
Picture archiving and communication system
Encyclopedia
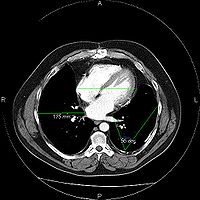
Medical imaging
Medical imaging is the technique and process used to create images of the human body for clinical purposes or medical science...
technology which provides economical storage of, and convenient access to, images from multiple modalities (source machine types). Electronic images
Digital image
A digital image is a numeric representation of a two-dimensional image. Depending on whether or not the image resolution is fixed, it may be of vector or raster type...
and reports are transmitted digitally via PACS; this eliminates the need to manually file, retrieve, or transport film jackets. The universal format for PACS image storage and transfer is DICOM (Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine). Non-image data, such as scanned
Image scanner
In computing, an image scanner—often abbreviated to just scanner—is a device that optically scans images, printed text, handwriting, or an object, and converts it to a digital image. Common examples found in offices are variations of the desktop scanner where the document is placed on a glass...
documents, may be incorporated using consumer industry standard formats like PDF (Portable Document Format)
Portable Document Format
Portable Document Format is an open standard for document exchange. This file format, created by Adobe Systems in 1993, is used for representing documents in a manner independent of application software, hardware, and operating systems....
, once encapsulated in DICOM. A PACS consists of four major components: The imaging modalities such as X-ray computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging , nuclear magnetic resonance imaging , or magnetic resonance tomography is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to visualize detailed internal structures...
(MRI), a secured network
Computer network
A computer network, often simply referred to as a network, is a collection of hardware components and computers interconnected by communication channels that allow sharing of resources and information....
for the transmission of patient information, workstation
Workstation
A workstation is a high-end microcomputer designed for technical or scientific applications. Intended primarily to be used by one person at a time, they are commonly connected to a local area network and run multi-user operating systems...
s for interpreting and reviewing images, and archives for the storage and retrieval of images and reports. Combined with available and emerging web
World Wide Web
The World Wide Web is a system of interlinked hypertext documents accessed via the Internet...
technology, PACS has the ability to deliver timely and efficient access to images, interpretations, and related data. PACS breaks down the physical and time barriers associated with traditional film-based
Photographic film
Photographic film is a sheet of plastic coated with an emulsion containing light-sensitive silver halide salts with variable crystal sizes that determine the sensitivity, contrast and resolution of the film...
image retrieval, distribution, and display.
Types of images
Most PACSs handle images from various medical imaging instruments, including ultrasound (US), magnetic resonance (MR)Magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging , nuclear magnetic resonance imaging , or magnetic resonance tomography is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to visualize detailed internal structures...
, positron emission tomography (PET)
Positron emission tomography
Positron emission tomography is nuclear medicine imaging technique that produces a three-dimensional image or picture of functional processes in the body. The system detects pairs of gamma rays emitted indirectly by a positron-emitting radionuclide , which is introduced into the body on a...
, computed tomography (CT)
Computed tomography
X-ray computed tomography or Computer tomography , is a medical imaging method employing tomography created by computer processing...
, endoscopy (ENDO)
Endoscopy
Endoscopy means looking inside and typically refers to looking inside the body for medical reasons using an endoscope , an instrument used to examine the interior of a hollow organ or cavity of the body. Unlike most other medical imaging devices, endoscopes are inserted directly into the organ...
, mammograms (MG)
Mammography
Mammography is the process of using low-energy-X-rays to examine the human breast and is used as a diagnostic and a screening tool....
, Digital radiography (DR), computed radiography (CR)
Computed radiography
Computed Radiography uses very similar equipment to conventional radiography except that in place of a film to create the image, an imaging plate made of photostimulable phosphor is used. The imaging plate housed in a special cassette and placed under the body part or object to be examined and...
ophthalmology, etc. Additional types of image formats are always being added. Clinical areas beyond radiology; cardiology, oncology, gastroenterology and even the laboratory are creating medical images that can be incorporated into PACS. (see DICOM Application areas).
Uses
PACS has four main uses:- Hard copy replacement: PACS replaces hard-copyHard copyIn information handling, a hard copy is a permanent reproduction, or copy, in the form of a physical object, of any media suitable for direct use by a person , of displayed or transmitted data...
based means of managing medical images, such as film archives. With the decreasing price of digital storage, PACSs provide a growing cost and space advantage over film archives in addition to the instant access to prior images at the same institution. Digital copies are referred to as Soft-copy. - Remote access: It expands on the possibilities of conventional systems by providing capabilities of off-site viewing and reporting (distance educationDistance educationDistance education or distance learning is a field of education that focuses on teaching methods and technology with the aim of delivering teaching, often on an individual basis, to students who are not physically present in a traditional educational setting such as a classroom...
