
Phosphatidate cytidylyltransferase
Encyclopedia
Phosphatidate cytidylyltransferase (also known as CDP- diacylglycerol synthase) (CDS) is the enzyme
that catalyzes the synthesis
of CDP-diacylglycerol from cytidine triphosphate
and phosphatidate
.
Thus, the two substrates
of this enzyme are cytidine triphosphate, or CTP, and phosphatidate, whereas its two products
are diphosphate and CDP-diacylglycerol.
CDP-diacylglycerol is an important branch point intermediate in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms. CDS is a membrane-bound enzyme.
This enzyme belongs to the family of transferase
s, specifically those transferring phosphorus
-containing nucleotide
groups (nucleotidyltransferase
s). The systematic name of this enzyme class is CTP:phosphatidate cytidylyltransferase. Other names in common use include CDP diglyceride pyrophosphorylase, CDP-diacylglycerol synthase, CDP-diacylglyceride synthetase, cytidine diphosphoglyceride pyrophosphorylase, phosphatidate cytidyltransferase, phosphatidic acid cytidylyltransferase, CTP:1,2-diacylglycerophosphate-cytidyl transferase, CTP-diacylglycerol synthetase, DAG synthetase, and CDP-DG. This enzyme participates in glycerophospholipid metabolism and phosphatidylinositol signaling system.
Enzyme
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions. In enzymatic reactions, the molecules at the beginning of the process, called substrates, are converted into different molecules, called products. Almost all chemical reactions in a biological cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates...
that catalyzes the synthesis
Biosynthesis
Biosynthesis is an enzyme-catalyzed process in cells of living organisms by which substrates are converted to more complex products. The biosynthesis process often consists of several enzymatic steps in which the product of one step is used as substrate in the following step...
of CDP-diacylglycerol from cytidine triphosphate
Cytidine triphosphate
Cytidine triphosphate is a pyrimidine nucleoside triphosphate.CTP is a substrate in the synthesis of RNA.CTP is a high-energy molecule equal to ATP, but its role in the organism is more specific than that of ATP....
and phosphatidate
Phosphatidate
Phosphatidic acids are the acid forms of phosphatidates, a part of common phospholipids, major constituents of cell membranes. Phosphatidic acids are the simplest diacyl-glycerophospholipids.-Structure:...
.
- CTP + phosphatidate
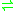 diphosphate + CDP-diacylglycerol
diphosphate + CDP-diacylglycerol
Thus, the two substrates
Substrate (biochemistry)
In biochemistry, a substrate is a molecule upon which an enzyme acts. Enzymes catalyze chemical reactions involving the substrate. In the case of a single substrate, the substrate binds with the enzyme active site, and an enzyme-substrate complex is formed. The substrate is transformed into one or...
of this enzyme are cytidine triphosphate, or CTP, and phosphatidate, whereas its two products
Product (chemistry)
Product are formed during chemical reactions as reagents are consumed. Products have lower energy than the reagents and are produced during the reaction according to the second law of thermodynamics. The released energy comes from changes in chemical bonds between atoms in reagent molecules and...
are diphosphate and CDP-diacylglycerol.
CDP-diacylglycerol is an important branch point intermediate in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms. CDS is a membrane-bound enzyme.
This enzyme belongs to the family of transferase
Transferase
In biochemistry, a transferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of a functional group from one molecule to another . For example, an enzyme that catalyzed this reaction would be a transferase:In this example, A would be the donor, and B would be the acceptor...
s, specifically those transferring phosphorus
Phosphorus
Phosphorus is the chemical element that has the symbol P and atomic number 15. A multivalent nonmetal of the nitrogen group, phosphorus as a mineral is almost always present in its maximally oxidized state, as inorganic phosphate rocks...
-containing nucleotide
Nucleotide
Nucleotides are molecules that, when joined together, make up the structural units of RNA and DNA. In addition, nucleotides participate in cellular signaling , and are incorporated into important cofactors of enzymatic reactions...
groups (nucleotidyltransferase
Nucleotidyltransferase
Nucleotidyltransferases are transferase enzymes of phosphorus-containing groups, e.g., substituents of nucleotidylic acids or simply nucleoside monophosphates...
s). The systematic name of this enzyme class is CTP:phosphatidate cytidylyltransferase. Other names in common use include CDP diglyceride pyrophosphorylase, CDP-diacylglycerol synthase, CDP-diacylglyceride synthetase, cytidine diphosphoglyceride pyrophosphorylase, phosphatidate cytidyltransferase, phosphatidic acid cytidylyltransferase, CTP:1,2-diacylglycerophosphate-cytidyl transferase, CTP-diacylglycerol synthetase, DAG synthetase, and CDP-DG. This enzyme participates in glycerophospholipid metabolism and phosphatidylinositol signaling system.

