
Pharyngeal consonant
Encyclopedia
A pharyngeal consonant is a type of consonant
which is articulated with the root of the tongue
against the pharynx
.
(IPA):
, Berber
, Cushitic
, Northwest Caucasian
, and Northeast Caucasian
language families) and in British Columbia (in the Salishan language family
). There are scattered reports of pharyngeals elsewhere, such as in the Nilo-Saharan
Tama language
. In Finnish
, a weak pharyngeal fricative is the realization of /h/ next to the vowel /ɑ/, but since this is mere allophony
, it is transcribed as /h/. According to the laryngeal theory, the Proto-Indo-European language
might also have contained pharyngeal consonants.
Note that reported pharyngeals frequently turn out to be epiglottals
. Such was the case for Dahalo
and northern Haida
, for example, and is likely to be true for many if not most of the others. This is perhaps because 'epiglottal' was only recently recognized as a distinct place of articulation, rather than a variant of 'pharyngeal'. Contrastive pharyngeals and epiglottals are known only from the Richa dialect of Aghul
, a Lezgian language
of Dagestan: /ħaw/ "udder" vs. /ʜatʃ/ "apple" and /ʕan/ "belly" vs. /ʢakʷ/ "light".
Recently, a possible new place of articulation, epiglotto-pharyngeal
, was reported.
Consonant
In articulatory phonetics, a consonant is a speech sound that is articulated with complete or partial closure of the vocal tract. Examples are , pronounced with the lips; , pronounced with the front of the tongue; , pronounced with the back of the tongue; , pronounced in the throat; and ,...
which is articulated with the root of the tongue
Tongue
The tongue is a muscular hydrostat on the floors of the mouths of most vertebrates which manipulates food for mastication. It is the primary organ of taste , as much of the upper surface of the tongue is covered in papillae and taste buds. It is sensitive and kept moist by saliva, and is richly...
against the pharynx
Pharynx
The human pharynx is the part of the throat situated immediately posterior to the mouth and nasal cavity, and anterior to the esophagus and larynx. The human pharynx is conventionally divided into three sections: the nasopharynx , the oropharynx , and the laryngopharynx...
.
Pharyngeal consonants in the IPA
Pharyngeal consonants in the International Phonetic AlphabetInternational Phonetic Alphabet
The International Phonetic Alphabet "The acronym 'IPA' strictly refers [...] to the 'International Phonetic Association'. But it is now such a common practice to use the acronym also to refer to the alphabet itself that resistance seems pedantic...
(IPA):
| IPA | Description | Example (Somali Somali language The Somali language is a member of the East Cushitic branch of the Afro-Asiatic language family. Its nearest relatives are Afar and Oromo. Somali is the best documented of the Cushitic languages, with academic studies beginning before 1900.... ) |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Orthography | IPA | Meaning | ||
 |
pharyngeal approximant Voiced pharyngeal fricative The voiced pharyngeal approximant or fricative is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents it is , and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is ?\.... |
caadi | [ʕaːdi] | normal |
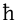 |
voiceless pharyngeal fricative Voiceless pharyngeal fricative The voiceless pharyngeal fricative is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is h-bar .-Features:Features of the voiceless pharyngeal fricative:... |
xood | [ħoːd] | cane |
- Pharyngeal plosivesStop consonantIn phonetics, a plosive, also known as an occlusive or an oral stop, is a stop consonant in which the vocal tract is blocked so that all airflow ceases. The occlusion may be done with the tongue , lips , and &...
are thought to be impossible. Note that when they are posited, they are sometimes transcribed with a small capital Q, [Q]. - Although traditionally placed in the fricative row of the IPAInternational Phonetic AlphabetThe International Phonetic Alphabet "The acronym 'IPA' strictly refers [...] to the 'International Phonetic Association'. But it is now such a common practice to use the acronym also to refer to the alphabet itself that resistance seems pedantic...
chart, [ʕ] is usually an approximant. The IPA symbol itself is ambiguous, but no language has a distinct fricative and approximant at this place of articulation. Sometimes the lowering diacritic is used to specify that the manner is approximant: [ʕ̞].
Characteristics
Pharyngeals are known primarily from two areas of the world: in North-Africa/Mideast (in the SemiticSemitic languages
The Semitic languages are a group of related languages whose living representatives are spoken by more than 270 million people across much of the Middle East, North Africa and the Horn of Africa...
, Berber
Berber languages
The Berber languages are a family of languages indigenous to North Africa, spoken from Siwa Oasis in Egypt to Morocco , and south to the countries of the Sahara Desert...
, Cushitic
Cushitic languages
The Cushitic languages are a branch of the Afroasiatic language family spoken in the Horn of Africa, Tanzania, Kenya, Sudan and Egypt. They are named after the Biblical character Cush, who was identified as an ancestor of the speakers of these specific languages as early as AD 947...