, telediagnosis). It enables practitioners in different physical locations to access the same information simultaneously for teleradiologyTeleradiologyTeleradiology is the transmission of radiological patient images, such as x-rays, CTs, and MRIs, from one location to another for the purposes of sharing studies with other radiologists and physicians. Teleradiology is a growth technology given that imaging procedures are growing approximately 15%...
. - Electronic image integration platform: PACS provides the electronic platform for radiology images interfacing with other medical automation systems such as Hospital Information SystemHospital information systemThere are various titles and acronyms which all declare similar approaches to managing the information flow and storage in hospital routine services, as*Hospital Information System , or*Healthcare Information System, or...
(HIS), Electronic Medical RecordElectronic medical recordAn electronic medical record is a computerized medical record created in an organization that delivers care, such as a hospital or physician's office...
(EMR), Practice Management Software, and Radiology Information SystemRadiology Information SystemA radiology information system is a computerized database used by radiology departments to store, manipulate and distribute patient radiological data and imagery. The system generally consists of patient tracking and scheduling, result reporting and image tracking capabilities...
(RIS). - Radiology Workflow Management: PACS is used by radiology personnel to manage the workflow of patient exams.
PACS is offered by virtually all the major medical imaging equipment manufacturers, medical IT companies and many independent software companies. Basic PACS software can be found free on the Internet.
Architecture
The architecture is the physical implementation of required functionality, or what one sees from the outside. There are different views, depending on the user. A radiologist typically sees a viewing station, a technologist a QA workstation, while a PACS administrator might spend most of their time in the climate-controlled computer room. The composite view is rather different for the various vendors.Typically a PACS consists of a multitude of devices. The first step in typical PACS systems is the modality. Modalities are typically computed tomography (CT), ultrasound, nuclear medicine, positron emission tomography (PET), and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Depending on the facility's workflow most modalities send to a quality assurance (QA) workstation or sometimes called a PACS gateway. The QA workstation is a checkpoint to make sure patient demographics are correct as well as other important attributes of a study. If the study information is correct the images are passed to the archive for storage. The central storage device (archive) stores images and in some cases reports, measurements and other information that resides with the images. The next step in the PACS workflow is the reading workstations. The reading workstation is where the radiologist reviews the patient's study and formulates their diagnosis. Normally tied to the reading workstation is a reporting package that assists the radiologist with dictating the final report. Reporting software is optional and there are various ways in which doctors prefer to dictate their report. Ancillary to the workflow mentioned, there is normally CD/DVD authoring software used to burn patient studies for distribution to patients or referring physicians. The diagram above shows a typical workflow in most imaging centers and hospitals. Note that this section does not cover integration to a Radiology Information System, Hospital Information System and other such front-end system that relates to the PACS workflow.
More and more PACS include web-based interfaces to utilize the internet or a Wide Area Network
Wide area network
A wide area network is a telecommunication network that covers a broad area . Business and government entities utilize WANs to relay data among employees, clients, buyers, and suppliers from various geographical locations...
as their means of communication, usually via VPN (Virtual Private Network) or SSL (Secure Sockets Layer). The client side software may use ActiveX
ActiveX
ActiveX is a framework for defining reusable software components in a programming language-independent way. Software applications can then be composed from one or more of these components in order to provide their functionality....
, JavaScript
JavaScript
JavaScript is a prototype-based scripting language that is dynamic, weakly typed and has first-class functions. It is a multi-paradigm language, supporting object-oriented, imperative, and functional programming styles....
and/or a Java Applet
Java applet
A Java applet is an applet delivered to users in the form of Java bytecode. Java applets can run in a Web browser using a Java Virtual Machine , or in Sun's AppletViewer, a stand-alone tool for testing applets...
. More robust PACS clients are full applications which can utilize the full resources of the computer they are executing on and are unaffected by the frequent unattended Web Browser
Web browser
A web browser is a software application for retrieving, presenting, and traversing information resources on the World Wide Web. An information resource is identified by a Uniform Resource Identifier and may be a web page, image, video, or other piece of content...
and Java updates. As the need for distribution of images and reports become more widespread there is a push for PACS systems to support DICOM part 18 of the DICOM standard. Web Access to DICOM Objects (WADO) creates the necessary standard to expose images and reports over the web through truly portable medium. Without stepping outside the focus of the PACS architecture, WADO becomes the solution to cross platform capability and can increase the distribution of images and reports to referring physicians and patients.
