
Physics of flying discs
Encyclopedia
A flying disc can fly through the air because of the combination of the lift
and drag
forces it generates when it hits the oncoming air flow.
The trajectory
of a disk is affected by its shape
, mass
, spin
, attitude
, deformation etc.
Although wind
effects are not intrinsic to disc flight, the apparent effect of wind on a thrown disc's trajectory and behavior is quite strong from the perspective of a ground-based observer.
.jpg)
in different directions are of an appropriate relationship, allowing its flight path to be more efficient in the direction in which it is thrown; and it can therefore be thrown farther than a ball
. It must be made of an adequately dense material such that its velocity change due to air resistance is low and the force exerted by gravity is low enough for air flight. Additionally, the shape of the disc must be suited to the throwing action: a flat disc would be inappropriate due to the lack of grip that the thrower could get from the disc, resulting in accidental release.
and the aerobie ring. Although these designs are very different, they both use air resistance in the same way to fly.
Because of this effect the disc is able to fly a longer horizontal distance in a flatter parabola
.
 The Aerobie
The Aerobie
Superdisk is an alternative design of flying disc that, although somewhat differently shaped, still has very similar properties to the conventional disc. It has less air resistance.
Because there is less resistance to motion, the Aerobie discs can fly farther than the conventional disc. The Aerobie flying ring has minimal drag and has held several world records for the longest flight by a human-thrown projectile.
However, due to the lack of a rim, the Aerobie is less suited to angled, curved flights and air-bouncing.
stabilizes the disc in the same way that it keeps a gyroscope
steady, with the angular force forcing the mass of the disc away from the centre of mass, perpendicular to the axis of rotation. Any unequal force acting on a particular area of the disc is quickly redirected to be equal over the circumference of the disc.
As the disc spins faster, it becomes more stable due to the rapidity of the equalisation of forces.
are mainly 175 g in mass, heavier than the majority of discs and considerably heavier than an aerobie.
Lift (force)
A fluid flowing past the surface of a body exerts a surface force on it. Lift is the component of this force that is perpendicular to the oncoming flow direction. It contrasts with the drag force, which is the component of the surface force parallel to the flow direction...
and drag
Drag (physics)
In fluid dynamics, drag refers to forces which act on a solid object in the direction of the relative fluid flow velocity...
forces it generates when it hits the oncoming air flow.
The trajectory
Trajectory
A trajectory is the path that a moving object follows through space as a function of time. The object might be a projectile or a satellite, for example. It thus includes the meaning of orbit—the path of a planet, an asteroid or a comet as it travels around a central mass...
of a disk is affected by its shape
Shape
The shape of an object located in some space is a geometrical description of the part of that space occupied by the object, as determined by its external boundary – abstracting from location and orientation in space, size, and other properties such as colour, content, and material...
, mass
Mass
Mass can be defined as a quantitive measure of the resistance an object has to change in its velocity.In physics, mass commonly refers to any of the following three properties of matter, which have been shown experimentally to be equivalent:...
, spin
Rotation
A rotation is a circular movement of an object around a center of rotation. A three-dimensional object rotates always around an imaginary line called a rotation axis. If the axis is within the body, and passes through its center of mass the body is said to rotate upon itself, or spin. A rotation...
, attitude
Angle of attack
Angle of attack is a term used in fluid dynamics to describe the angle between a reference line on a lifting body and the vector representing the relative motion between the lifting body and the fluid through which it is moving...
, deformation etc.
Although wind
Wind
Wind is the flow of gases on a large scale. On Earth, wind consists of the bulk movement of air. In outer space, solar wind is the movement of gases or charged particles from the sun through space, while planetary wind is the outgassing of light chemical elements from a planet's atmosphere into space...
effects are not intrinsic to disc flight, the apparent effect of wind on a thrown disc's trajectory and behavior is quite strong from the perspective of a ground-based observer.
.jpg)
Suitability of a disc
A disc is suitable for flight if its air resistancesDrag (physics)
In fluid dynamics, drag refers to forces which act on a solid object in the direction of the relative fluid flow velocity...
in different directions are of an appropriate relationship, allowing its flight path to be more efficient in the direction in which it is thrown; and it can therefore be thrown farther than a ball
Ball
A ball is a round, usually spherical but sometimes ovoid, object with various uses. It is used in ball games, where the play of the game follows the state of the ball as it is hit, kicked or thrown by players. Balls can also be used for simpler activities, such as catch, marbles and juggling...
. It must be made of an adequately dense material such that its velocity change due to air resistance is low and the force exerted by gravity is low enough for air flight. Additionally, the shape of the disc must be suited to the throwing action: a flat disc would be inappropriate due to the lack of grip that the thrower could get from the disc, resulting in accidental release.
