example 10BASE5
, 100BASE-T and 1000BASE-SX, implies baseband digital transmission, i.e. that a line code
and an unfiltered wire are used.
This is as opposed to 10PASS-TS
Ethernet, where "PASS" implies passband transmission. Passband digital transmission requires a digital modulation scheme, often provided by modem
equipment. In the 10PASS-TS case the VDSL standard is utilized, which is based on the Discrete multi-tone modulation (DMT) scheme. Other examples of passband network access technologies are wireless networks and cable modem
s.
A signal "at baseband" is usually considered to include frequencies from near 0 Hz
up to the highest frequency in the signal with significant power.
In general, signals can be described as including a whole range of different frequencies added together
. In telecommunication
s in particular, it is often the case that those parts of the signal which are at low frequencies are 'copied' up to higher frequencies for transmission
purposes, since there are few communications media that will pass low frequencies without distortion. Then, the original, low frequency components are referred to as the baseband signal. Typically, the new, high-frequency copy is referred to as the 'RF' (radio-frequency
) signal. A baseband signal is a low frequency signal which when modulated is transmitted on various channels.
The concept of baseband signals is most often applied to real-valued signals, and systems that handle real-valued signals. Fourier analysis of such signals includes a negative-frequency band, but the negative-frequency information is just a mirror of the positive-frequency information, not new information. For complex-valued signals, on the other hand, the negative frequencies carry new information. In that case, the full two-sided bandwidth is generally quoted, rather than just the half measured from zero; the concept of baseband can be applied by treating the real and imaginary parts of the complex-valued signal as two different real signals.
, PSK
and QAM
, but not FSK
) – a complex valued representation of the modulated physical signal (the so called passband
signal or RF
signal). The equivalent baseband signal is where
where  is the inphase signal,
is the inphase signal, 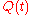 the quadrature phase signal, and
the quadrature phase signal, and  the imaginary unit. In a digital modulation method, the
the imaginary unit. In a digital modulation method, the 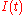 and
and 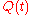 signals of each modulation symbol are evident from the constellation diagram
signals of each modulation symbol are evident from the constellation diagram
. The frequency spectrum of this signal includes negative as well as positive frequencies. The physical passband signal corresponds to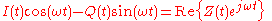
where is the carrier angular frequency in rad/s.
is the carrier angular frequency in rad/s.
In an equivalent baseband model of a communication system, the modulated signal is replaced by a complex valued equivalent baseband signal with carrier frequency of 0 hertz, and the RF
channel is replaced by an equivalent baseband channel model where the frequency response is transferred to baseband frequencies.
a higher frequency carrier wave
in order that it may be transmitted via radio. Modulation results in shifting the signal up to much higher frequencies (radio frequencies, or RF) than it originally spanned. A key consequence of the usual double-sideband amplitude modulation
(AM) is that, usually, the range of frequencies the signal spans (its spectral bandwidth) is doubled. Thus, the RF bandwidth of a signal (measured from the lowest frequency as opposed to 0 Hz) is usually twice its baseband bandwidth. Steps may be taken to reduce this effect, such as single-sideband modulation
; the highest frequency of such signals greatly exceeds the baseband bandwidth.
Some signals can be treated as baseband or not, depending on the situation. For example, a switched analog connection in the telephone network has energy below 300 Hz and above 3400 Hz removed by bandpass filtering; since the signal has no energy very close to zero frequency, it may not be considered a baseband signal, but in the telephone systems frequency-division multiplexing
hierarchy, it is usually treated as a baseband signal, by comparison with the modulated signals used for long-distance transmission. The 300 Hz lower band edge in this case is treated as "near zero", being a small fraction of the upper band edge.
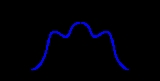
The figure shows what happens with AM modulation:
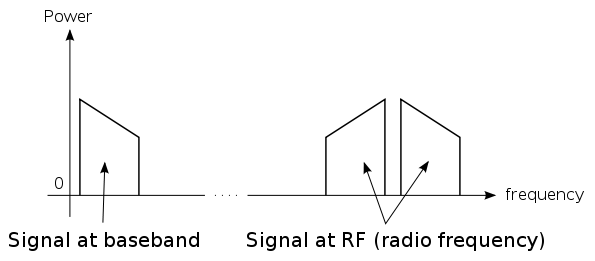 The simplest definition is that a signal's baseband bandwidth is its bandwidth before modulation
The simplest definition is that a signal's baseband bandwidth is its bandwidth before modulation
and multiplexing
, or after demultiplexing and demodulation
.
The composite video
signal created by devices such as most newer VCRs, game consoles and DVD
players is a commonly used baseband signal.
Signal processing
Signal processing is an area of systems engineering, electrical engineering and applied mathematics that deals with operations on or analysis of signals, in either discrete or continuous time...