PACS image backup is a critical, but sometimes overlooked, part of the PACS Architecture (see below). HIPAA requires that backup copies of patient images be made in case of image loss from the PACS. There are several methods of backing up the images, but they typically involve automatically sending copies of the images to a separate computer for storage, preferably off-site.
Querying (C-FIND) and Image Retrieval (C-MOVE)
The communication with the PACS server is done through dicom objects that are similar to dicom images, but with different tags. A query typically looks as follows:- The client establishes the network connection to the PACS server.
- The client prepares a query object which is an empty dicom dataset object.
- The client fills in the query object with the keys that should be matched. E.g. to query for a patient ID, the patient ID tag is filled with the patient's ID.
- The client creates empty tags (tags with zero length string values) for all the tags it wishes to receive from the server. E.g. if the client wishes to receive an ID that it can use to receive images (see image retrieval) it should create the tag SOPInstanceID (0008,0018) in the query object.
- The query object is sent to the server.
- The server sends back to the client a list of response dicom objects.
- The client extracts the tags that are of interest from the response dicom objects.
Images are retrieved from a PACS server through a C-MOVE request, as defined by the DICOM network protocol. This request specifies where an image instance should be sent through an identifier known as the destination Application Entity Title (AE Title). The server must be configured with mapping of the AE Title to a TCP/IP address and port, and as a consequence the server must know in advance all the AE Titles that it will ever be requested to send images to.
Typically a radiologist is looking for prior studies on a patient to compare the progression of some pathology. In some cases prior studie(s) may be on an off-site archive or a long term storage device. In the example being used, the radiologist or radiology technical must query the off-site or long term archive for the prior exam(s). The archive receives the C-FIND and if the C-FIND is successful the archive invokes a C-MOVE on the study to the called AE Title, in-turn sending the study from the archive to the device requesting the study.
Image archival and backup
Digital medical images are typically stored locally on a PACS for retrieval. It is important (and required in the USA by the Security Rule's Administrative Safeguards section of HIPAA) that facilities have a means of recovering images in the event of an error or disaster.While each facility is different, the goal in image back-up is to make it automatic and as easy to administer as possible. The hope is that the copies won't ever be needed, but, as with other disaster recovery
Disaster recovery
Disaster recovery is the process, policies and procedures related to preparing for recovery or continuation of technology infrastructure critical to an organization after a natural or human-induced disaster. Disaster recovery is a subset of business continuity...
and business continuity
Business continuity
Business continuity is the activity performed by an organization to ensure that critical business functions will be available to customers, suppliers, regulators, and other entities that must have access to those functions. These activities include many daily chores such as project management,...
planning, they need to be available if needed.
Ideally, copies of images should be streamed off-site as they are created. (If using the Internet
Internet
The Internet is a global system of interconnected computer networks that use the standard Internet protocol suite to serve billions of users worldwide...
, the Security Rule's Technical Safeguards section of HIPAA requires that the images be encrypted during transmission.) Depending on upload bandwidth and image volume, this may not be practical if the back-up system cannot be configured to tune bandwidth usage and frequency of back-ups. Other options include removable media (hard drives, DVDs or other media that can hold many patients' images) that is physically transferred off-site. The content of these copies must be protected via encryption from exposure to unauthorized personnel or stiff penalties can be assessed.
Images may be stored both locally and remotely on off-line media such as tape or optical media, or partially or exclusively on hard disks ("spinning") media. The latter is becoming more common. The hard drives may be configured and attached to the PACS server in various ways, either as Direct-Attached Storage (DAS), Network-attached storage
Network-attached storage
Network-attached storage is file-level computer data storage connected to a computer network providing data access to heterogeneous clients. NAS not only operates as a file server, but is specialized for this task either by its hardware, software, or configuration of those elements...
(NAS), or via a Storage Area Network
Storage area network
A storage area network is a dedicated network that provides access to consolidated, block level data storage. SANs are primarily used to make storage devices, such as disk arrays, tape libraries, and optical jukeboxes, accessible to servers so that the devices appear like locally attached devices...
(SAN).
However the storage is attached, the drives themselves are usually configured as a Redundant Array of Inexpensive (or Independent) Discs RAID
RAID
RAID is a storage technology that combines multiple disk drive components into a logical unit...