Air resistance
The two major types of flying disc are the conventional design used in both Ultimate and Disc GolfDisc golf
Disc golf is a disc game in which individual players throw a flying disc into a basket or at a target. According to the Professional Disc Golf Association, "The object of the game is to traverse a course from beginning to end in the fewest number of throws of the disc." Of the more than 3000...
and the aerobie ring. Although these designs are very different, they both use air resistance in the same way to fly.
Effect on flight distance
When a spherical ball flies through the air, it has the same cross-sectional profile causing air resistance in all directions, while a flying disc does not. Its shape causes it to have much more vertical air resistance (assuming horizontal flight) than horizontal air resistance. This is partly due to the large circular cross-sectional area vertically, but is enhanced by the rim around the edge of the disc which encloses air inside the disc in the same way as a parachute.Because of this effect the disc is able to fly a longer horizontal distance in a flatter parabola
Parabola
In mathematics, the parabola is a conic section, the intersection of a right circular conical surface and a plane parallel to a generating straight line of that surface...
.
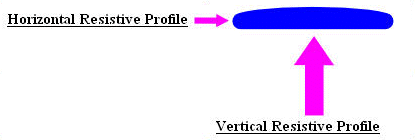 |
| In the image above the arrows represent the force of air resistance acting upon the disc in horizontal and vertical components. |
 |
| The flight of a disc lasts longer than that of a ball due to high resistance to vertical velocity. The disc lands only when its velocity has decreased, therefore almost floating to the ground. The ball, on the other hand, hits the ground when it is still travelling at a high speed horizontally causing it usually to bounce or roll. |
Effect on shape of path
The angle at which the disc is thrown alters the ratios of air resistances in different directions, affecting the direction of flight. 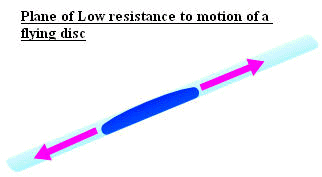 |
| The plane that matches the angle of the disc, as shown in the diagram, is the easiest direction for the disc to move in due to low air resistance, so if the disc is pitched or tilted it will follow a curved path as shown below. |
 |
| The tilt of the disc can also cause the disc to ascend vertically if the disc is tilted upwards, without the need for the disc to be thrown in the upwards direction. This is because of the lift effect caused by the rim of the disc. This is the same principle that is used in the wing of an aeroplane. A disc that is thrown downwards at a tilted angle, and then ascends, performs a movement known as the air-bounce (or air-hop). The diagram below shows the airflow acting upon the disc. |
 |
 |
The Aerobie

Aerobie
An Aerobie is a flying ring used in a manner similar to a flying disc , for recreational catches between two or more individuals. The Aerobie is a ring, rather than a disc. An Aerobie is also lighter, and is more stable in flight. It can be bent to tune it for straighter flight. Since it has very...
Superdisk is an alternative design of flying disc that, although somewhat differently shaped, still has very similar properties to the conventional disc. It has less air resistance.
Because there is less resistance to motion, the Aerobie discs can fly farther than the conventional disc. The Aerobie flying ring has minimal drag and has held several world records for the longest flight by a human-thrown projectile.
However, due to the lack of a rim, the Aerobie is less suited to angled, curved flights and air-bouncing.
Spin of the disc
The spin of the disc helps to keep the disc stable in flight and prevent unplanned tilting. This is because a large angular momentumAngular momentum
In physics, angular momentum, moment of momentum, or rotational momentum is a conserved vector quantity that can be used to describe the overall state of a physical system...
stabilizes the disc in the same way that it keeps a gyroscope
Gyroscope
A gyroscope is a device for measuring or maintaining orientation, based on the principles of angular momentum. In essence, a mechanical gyroscope is a spinning wheel or disk whose axle is free to take any orientation...
steady, with the angular force forcing the mass of the disc away from the centre of mass, perpendicular to the axis of rotation. Any unequal force acting on a particular area of the disc is quickly redirected to be equal over the circumference of the disc.
As the disc spins faster, it becomes more stable due to the rapidity of the equalisation of forces.
The center of mass
On neither the aerobie nor the conventional design is the center of mass located on the disc itself. It is instead located in the space in the disc's center in the case of the aerobie, or just below the center of the physical disc in the case of a Frisbee.Mass of the disc
The force required to accelerate the disc is directly proportional to the mass of the disc. This decreases the acceleration of the disc, assuming that the force of projection is constant. Therefore, discs come in a variety of weights, although those used for UltimateUltimate (sport)
Ultimate is a sport played with a 175 gram flying disc. The object of the game is to score points by passing the disc to a player in the opposing end zone, similar to an end zone in American football or rugby...
are mainly 175 g in mass, heavier than the majority of discs and considerably heavier than an aerobie.