, baseband is an adjective that describes signals and systems whose range of frequencies is measured from close to 0 hertz to a cut-off frequency, a maximum bandwidth or highest signal frequency; it is sometimes used as a noun for a band of frequencies starting close to zero. Baseband can often be considered as a synonym to lowpass or non-modulated, and antonym to passband
Passband
A passband is the range of frequencies or wavelengths that can pass through a filter without being attenuated.A bandpass filtered signal , is known as a bandpass signal, as opposed to a baseband signal....
, bandpass, carrier-modulated
Modulation
In electronics and telecommunications, modulation is the process of varying one or more properties of a high-frequency periodic waveform, called the carrier signal, with a modulating signal which typically contains information to be transmitted...
or radio frequency (RF) signal.
Baseband bandwidth
A baseband bandwidth is equal to the highest frequency of a signal or system, or an upper bound on such frequencies, for example the upper cut-off frequency of a passband filter. By contrast, passband bandwidth is the difference between a highest frequency and a nonzero lowest frequency.Baseband channel
A baseband channel or lowpass channel (or system, or network) is a communication channel that can transfer frequencies that are very near zero. Examples are serial cables and local area networkLocal area network
A local area network is a computer network that interconnects computers in a limited area such as a home, school, computer laboratory, or office building...
s (LANs), as opposed to passband
Passband
A passband is the range of frequencies or wavelengths that can pass through a filter without being attenuated.A bandpass filtered signal , is known as a bandpass signal, as opposed to a baseband signal....
channels such as radio frequency channels and passband filtered wires of the analog telephone network. Frequency division multiplexing (FDM) allows an analog telephone wire to carry a baseband telephone call, concurrently as one or several carrier-modulated telephone calls.
Digital baseband transmission
Digital baseband transmission, also known as line coding, aims at transferring a digital bit stream over base-band channel, typically an unfiltered wire, as opposed to passbandPassband
A passband is the range of frequencies or wavelengths that can pass through a filter without being attenuated.A bandpass filtered signal , is known as a bandpass signal, as opposed to a baseband signal....
transmission, also known as carrier-modulated transmission. Passband transmission makes communication possible over a bandpass filtered channel, such as the telephone network local-loop or a band-limited wireless channel.
An unfiltered wire is intrinsically a low-pass transmission channel, while a line code is intrinsically a pulse wave signal that occupies a frequency spectrum
Fourier series
In mathematics, a Fourier series decomposes periodic functions or periodic signals into the sum of a set of simple oscillating functions, namely sines and cosines...
of infinite bandwidth. According to the Nyquist theorem
Nyquist rate
In signal processing, the Nyquist rate, named after Harry Nyquist, is two times the bandwidth of a bandlimited signal or a bandlimited channel...
, error-free detection of the line code requires a channel bandwidth of at least the Nyquist rate
Nyquist rate
In signal processing, the Nyquist rate, named after Harry Nyquist, is two times the bandwidth of a bandlimited signal or a bandlimited channel...
, which is half the line code pulse rate.
Baseband transmission in Ethernet
The word "BASE" in Ethernet physical layerEthernet physical layer
The Ethernet physical layer is the physical layer component of the Ethernet family of computer network standards.The Ethernet physical layer evolved over a considerable time span and encompasses quite a few physical media interfaces and several magnitudes of speed...
standards, for example 10BASE5
10BASE5
10BASE5 was the original commercially available variant of Ethernet.For its physical layer it used cable similar to RG-8/U coaxial cable but with extra braided shielding. This is a stiff, diameter cable with an impedance of 50 ohms , a solid center conductor, a foam insulating filler, a shielding...
, 100BASE-T and 1000BASE-SX, implies baseband digital transmission, i.e. that a line code
Line code
In telecommunication, a line code is a code chosen for use within a communications system for baseband transmission purposes...
and an unfiltered wire are used.
This is as opposed to 10PASS-TS
10PASS-TS
10PASS-TS is an IEEE 802.3-2008 Physical Layer specification for a full-duplex short reach point-to-point Ethernet link over voice-grade copper wiring, used in Ethernet in the first mile applications....
Ethernet, where "PASS" implies passband transmission. Passband digital transmission requires a digital modulation scheme, often provided by modem
Modem
A modem is a device that modulates an analog carrier signal to encode digital information, and also demodulates such a carrier signal to decode the transmitted information. The goal is to produce a signal that can be transmitted easily and decoded to reproduce the original digital data...
equipment. In the 10PASS-TS case the VDSL standard is utilized, which is based on the Discrete multi-tone modulation (DMT) scheme. Other examples of passband network access technologies are wireless networks and cable modem
Cable modem
A cable modem is a type of network bridge and modem that provides bi-directional data communication via radio frequency channels on a HFC and RFoG infrastructure. Cable modems are primarily used to deliver broadband Internet access in the form of cable Internet, taking advantage of the high...
s.