, which may be configured to provide appropriate combination of faster disk access or protection against the failure of one (or even two) discs in the physical RAID array. Typically, failed drives may be physically replaced (hot swapping
Hot swapping
Hot swapping and hot plugging are terms used to describe the functions of replacing computer system components without shutting down the system...
) without interruption of service. Since costs of computers has fallen, some sites opt for fully redundant Archives, rather than just protecting the drives through RAID. Further, RAIDs are fragile and can be rendered useless by one erroneous hit on the controller.
Data stored on disk may also be backed up to tape or optical media or copied, in real time, to a slower, inexpensive disc in another machine at another location. Some sites make two such backups and remove them from the site on a rotating basis.
In the event that it is necessary to reconstruct a PACS partially or completely from the back-up images, some means of rapidly transferring all of its images back to the PACS is required, preferably whilst the PACS continues to receive and provide current images.
The back-up infrastructure may also be capable of supporting the migration of images to a new PACS. Due to the high volume of images that need
to be archived many rad centers are migrating their systems to a Cloud-based PACS.
Integration
However, until PACS penetration is complete, individual islands of digital imaging not yet connected to a central PACS may exist. These may take the form of a localized, modality-specific network of modalities, workstations and storage (a so-called "mini-PACS"), or may consist of a small cluster of modalities directly connected to reading workstations without long term storage or management. Such systems are also often not connected to the departmental information system. Historically, Ultrasound, Nuclear Medicine and Cardiology Cath Labs are often departments that adopt such an approach.
More recently, Full Field digital mammography
Digital mammography
Digital mammography is a specialized form of mammography that uses digital receptors and computers instead of x-ray film to help examine breast tissue for breast cancer. The electrical signals can be read on computer screens, permitting more manipulation of images to theoretically allow...
(FFDM) has taken a similar approach, largely because of the large image size, highly specialized reading workflow and display requirements, and intervention by regulators. The rapid deployment of FFDM in the US following the DMIST
Digital Mammographic Imaging Screening Trial
The Digital Mammographic Imaging Screening Trial , is a multi-institutional research study on the efficacy for screening of Full Field digital mammography compared to conventional film-screen mammography that was sponsored by the U.S...
study has led to the integration of Digital Mammography and PACS becoming more commonplace.
All PACS, whether they span the entire enterprise or are localized within a department, should also interface with existing hospital information systems: Hospital information system
Hospital information system
There are various titles and acronyms which all declare similar approaches to managing the information flow and storage in hospital routine services, as*Hospital Information System , or*Healthcare Information System, or...
(HIS) and Radiology Information System
Radiology Information System
A radiology information system is a computerized database used by radiology departments to store, manipulate and distribute patient radiological data and imagery. The system generally consists of patient tracking and scheduling, result reporting and image tracking capabilities...
(RIS).
There are several data flowing into PACS as inputs for next procedures and back to HIS as results corresponding inputs:
In: Patient Identification and Orders for examination. These data are sent from HIS to RIS via integration interface, in most of hospital, via HL7 protocol. Patient ID and Orders will be sent to Modality (CT,MR,etc) via DICOM protocol (Worklist). Images will be created after images scanning and then forwarded to PACS Server. Diagnosis Report is created based on the images retrieved for presenting from PACS Server by physician/radiologist and then saved to RIS System.
Out: Diagnosis Report and Images created accordingly. Diagnosis Report is sent back to HIS via HL7 usually and Images are sent back to HIS via DICOM usually if there is a DICOM Viewer integrated with HIS in hospitals (In most of cases, Clinical Physician gets reminder of Diagnosis Report coming and then queries images from PACS Server).
Interfacing between multiple systems provides a more consistent and more reliable dataset:
- Less risk of entering an incorrect patient ID for a study – modalities that support DICOM worklists can retrieve identifying patient information (patient name, patient number, accession number) for upcoming cases and present that to the technologist, preventing data entry errors during acquisition. Once the acquisition is complete, the PACS can compare the embedded image data with a list of scheduled studies from RIS, and can flag a warning if the image data does not match a scheduled study.
- Data saved in the PACS can be tagged with unique patient identifiers (such as a social security numberSocial Security numberIn the United States, a Social Security number is a nine-digit number issued to U.S. citizens, permanent residents, and temporary residents under section 205 of the Social Security Act, codified as . The number is issued to an individual by the Social Security Administration, an independent...
or NHS number) obtained from HIS. Providing a robust method of merging datasets from multiple hospitals, even where the different centers use different ID systems internally.