, Northwest Caucasian
Northwest Caucasian languages
The Northwest Caucasian languages, also called Abkhazo-Adyghean, or sometimes Pontic as opposed to Caspian for the Northeast Caucasian languages, are a group of languages spoken in the Caucasus region, chiefly in Russia , the disputed territory of Abkhazia, and Turkey, with smaller communities...
, and Northeast Caucasian
Northeast Caucasian languages
The Northeast Caucasian languages constitute a language family spoken in the Russian republics of Dagestan, Chechnya, Ingushetia, northern Azerbaijan, and in northeastern Georgia, as well as in diaspora populations in Russia, Turkey, and the Middle East...
language families) and in British Columbia (in the Salishan language family
Salishan languages
The Salishan languages are a group of languages of the Pacific Northwest...
). There are scattered reports of pharyngeals elsewhere, such as in the Nilo-Saharan
Nilo-Saharan languages
The Nilo-Saharan languages are a proposed family of African languages spoken by some 50 million people, mainly in the upper parts of the Chari and Nile rivers , including historic Nubia, north of where the two tributaries of Nile meet...
Tama language
Tama language
The Tama language is a Nilo-Saharan language spoken in western Sudan and eastern Chad. It is a member of the Taman language group of the Western branch of Nilo-Saharan.-External links:**...
. In Finnish
Finnish language
Finnish is the language spoken by the majority of the population in Finland Primarily for use by restaurant menus and by ethnic Finns outside Finland. It is one of the two official languages of Finland and an official minority language in Sweden. In Sweden, both standard Finnish and Meänkieli, a...
, a weak pharyngeal fricative is the realization of /h/ next to the vowel /ɑ/, but since this is mere allophony
Allophone
In phonology, an allophone is one of a set of multiple possible spoken sounds used to pronounce a single phoneme. For example, and are allophones for the phoneme in the English language...
, it is transcribed as /h/. According to the laryngeal theory, the Proto-Indo-European language
Proto-Indo-European language
The Proto-Indo-European language is the reconstructed common ancestor of the Indo-European languages, spoken by the Proto-Indo-Europeans...
might also have contained pharyngeal consonants.
Note that reported pharyngeals frequently turn out to be epiglottals
Epiglottal consonant
An epiglottal consonant is a consonant that is articulated with the aryepiglottic folds against the epiglottis. They are occasionally called aryepiglottal consonants.-Epiglottal consonants in the IPA:...
. Such was the case for Dahalo
Dahalo language
Dahalo is an endangered South Cushitic language spoken by at most 400 people on the Kenyan coast near the mouth of the Tana River. The Dahalo, former elephant hunters, are dispersed among Swahili and other Bantu peoples, with no villages of their own, and are bilingual in those languages...
and northern Haida
Haida language
The Haida language is the language of the Haida people. It contains seven vowels and well over 30 consonants.-History:The first documented contact between the Haida and Europeans was in 1774, on Juan Pérez's exploratory voyage. At this time Haidas inhabited the Queen Charlotte Islands, Dall...
, for example, and is likely to be true for many if not most of the others. This is perhaps because 'epiglottal' was only recently recognized as a distinct place of articulation, rather than a variant of 'pharyngeal'. Contrastive pharyngeals and epiglottals are known only from the Richa dialect of Aghul
Aghul language
Aghul, also spelled Agul, is a language spoken by the Aguls who live in southern Dagestan, Russia and in Azerbaijan. It is spoken by about 28,300 people .-Classification:...
, a Lezgian language
Lezgic languages
The Lezgic languages are one the seven branches of the Northeast Caucasian language family. Lezgian and Tabasaran are literary languages.-Classification:* Peripheral: Archi – 1200 speakers* Samur ** Eastern Samur*** Udi – 5000 speakers...
of Dagestan: /ħaw/ "udder" vs. /ʜatʃ/ "apple" and /ʕan/ "belly" vs. /ʢakʷ/ "light".
Recently, a possible new place of articulation, epiglotto-pharyngeal
Epiglotto-pharyngeal consonant
An epiglotto-pharyngeal consonant is a newly reported type of consonant, articulated with the epiglottis against the back wall of the pharynx. This contrasts with the pharyngeal consonants, where the root of the tongue contacts the back wall of the pharynx, and prototypical epiglottal consonants,...
, was reported.
See also
- Place of articulationPlace of articulationIn articulatory phonetics, the place of articulation of a consonant is the point of contact where an obstruction occurs in the vocal tract between an articulatory gesture, an active articulator , and a passive location...
- Pharyngealization
- List of phonetics topics
- AyinAyin' or ' is the sixteenth letter in many Semitic abjads, including Phoenician, Aramaic, Hebrew and Arabic . It is the twenty-first letter in the new Persian alphabet...
- HethHeth (letter)' or ' is the reconstructed name of the eighth letter of the Proto-Canaanite alphabet, continued in descended Semitic alphabets as Phoenician , Syriac , Hebrew ḥēth , Arabic , and Berber .Heth originally represented a voiceless fricative, either pharyngeal , or...