Baseband signal
A baseband signal or lowpass signal is a signal that can include frequencies that are very near zero, by comparison with its highest frequency (for example, a sound waveform can be considered as a baseband signal, whereas a radio signal or any other modulated signal is not).A signal "at baseband" is usually considered to include frequencies from near 0 Hz
Hertz
The hertz is the SI unit of frequency defined as the number of cycles per second of a periodic phenomenon. One of its most common uses is the description of the sine wave, particularly those used in radio and audio applications....
up to the highest frequency in the signal with significant power.
In general, signals can be described as including a whole range of different frequencies added together
Spectral density
In statistical signal processing and physics, the spectral density, power spectral density , or energy spectral density , is a positive real function of a frequency variable associated with a stationary stochastic process, or a deterministic function of time, which has dimensions of power per hertz...
. In telecommunication
Telecommunication
Telecommunication is the transmission of information over significant distances to communicate. In earlier times, telecommunications involved the use of visual signals, such as beacons, smoke signals, semaphore telegraphs, signal flags, and optical heliographs, or audio messages via coded...
s in particular, it is often the case that those parts of the signal which are at low frequencies are 'copied' up to higher frequencies for transmission
Transmission (telecommunications)
Transmission, in telecommunications, is the process of sending, propagating and receiving an analogue or digital information signal over a physical point-to-point or point-to-multipoint transmission medium, either wired, optical fiber or wireless...
purposes, since there are few communications media that will pass low frequencies without distortion. Then, the original, low frequency components are referred to as the baseband signal. Typically, the new, high-frequency copy is referred to as the 'RF' (radio-frequency
Radio frequency
Radio frequency is a rate of oscillation in the range of about 3 kHz to 300 GHz, which corresponds to the frequency of radio waves, and the alternating currents which carry radio signals...
) signal. A baseband signal is a low frequency signal which when modulated is transmitted on various channels.
The concept of baseband signals is most often applied to real-valued signals, and systems that handle real-valued signals. Fourier analysis of such signals includes a negative-frequency band, but the negative-frequency information is just a mirror of the positive-frequency information, not new information. For complex-valued signals, on the other hand, the negative frequencies carry new information. In that case, the full two-sided bandwidth is generally quoted, rather than just the half measured from zero; the concept of baseband can be applied by treating the real and imaginary parts of the complex-valued signal as two different real signals.
Equivalent baseband signal
An equivalent baseband signal or equivalent lowpass signal is – in analog and digital modulation methods with constant carrier frequency (for example ASKAmplitude-shift keying
Amplitude-shift keying is a form of modulation that represents digital data as variations in the amplitude of a carrier wave.Any digital modulation scheme uses a finite number of distinct signals to represent digital data. ASK uses a finite number of amplitudes, each assigned a unique pattern of...
, PSK
Phase-shift keying
Phase-shift keying is a digital modulation scheme that conveys data by changing, or modulating, the phase of a reference signal ....
and QAM
Quadrature amplitude modulation
Quadrature amplitude modulation is both an analog and a digital modulation scheme. It conveys two analog message signals, or two digital bit streams, by changing the amplitudes of two carrier waves, using the amplitude-shift keying digital modulation scheme or amplitude modulation analog...
, but not FSK
Frequency-shift keying
Frequency-shift keying is a frequency modulation scheme in which digital information is transmitted through discrete frequency changes of a carrier wave. The simplest FSK is binary FSK . BFSK uses a pair of discrete frequencies to transmit binary information. With this scheme, the "1" is called...
) – a complex valued representation of the modulated physical signal (the so called passband
Passband
A passband is the range of frequencies or wavelengths that can pass through a filter without being attenuated.A bandpass filtered signal , is known as a bandpass signal, as opposed to a baseband signal....
signal or RF
Radio frequency
Radio frequency is a rate of oscillation in the range of about 3 kHz to 300 GHz, which corresponds to the frequency of radio waves, and the alternating currents which carry radio signals...
signal). The equivalent baseband signal is
 where
where  is the inphase signal,
is the inphase signal, 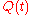 the quadrature phase signal, and
the quadrature phase signal, and  the imaginary unit. In a digital modulation method, the
the imaginary unit. In a digital modulation method, the 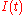 and
and 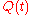 signals of each modulation symbol are evident from the constellation diagram
signals of each modulation symbol are evident from the constellation diagramConstellation diagram
A constellation diagram is a representation of a signal modulated by a digital modulation scheme such as quadrature amplitude modulation or phase-shift keying. It displays the signal as a two-dimensional scatter diagram in the complex plane at symbol sampling instants...