An interface can also improve workflow patterns:
- When a study has been reported by a radiologist the PACS can mark it as read. This avoids needless double-reading. The report can be attached to the images and be viewable via a single interface.
- Improved use of online storage and nearline storageNearline storageNearline storage is a term used in computer science to describe an intermediate type of data storage that represents a compromise between online storage and offline storage/archiving...
in the image archive. The PACS can obtain lists of appointments and admissions in advance, allowing images to be pre-fetched from off-line storage or near-line storage onto online disk storage.
Recognition of the importance of integration has led a number of suppliers to develop fully integrated RIS/PACS. These may offer a number of advanced features:
- Dictation of reports can be integrated into a single system. The recording is automatically sent to a transcript writer's workstation for typing, but it can also be made available for access by physicians, avoiding typing delays for urgent results, or retained in case of typing error.
- Provides a single tool for quality control and audit purposes. Rejected images can be tagged, allowing later analysis (as may be required under radiation protection legislation). Workloads and turn-around time can be reported automatically for management purposes.
History
The principles of PACS were first discussed at meetings of radiologists in 1982. Various people are credited with the coinage of the term PACS. Cardiovascular radiologist Dr Andre Duerinckx reported in 1983 that he had first used the term in 1981. Dr Samuel Dwyer, though, credits Dr Judith M. Prewitt for introducing the term.Dr Harold Glass, a medical physicist working in London in the early 1990s secured UK Government funding and managed the project over many years which transformed Hammersmith Hospital in London as the first filmless hospital in the United Kingdom. Dr Glass died a few months after the project came live but is credited with being one of the pioneers of PACS.
The first large-scale PACS installation was in 1982 at the University of Kansas, Kansas City. This first installation became more of a teaching experience of what not to do rather than what to do in a PACS installation.
Regulatory concerns
In the US PACS are classified as Medical Devices, and hence if for sale are regulated by the USFDA. In general they are subject to Class 2 controls and hence require a 510(k), though individual PACS components may be subject to less stringent general controls. Some specific applications, such as the use for primary mammography interpretation, are additionally regulated within the scope of the Mammography Quality Standards Act.See also
- X-rayX-rayX-radiation is a form of electromagnetic radiation. X-rays have a wavelength in the range of 0.01 to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30 petahertz to 30 exahertz and energies in the range 120 eV to 120 keV. They are shorter in wavelength than UV rays and longer than gamma...
- DICOM
- eMixEMixeMix, which stands for Electronic Medical Information Exchange, is a cloud computing-based technology for secure sharing of medical imaging studies and reports between disparate healthcare facilities and physicians...
- Medical deviceMedical deviceA medical device is a product which is used for medical purposes in patients, in diagnosis, therapy or surgery . Whereas medicinal products achieve their principal action by pharmacological, metabolic or immunological means. Medical devices act by other means like physical, mechanical, thermal,...
- Medical imagingMedical imagingMedical imaging is the technique and process used to create images of the human body for clinical purposes or medical science...
- Medical softwareMedical softwareIn computers, medical software is a significant branch of software engineering. Many medical devices that monitor or control patients are predominantly controlled by software. Medical devices are frequently regulated and must comply with local and regional laws. In the European Union, these...
- Computed axial tomography
- TelemedicineTelemedicineTelemedicine is the use of telecommunication and information technologies in order to provide clinical health care at a distance. It helps eliminate distance barriers and can improve access to medical services that would often not be consistently available in distant rural communities...
- Electronic health recordElectronic Health RecordAn electronic health record is an evolving concept defined as a systematic collection of electronic health information about individual patients or populations...
(EHR) - RadiologyRadiologyRadiology is a medical specialty that employs the use of imaging to both diagnose and treat disease visualized within the human body. Radiologists use an array of imaging technologies to diagnose or treat diseases...
- Radiology Information SystemRadiology Information SystemA radiology information system is a computerized database used by radiology departments to store, manipulate and distribute patient radiological data and imagery. The system generally consists of patient tracking and scheduling, result reporting and image tracking capabilities...
- Electronic Medical RecordElectronic medical recordAn electronic medical record is a computerized medical record created in an organization that delivers care, such as a hospital or physician's office...
(EMR)
External links
- Teleradiology, PACS and DICOM Software List of free PACS and DICOM software available on the web
- History of PACS
- PACS History Web Site
- USC IPILab Research Article on Backup