. The frequency spectrum of this signal includes negative as well as positive frequencies. The physical passband signal corresponds to
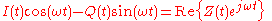
where
 is the carrier angular frequency in rad/s.
is the carrier angular frequency in rad/s.In an equivalent baseband model of a communication system, the modulated signal is replaced by a complex valued equivalent baseband signal with carrier frequency of 0 hertz, and the RF
Radio frequency
Radio frequency is a rate of oscillation in the range of about 3 kHz to 300 GHz, which corresponds to the frequency of radio waves, and the alternating currents which carry radio signals...
channel is replaced by an equivalent baseband channel model where the frequency response is transferred to baseband frequencies.
Modulation
A signal at baseband is often used to modulateModulation
In electronics and telecommunications, modulation is the process of varying one or more properties of a high-frequency periodic waveform, called the carrier signal, with a modulating signal which typically contains information to be transmitted...
a higher frequency carrier wave
Carrier wave
In telecommunications, a carrier wave or carrier is a waveform that is modulated with an input signal for the purpose of conveying information. This carrier wave is usually a much higher frequency than the input signal...
in order that it may be transmitted via radio. Modulation results in shifting the signal up to much higher frequencies (radio frequencies, or RF) than it originally spanned. A key consequence of the usual double-sideband amplitude modulation
Amplitude modulation
Amplitude modulation is a technique used in electronic communication, most commonly for transmitting information via a radio carrier wave. AM works by varying the strength of the transmitted signal in relation to the information being sent...
(AM) is that, usually, the range of frequencies the signal spans (its spectral bandwidth) is doubled. Thus, the RF bandwidth of a signal (measured from the lowest frequency as opposed to 0 Hz) is usually twice its baseband bandwidth. Steps may be taken to reduce this effect, such as single-sideband modulation
Single-sideband modulation
Single-sideband modulation or Single-sideband suppressed-carrier is a refinement of amplitude modulation that more efficiently uses electrical power and bandwidth....
; the highest frequency of such signals greatly exceeds the baseband bandwidth.
Some signals can be treated as baseband or not, depending on the situation. For example, a switched analog connection in the telephone network has energy below 300 Hz and above 3400 Hz removed by bandpass filtering; since the signal has no energy very close to zero frequency, it may not be considered a baseband signal, but in the telephone systems frequency-division multiplexing
Frequency-division multiplexing
Frequency-division multiplexing is a form of signal multiplexing which involves assigning non-overlapping frequency ranges to different signals or to each "user" of a medium.- Telephone :...
hierarchy, it is usually treated as a baseband signal, by comparison with the modulated signals used for long-distance transmission. The 300 Hz lower band edge in this case is treated as "near zero", being a small fraction of the upper band edge.
The figure shows what happens with AM modulation:

Modulation
In electronics and telecommunications, modulation is the process of varying one or more properties of a high-frequency periodic waveform, called the carrier signal, with a modulating signal which typically contains information to be transmitted...
and multiplexing
Multiplexing
The multiplexed signal is transmitted over a communication channel, which may be a physical transmission medium. The multiplexing divides the capacity of the low-level communication channel into several higher-level logical channels, one for each message signal or data stream to be transferred...
, or after demultiplexing and demodulation
Demodulation
Demodulation is the act of extracting the original information-bearing signal from a modulated carrier wave.A demodulator is an electronic circuit that is used to recover the information content from the modulated carrier wave.These terms are traditionally used in connection with radio receivers,...
.
The composite video
Composite video
Composite video is the format of an analog television signal before it is combined with a sound signal and modulated onto an RF carrier. In contrast to component video it contains all required video information, including colors in a single line-level signal...
signal created by devices such as most newer VCRs, game consoles and DVD
DVD
A DVD is an optical disc storage media format, invented and developed by Philips, Sony, Toshiba, and Panasonic in 1995. DVDs offer higher storage capacity than Compact Discs while having the same dimensions....
players is a commonly used baseband signal.
See also
- BroadbandBroadbandThe term broadband refers to a telecommunications signal or device of greater bandwidth, in some sense, than another standard or usual signal or device . Different criteria for "broad" have been applied in different contexts and at different times...
– generally refers to transmission of data over numerous frequencies - WidebandWidebandIn communications, wideband is a relative term used to describe a wide range of frequencies in a spectrum. A system is typically described as wideband if the message bandwidth significantly exceeds the channel's coherence bandwidth....
– a communications medium or signal that spans a large (continuous) range of frequencies, or is wide compared to something else - NarrowbandNarrowbandIn radio, narrowband describes a channel in which the bandwidth of the message does not significantly exceed the channel's coherence bandwidth. It is a common misconception that narrowband refers to a channel which occupies only a "small" amount of space on the radio spectrum.The opposite of...
– the opposite of wideband

